Mulching improves soil health by retaining moisture, regulating temperature, and suppressing weeds, which reduces the need for chemical interventions. Organic mulches break down over time, enriching the soil with nutrients vital for plant growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover the best mulching techniques and materials tailored for your garden.
Table of Comparison
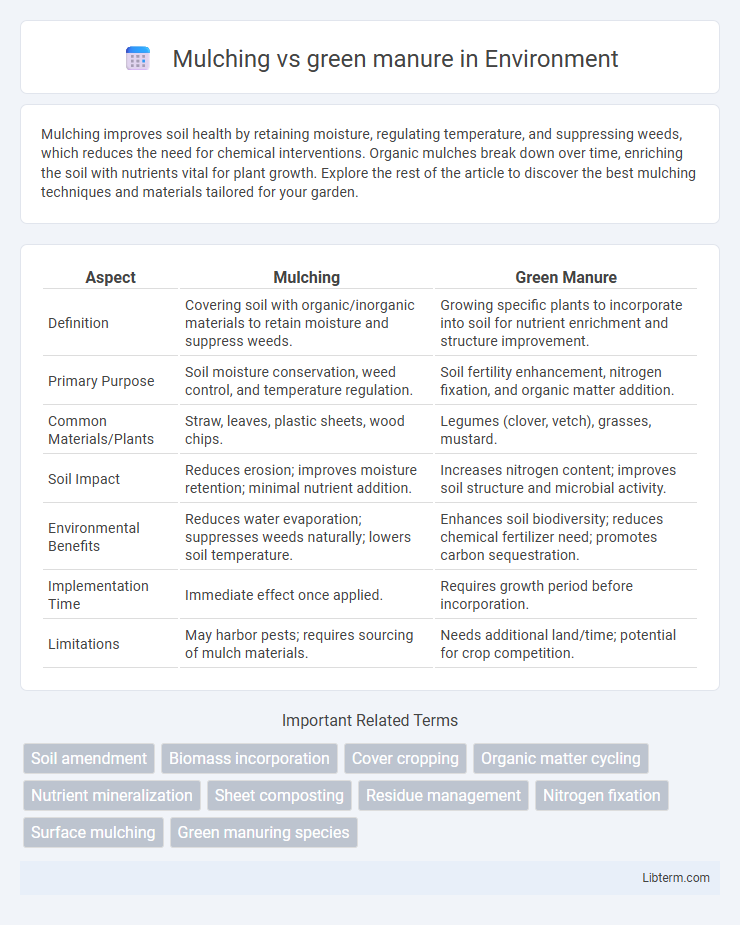
| Aspect | Mulching | Green Manure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Covering soil with organic/inorganic materials to retain moisture and suppress weeds. | Growing specific plants to incorporate into soil for nutrient enrichment and structure improvement. |
| Primary Purpose | Soil moisture conservation, weed control, and temperature regulation. | Soil fertility enhancement, nitrogen fixation, and organic matter addition. |
| Common Materials/Plants | Straw, leaves, plastic sheets, wood chips. | Legumes (clover, vetch), grasses, mustard. |
| Soil Impact | Reduces erosion; improves moisture retention; minimal nutrient addition. | Increases nitrogen content; improves soil structure and microbial activity. |
| Environmental Benefits | Reduces water evaporation; suppresses weeds naturally; lowers soil temperature. | Enhances soil biodiversity; reduces chemical fertilizer need; promotes carbon sequestration. |
| Implementation Time | Immediate effect once applied. | Requires growth period before incorporation. |
| Limitations | May harbor pests; requires sourcing of mulch materials. | Needs additional land/time; potential for crop competition. |
Introduction to Mulching and Green Manure
Mulching involves covering soil with organic or inorganic materials to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature, enhancing plant growth and soil health. Green manure refers to the practice of growing specific plants, such as legumes or cover crops, that are later incorporated into the soil to enrich it with nutrients, improve soil structure, and increase microbial activity. Both mulching and green manure contribute to sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility and reducing erosion.
Defining Mulching: Methods and Materials
Mulching involves covering the soil surface with organic or inorganic materials such as straw, wood chips, plastic sheets, or compost to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Common mulching methods include surface mulching, where materials are spread evenly, and living mulching, which uses plants like cover crops to protect the soil. Effective mulching enhances soil health by reducing erosion and improving nutrient retention, making it a critical practice in sustainable agriculture.
Understanding Green Manure: Types and Benefits
Green manure involves growing specific cover crops such as clover, vetch, or rye that are later incorporated into the soil to enhance fertility and organic matter content. This practice improves soil structure, increases nitrogen levels through biological fixation, and suppresses weeds naturally. Unlike mulching, which primarily protects soil surface and conserves moisture, green manure actively enriches soil nutrients, promotes microbial activity, and supports sustainable crop rotations.
Soil Health: Mulching vs Green Manure
Mulching improves soil health by conserving moisture, regulating temperature, and suppressing weeds, which enhances microbial activity and reduces erosion. Green manure enriches soil fertility by adding organic matter and nitrogen through the decomposition of cover crops, promoting nutrient cycling and improving soil structure. Both practices support soil health but mulch primarily acts as a protective layer, while green manure directly contributes nutrients and organic content.
Nutrient Contribution: Comparing Techniques
Mulching conserves soil moisture and gradually releases nutrients through the decomposition of organic materials such as straw, leaves, or wood chips, enhancing soil fertility over time. Green manure involves growing specific cover crops like legumes that fix atmospheric nitrogen and are incorporated into the soil to rapidly increase nutrient levels, particularly nitrogen and organic matter. Green manure typically provides a quicker and more substantial nutrient boost compared to mulching, which offers a slower, sustained nutrient release.
Impact on Soil Structure and Moisture Retention
Mulching enhances soil structure by creating a protective organic layer that reduces erosion and improves moisture retention through decreased evaporation. Green manure crops, when incorporated into the soil, boost organic matter content and aggregate stability, leading to improved soil porosity and water infiltration. Both practices significantly increase soil moisture capacity but mulching provides more immediate surface protection, while green manure contributes long-term soil fertility and structure improvement.
Weed Suppression: Effectiveness of Mulch vs Green Cover
Mulching provides a physical barrier that effectively suppresses weed growth by blocking sunlight and reducing seed germination directly on the soil surface. Green manure, through rapid biomass growth and ground coverage, competes with weeds by shading and nutrient uptake, but may not prevent weed seeds already present from germinating. Studies show that thick organic mulches typically offer more consistent and immediate weed suppression compared to green manure crops, which require additional management for optimal effectiveness.
Practical Considerations: Application and Timing
Mulching involves applying organic or inorganic materials on the soil surface to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate temperature, typically done after planting or during crop growth. Green manure requires growing specific cover crops like legumes or grasses and incorporating them into the soil before planting the main crop to enhance soil fertility and structure. Timing for mulching is flexible but most effective when soil moisture is adequate, whereas green manure must be carefully timed to allow for crop residue decomposition without delaying the planting schedule.
Environmental Sustainability: Mulching vs Green Manuring
Mulching conserves soil moisture, reduces erosion, and suppresses weeds, promoting healthier soil ecosystems. Green manuring enhances soil fertility by adding organic matter and nitrogen, improving soil structure and microbial activity. Both methods contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing chemical inputs and enhancing soil health, but green manuring offers greater nutrient recycling benefits.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Garden
Mulching improves soil moisture retention, temperature regulation, and weed suppression by applying organic or inorganic layers directly onto the soil surface. Green manure involves growing specific cover crops like clover or legumes that are later incorporated into the soil to enhance nutrient content, especially nitrogen fixation. Selecting between mulching and green manure depends on your garden's needs for immediate weed control versus long-term soil fertility improvement.
Mulching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com