Urban sprawl refers to the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into surrounding rural land, leading to increased traffic congestion, environmental degradation, and loss of agricultural spaces. This phenomenon often results in longer commutes, increased pollution, and strained infrastructure, impacting the quality of life for residents. Explore the full article to understand the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to urban sprawl.
Table of Comparison
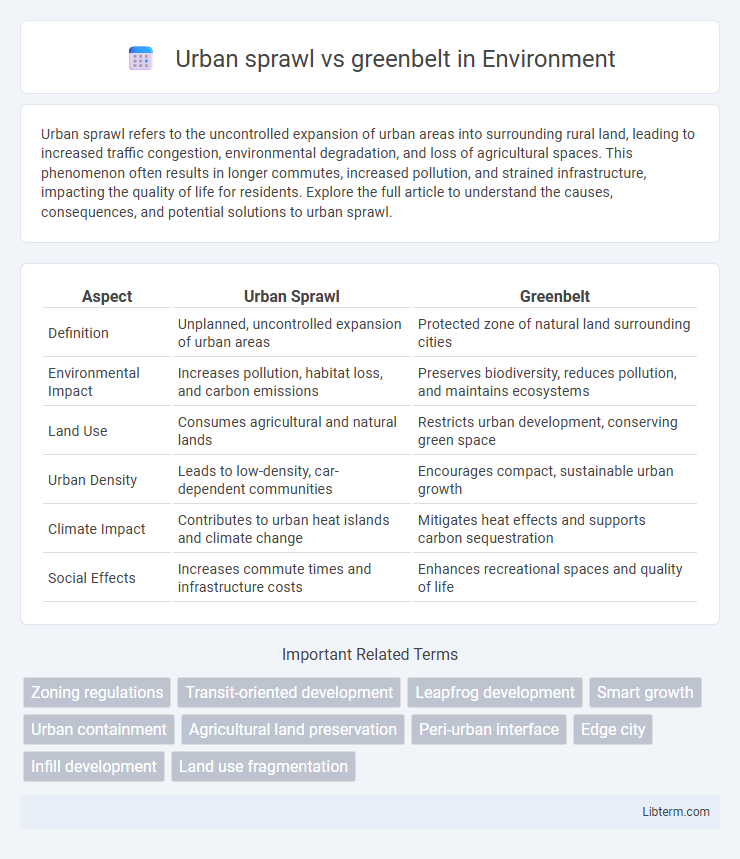
| Aspect | Urban Sprawl | Greenbelt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unplanned, uncontrolled expansion of urban areas | Protected zone of natural land surrounding cities |
| Environmental Impact | Increases pollution, habitat loss, and carbon emissions | Preserves biodiversity, reduces pollution, and maintains ecosystems |
| Land Use | Consumes agricultural and natural lands | Restricts urban development, conserving green space |
| Urban Density | Leads to low-density, car-dependent communities | Encourages compact, sustainable urban growth |
| Climate Impact | Contributes to urban heat islands and climate change | Mitigates heat effects and supports carbon sequestration |
| Social Effects | Increases commute times and infrastructure costs | Enhances recreational spaces and quality of life |
Defining Urban Sprawl and Greenbelts
Urban sprawl refers to the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into peripheral rural lands, characterized by low-density residential and commercial development. Greenbelts are designated zones of protected open space encircling cities, aimed at limiting urban growth and preserving natural landscapes. These greenbelts help contain sprawl by restricting outward expansion, promoting sustainable land use and environmental conservation.
Historical Evolution of Urban Sprawl
Urban sprawl emerged prominently in the mid-20th century as rapid industrialization and increased automobile ownership enabled cities to expand outward from dense urban cores into suburban and rural areas. This uncontrolled expansion often led to the consumption of greenbelt land, which was originally established in the early 20th century as a buffer to limit urban growth and preserve natural landscapes. The tension between urban sprawl and greenbelts highlights the challenges of sustainable city planning and the ongoing efforts to balance development with environmental conservation.
Purpose and Principles of Greenbelt Policy
Greenbelt policy aims to contain urban sprawl by preserving open spaces and limiting uncontrolled expansion of urban areas, thereby promoting sustainable land use and protecting natural ecosystems. The purpose of greenbelts is to maintain ecological balance, support agriculture, and enhance the quality of urban life by providing recreational opportunities and reducing air pollution. Principally, greenbelt policies enforce strict land-use regulations to prevent encroachment, encourage higher-density urban development, and safeguard green spaces for future generations.
Drivers and Causes of Urban Sprawl
Urban sprawl is primarily driven by population growth, affordable land prices, and increased automobile dependence, leading to the expansion of low-density residential and commercial areas. Zoning policies that favor single-family homes and limited public transportation infrastructure also contribute significantly to uncontrolled urban expansion. In contrast, greenbelts aim to contain sprawl by preserving open spaces and agricultural land, but enforcement and political support often determine their effectiveness.
Environmental Impacts of Urban Expansion
Urban sprawl causes habitat fragmentation, increased air pollution, and greater carbon emissions due to expanded vehicle use and energy consumption. Greenbelts serve as critical buffers that protect natural ecosystems, maintain biodiversity, and improve air and water quality by limiting urban expansion. Preserving greenbelts reduces soil erosion and mitigates urban heat island effects, promoting sustainable environmental health.
Greenbelts: Protecting Nature and Farmland
Greenbelts serve as designated zones of protected natural landscapes and farmland, preventing urban sprawl by restricting construction and development. These green areas enhance biodiversity, maintain ecological balance, and preserve agricultural land essential for local food production. By curbing unchecked expansion, greenbelts contribute to sustainable urban planning and support environmental conservation efforts.
Economic Effects: Sprawl vs Greenbelt
Urban sprawl drives higher infrastructure costs by extending roads, utilities, and public services over larger areas, reducing municipal efficiency and increasing tax burdens. Greenbelts help contain development, promoting denser urban cores that boost local economies through higher property values and reduced transportation expenses. Protecting greenbelts preserves agricultural lands and tourism revenue, while unchecked sprawl often leads to environmental degradation that can hamper long-term economic sustainability.
Social Consequences and Community Wellbeing
Urban sprawl often leads to fragmented communities, reduced social interactions, and limited access to essential services, negatively impacting community wellbeing. In contrast, greenbelts preserve open spaces that encourage outdoor activities, promote social cohesion, and support mental health by providing natural environments within urban areas. Maintaining greenbelts helps foster stronger neighborhoods and enhances overall quality of life by mitigating the isolating effects of unchecked urban expansion.
Urban Planning Strategies for Sustainable Growth
Urban planning strategies for sustainable growth emphasize controlling urban sprawl by implementing greenbelt zones that restrict unplanned expansion and protect natural ecosystems. Greenbelts serve as crucial buffers, preserving biodiversity, reducing air pollution, and encouraging higher-density development within urban cores. Efficient land use policies and smart growth principles promote compact cities that balance population needs with environmental sustainability.
Future Outlook: Balancing Development and Conservation
Urban sprawl continues to expand, threatening natural habitats and increasing carbon emissions, while greenbelts serve as critical buffers that preserve biodiversity and regulate urban temperatures. Future urban planning strategies emphasize integrating smart growth principles, prioritizing high-density development to minimize land consumption and maintain ecological corridors within greenbelts. Advancements in sustainable infrastructure and green technologies aim to balance economic growth with environmental conservation, ensuring resilient cities that protect green spaces for future generations.
Urban sprawl Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com