Eco-labeling serves as a valuable tool for consumers seeking environmentally friendly products by providing clear, trustworthy information on a product's ecological impact. It helps reduce harm to the environment by encouraging sustainable production practices and informed purchasing decisions. Explore the rest of this article to discover how eco-labeling can empower your choices and contribute to a greener future.
Table of Comparison
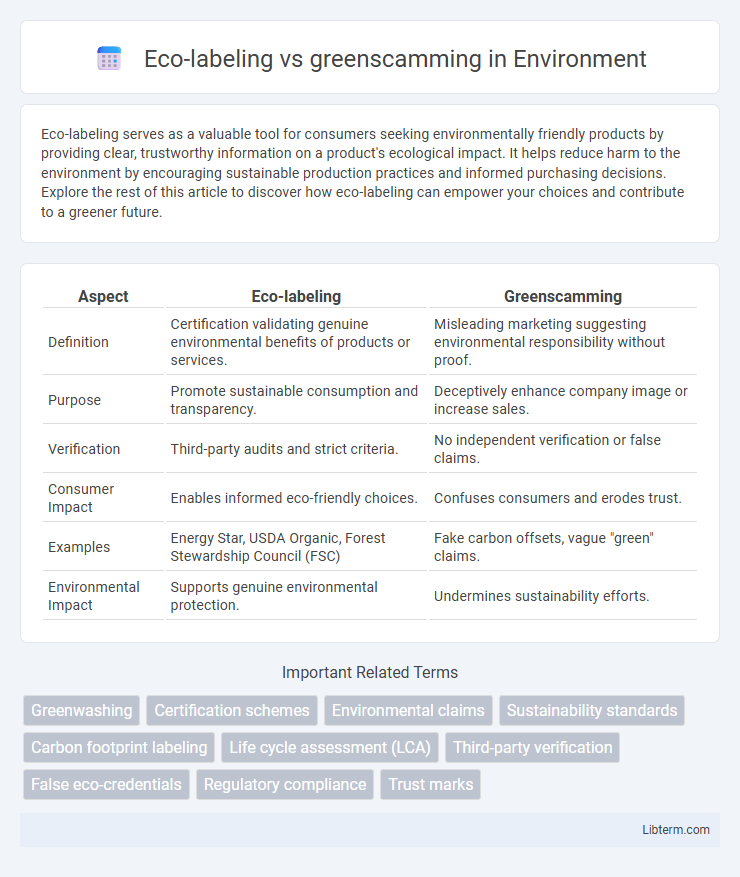
| Aspect | Eco-labeling | Greenscamming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Certification validating genuine environmental benefits of products or services. | Misleading marketing suggesting environmental responsibility without proof. |
| Purpose | Promote sustainable consumption and transparency. | Deceptively enhance company image or increase sales. |
| Verification | Third-party audits and strict criteria. | No independent verification or false claims. |
| Consumer Impact | Enables informed eco-friendly choices. | Confuses consumers and erodes trust. |
| Examples | Energy Star, USDA Organic, Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) | Fake carbon offsets, vague "green" claims. |
| Environmental Impact | Supports genuine environmental protection. | Undermines sustainability efforts. |
Understanding Eco-Labeling: Definition and Purpose
Eco-labeling involves certifying products based on environmental standards to guide consumers toward sustainable choices, ensuring transparency and accountability in green marketing. It serves as a credible tool for differentiating genuinely eco-friendly products from those using misleading claims. Understanding eco-labeling is essential to recognizing authentic sustainability efforts and avoiding greenscamming practices that exploit environmental concerns for profit.
The Rise of Greenwashing and Greenscamming
The rise of greenwashing and greenscamming challenges the credibility of eco-labeling by misleading consumers with false or exaggerated environmental claims. Companies exploit eco-labels without adhering to genuine sustainability standards, undermining trust in certified products and complicating efforts to promote responsible consumption. Increased regulatory scrutiny and consumer awareness are essential to distinguish authentic green certifications from deceptive marketing tactics.
Key Differences Between Eco-Labeling and Greenscamming
Eco-labeling provides verified, transparent certification that products meet specific environmental standards, ensuring consumer trust and promoting sustainable choices. Greenscamming, by contrast, involves misleading or false claims about environmental benefits intended to deceive consumers and boost sales without genuine environmental responsibility. The key difference lies in the authenticity and accountability of the environmental claims, where eco-labeling relies on third-party validation, while greenscamming predominantly lacks credible oversight.
Recognizing Legitimate Eco-Labels
Recognizing legitimate eco-labels requires verifying certifications from accredited organizations such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Energy Star, which adhere to strict environmental standards. Genuine eco-labels provide transparent criteria and third-party verification, ensuring products meet specific sustainability benchmarks. Consumers should be cautious of vague claims and labels lacking clear regulatory oversight, as these often indicate greenscamming practices designed to mislead about environmental benefits.
Common Tactics Used in Greenscamming
Greenscamming often involves misleading eco-labeling through tactics such as vague claims like "all-natural" without certification, selective disclosure of environmental impacts, and the use of unverified third-party endorsements. Companies may also exploit ambiguous terms or create fake eco-labels to deceive consumers into believing products are more sustainable than they truly are. These strategies undermine genuine eco-labeling efforts by eroding trust and making it difficult for buyers to identify truly green products.
The Impact on Consumer Trust and Behavior
Eco-labeling enhances consumer trust by providing transparent information about a product's environmental impact, encouraging more sustainable purchasing decisions. Greenscamming, involving misleading or false eco-friendly claims, erodes consumer confidence and leads to skepticism towards genuine green products. Studies indicate that clear, verified eco-labels significantly increase positive consumer behavior, whereas greenscamming diminishes brand loyalty and undermines environmental goals.
Regulatory Oversight and Industry Standards
Eco-labeling provides consumers with verified information about a product's environmental impact through regulatory oversight and established industry standards, ensuring transparency and credibility. Greenscamming, by contrast, often involves deceptive claims lacking rigorous verification, exploiting gaps in regulatory frameworks and inconsistent industry enforcement. Strengthening regulatory oversight and harmonizing industry standards are critical to distinguishing genuine eco-labeled products from misleading greenwashing practices.
Evaluating Environmental Claims: What to Look For
Evaluating environmental claims requires scrutinizing the credibility of eco-labels by verifying certification from recognized organizations such as EcoCert and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC). Look for transparency in product sourcing, measurable environmental impacts, and third-party audits that confirm claims to avoid greenscamming, where misleading or false eco-friendly assertions are made. Consumers should prioritize labels with clear criteria and measurable benefits to ensure genuine sustainability.
The Role of Certification Bodies
Certification bodies serve as the critical gatekeepers ensuring the credibility and transparency of eco-labeling initiatives by rigorously assessing products against established environmental criteria. Their stringent verification processes prevent greenscamming, which involves misleading claims of sustainability, by enforcing compliance and penalizing false advertising. Effective certification enhances consumer trust and promotes genuine eco-friendly practices, distinguishing authentic green products from deceptive marketing tactics.
Future Trends in Sustainable Product Verification
Future trends in sustainable product verification emphasize enhancing transparency through blockchain and AI-driven eco-labeling systems, ensuring authenticity and reducing greenscamming risks. Increasing consumer demand for verifiable environmental claims pushes companies to adopt third-party certifications and real-time monitoring technologies. Integration of digital passports and IoT-enabled tracking promises more reliable, tamper-proof sustainability verification across supply chains.
Eco-labeling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com