Corporate social responsibility (CSR) encompasses a company's commitment to ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and social welfare. Integrating CSR into business strategies enhances brand reputation, fosters customer loyalty, and drives long-term growth. Discover how your organization can leverage CSR to create meaningful impact in the full article.
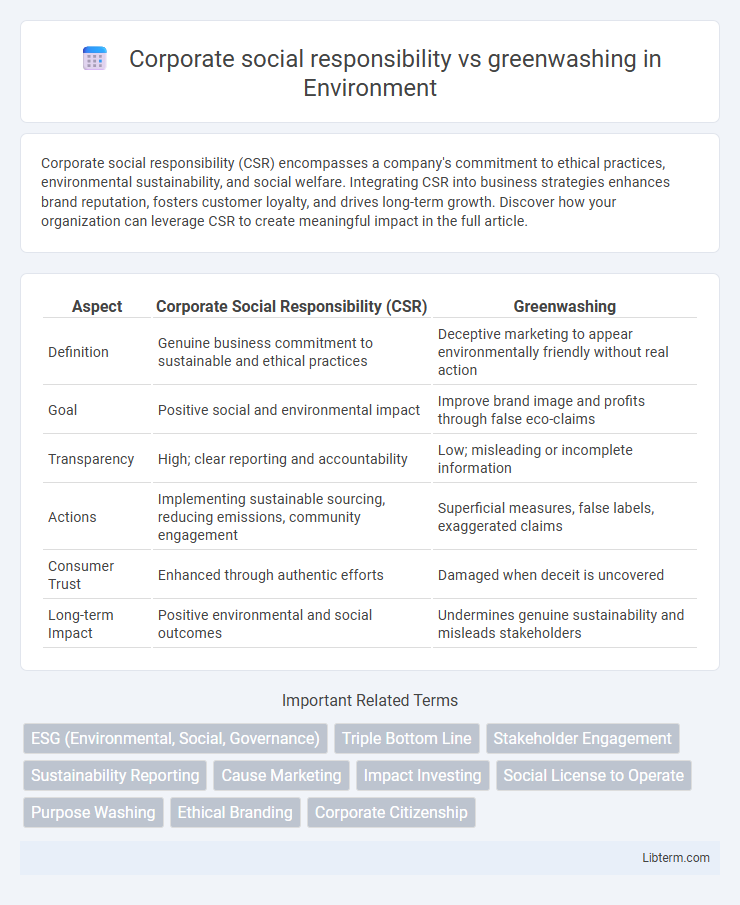
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) | Greenwashing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Genuine business commitment to sustainable and ethical practices | Deceptive marketing to appear environmentally friendly without real action |
| Goal | Positive social and environmental impact | Improve brand image and profits through false eco-claims |
| Transparency | High; clear reporting and accountability | Low; misleading or incomplete information |
| Actions | Implementing sustainable sourcing, reducing emissions, community engagement | Superficial measures, false labels, exaggerated claims |
| Consumer Trust | Enhanced through authentic efforts | Damaged when deceit is uncovered |
| Long-term Impact | Positive environmental and social outcomes | Undermines genuine sustainability and misleads stakeholders |
Understanding Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) involves companies integrating ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and social welfare into their business strategies to create long-term value for stakeholders. Authentic CSR initiatives prioritize transparency, measurable impact, and stakeholder engagement to address societal challenges such as climate change, labor rights, and community development. Distinguishing genuine CSR from greenwashing requires evaluating a company's commitment through verified sustainability reports, third-party audits, and consistency between public claims and actual corporate behavior.
Defining Greenwashing in Business Practices
Greenwashing in business practices involves misleading consumers by falsely portraying products, policies, or corporate social responsibility initiatives as environmentally friendly. This deceptive tactic aims to capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable practices without making meaningful environmental contributions. Companies engaging in greenwashing risk damaging their reputation and undermining genuine corporate social responsibility efforts.
Key Differences Between CSR and Greenwashing
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) involves authentic efforts by companies to integrate ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and social welfare into their business models, demonstrating transparency and accountability. Greenwashing occurs when companies misleadingly promote themselves as environmentally friendly through deceptive marketing without making significant sustainable changes. The key differences between CSR and greenwashing lie in genuine impact versus superficial claims, measurable outcomes versus vague promises, and stakeholder trust versus reputation manipulation.
The Importance of Authentic CSR Initiatives
Authentic corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives build trust, enhance brand reputation, and deliver measurable social or environmental impact, distinguishing companies from greenwashing practices that mislead stakeholders with false sustainability claims. Genuine CSR efforts involve transparent reporting, stakeholder engagement, and long-term commitment to ethical practices, reinforcing corporate accountability. By prioritizing authentic CSR, businesses contribute to sustainable development and mitigate risks associated with reputational damage from deceptive greenwashing tactics.
Common Tactics and Red Flags of Greenwashing
Common tactics of greenwashing include vague language, misleading eco-labels, and selective disclosure of environmental achievements that exaggerate a company's sustainability efforts. Red flags involve lack of third-party verification, inconsistent sustainability claims across platforms, and heavy emphasis on marketing over measurable environmental impact. Identifying these signs helps distinguish genuine corporate social responsibility initiatives from superficial greenwashing practices.
The Impact of CSR on Brand Reputation and Trust
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) significantly enhances brand reputation and consumer trust by demonstrating genuine commitment to ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and social welfare. In contrast, greenwashing--misleading claims about environmental efforts--can severely damage a company's credibility, leading to consumer skepticism and loss of loyalty. Transparent CSR initiatives backed by measurable outcomes build long-term brand equity and foster stronger stakeholder relationships.
Case Studies: Genuine CSR vs. Greenwashing Examples
Case studies reveal that genuine Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives, such as Patagonia's commitment to sustainable sourcing and transparent supply chains, demonstrate measurable environmental impact and social benefits. In contrast, greenwashing examples like Volkswagen's emissions scandal highlight misleading claims that damage brand trust and expose companies to legal repercussions. Analyzing these cases underscores the importance of authenticity and accountability in CSR efforts to avoid reputational risks and ensure positive stakeholder engagement.
How Consumers Can Identify Greenwashing
Consumers can identify greenwashing by scrutinizing product labels and marketing claims for vague language such as "eco-friendly" or "natural" without clear certifications like USDA Organic or Fair Trade. Analyzing a company's transparency regarding sustainability goals and verifying third-party audits or impact reports helps distinguish genuine corporate social responsibility from deceptive practices. Awareness of misleading visuals, such as heavy use of green imagery or nature themes with little substantive environmental action, also aids consumers in recognizing greenwashing tactics.
Regulatory Frameworks Addressing Greenwashing
Regulatory frameworks targeting greenwashing increasingly mandate transparent and verifiable environmental claims to safeguard genuine corporate social responsibility efforts. Laws such as the EU's Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the U.S. Federal Trade Commission's Green Guides establish clear guidelines on sustainability disclosures to prevent misleading marketing practices. Enforcement mechanisms include fines and reputational penalties, emphasizing accountability and promoting authentic sustainability initiatives.
Best Practices for Transparent and Sustainable CSR
Transparent and sustainable corporate social responsibility (CSR) prioritizes authentic environmental and social initiatives backed by measurable outcomes and third-party audits. Best practices include clear public reporting on goals and progress, engaging stakeholders in decision-making, and ensuring supply chain accountability to prevent greenwashing. Companies should integrate sustainability into core business strategies, fostering long-term commitment rather than superficial marketing efforts.
Corporate social responsibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com