Restoring natural habitats is essential for preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem health. Effective habitat restoration involves reestablishing native plant species, improving soil quality, and enhancing water availability to create a sustainable environment. Discover how you can contribute to successful habitat restoration efforts by exploring the strategies detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
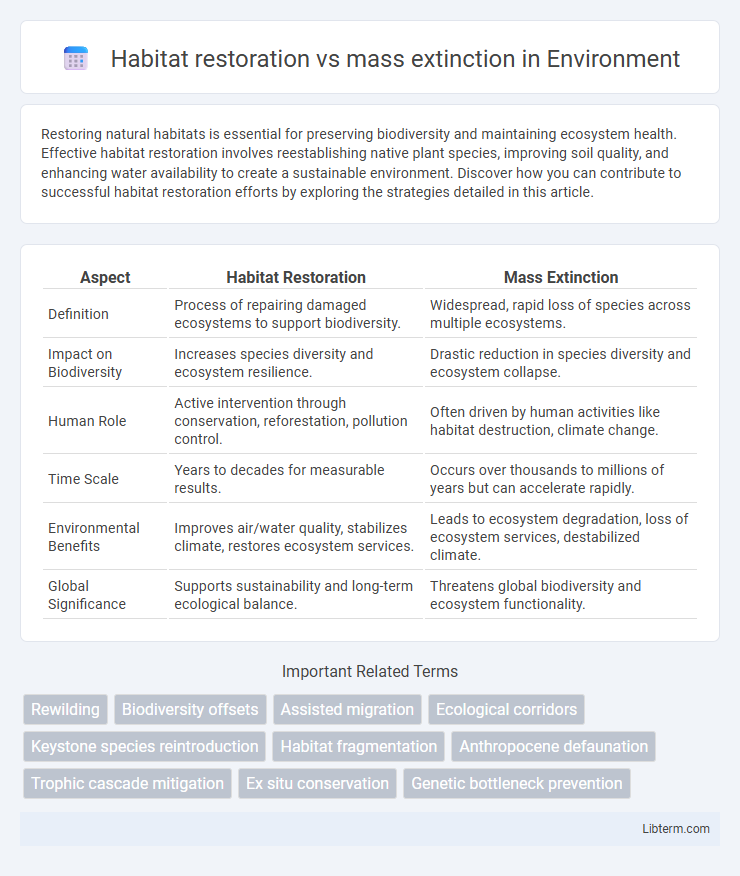
| Aspect | Habitat Restoration | Mass Extinction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of repairing damaged ecosystems to support biodiversity. | Widespread, rapid loss of species across multiple ecosystems. |
| Impact on Biodiversity | Increases species diversity and ecosystem resilience. | Drastic reduction in species diversity and ecosystem collapse. |
| Human Role | Active intervention through conservation, reforestation, pollution control. | Often driven by human activities like habitat destruction, climate change. |
| Time Scale | Years to decades for measurable results. | Occurs over thousands to millions of years but can accelerate rapidly. |
| Environmental Benefits | Improves air/water quality, stabilizes climate, restores ecosystem services. | Leads to ecosystem degradation, loss of ecosystem services, destabilized climate. |
| Global Significance | Supports sustainability and long-term ecological balance. | Threatens global biodiversity and ecosystem functionality. |
Understanding Mass Extinction: Causes and Consequences
Mass extinction events result from dramatic ecological disturbances such as habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species, leading to rapid biodiversity loss worldwide. Habitat restoration plays a crucial role in mitigating these impacts by rebuilding ecosystems, promoting species recovery, and restoring ecological balance. Effective restoration strategies involve reforestation, wetland rehabilitation, and invasive species control, which together help counteract the causes and consequences of mass extinction.
Habitat Loss as a Driver of Biodiversity Decline
Habitat loss, driven by deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion, remains the primary cause of biodiversity decline and a leading factor in mass extinction events. Effective habitat restoration efforts, such as reforestation and wetland rehabilitation, can mitigate species loss by rebuilding critical ecosystems and improving habitat connectivity. Prioritizing habitat restoration addresses fragmentation and degradation, which are essential to stabilizing populations and preserving global biodiversity.
The Science Behind Habitat Restoration
Habitat restoration employs ecological principles such as species reintroduction, native vegetation planting, and soil recovery to counteract biodiversity loss caused by habitat degradation. Scientific methods like remote sensing, GIS mapping, and genetic diversity assessments are critical for monitoring restoration success and adapting management strategies. Research shows that restoring habitat complexity directly supports species survival, enhancing ecosystem resilience against the accelerating threats of mass extinction.
Key Strategies for Effective Habitat Restoration
Key strategies for effective habitat restoration include reforestation with native plant species to rebuild ecosystems, controlling invasive species to prevent biodiversity loss, and restoring natural water cycles to support wildlife habitats. Implementing adaptive management practices based on ongoing ecological monitoring ensures resilience against environmental changes and prevents further species decline. Collaboration among governments, local communities, and conservation organizations strengthens efforts to reverse mass extinction trends through sustainable restoration initiatives.
Comparing Restoration Efforts across Ecosystems
Restoration efforts in wetlands, forests, and coral reefs show varied success rates due to differing ecological complexities and resource availability. Wetland restoration often involves reestablishing hydrology and native plant species, leading to measurable improvements in biodiversity within a few years. Coral reef restoration remains challenging due to climate stressors, requiring innovative techniques like coral gardening to combat bleaching and species loss.
Habitat Restoration: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Habitat restoration projects have successfully revived ecosystems such as the Florida Everglades and the Loess Plateau in China, leading to the return of native species and improved biodiversity. These initiatives demonstrate that combining scientific research with community involvement enhances restoration outcomes and resilience against environmental stresses. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of adaptive management, long-term monitoring, and integrating social and ecological goals to offset the impacts of mass extinction.
Barriers to Large-Scale Habitat Restoration
Large-scale habitat restoration faces significant barriers, including limited funding, land availability, and socio-political challenges that impede coordinated conservation efforts. Fragmented landscapes and invasive species further complicate restoration processes, hindering the recovery of native biodiversity essential to counteract mass extinction. Effective policy frameworks and community engagement are critical to overcoming these obstacles and promoting ecosystem resilience.
Restoration vs. Extinction: Can We Reverse the Trend?
Habitat restoration plays a critical role in mitigating biodiversity loss by rebuilding ecosystems, improving species survival rates, and enhancing ecosystem services, offering a tangible strategy to counteract ongoing mass extinction events. Scientific evidence shows that targeted restoration efforts, such as reforestation, wetland rehabilitation, and coral reef restoration, can stabilize endangered populations and increase genetic diversity, slowing or reversing extinction trends. While habitat restoration cannot fully undo the damage caused by habitat destruction and climate change, coordinated global initiatives and adequate funding are essential to maximize restoration's potential to alter the course of biodiversity loss effectively.
Policy and Community Roles in Habitat Restoration
Effective habitat restoration requires robust policy frameworks that enforce land protection, regulate pollution, and promote sustainable resource use to counter mass extinction trends. Community engagement plays a critical role by fostering local stewardship, supporting biodiversity monitoring, and ensuring restoration projects align with indigenous knowledge and social priorities. Collaborative efforts between policymakers and communities enhance resilience, mitigate habitat loss, and strengthen conservation outcomes on a global scale.
The Future of Biodiversity: Hope through Restoration Efforts
Habitat restoration plays a critical role in countering mass extinction by rebuilding ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity resilience, enabling species to recover and thrive. Effective restoration projects, such as reforestation and wetland rehabilitation, contribute to carbon sequestration and improve habitat connectivity, fostering long-term ecological stability. Advances in ecological science and community engagement offer promising strategies to reverse biodiversity losses and secure a sustainable future for endangered species worldwide.
Habitat restoration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com