Calcareous soil is rich in calcium carbonate, making it alkaline and often challenging for certain plants to absorb nutrients effectively. This type of soil influences plant growth by affecting nutrient availability, particularly iron, phosphorus, and manganese. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to manage calcareous soil for healthier gardens and crops.
Table of Comparison
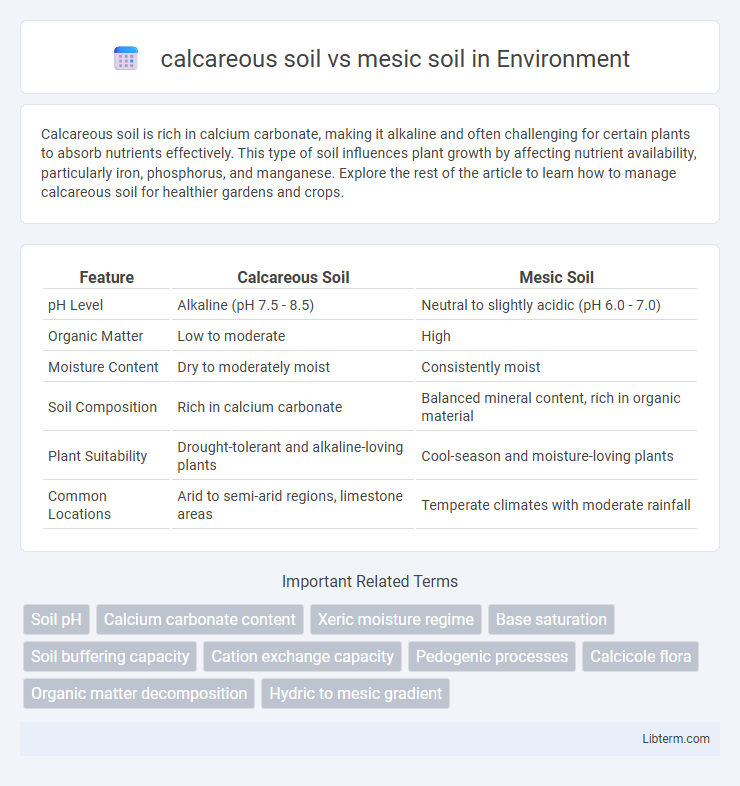
| Feature | Calcareous Soil | Mesic Soil |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | Alkaline (pH 7.5 - 8.5) | Neutral to slightly acidic (pH 6.0 - 7.0) |
| Organic Matter | Low to moderate | High |
| Moisture Content | Dry to moderately moist | Consistently moist |
| Soil Composition | Rich in calcium carbonate | Balanced mineral content, rich in organic material |
| Plant Suitability | Drought-tolerant and alkaline-loving plants | Cool-season and moisture-loving plants |
| Common Locations | Arid to semi-arid regions, limestone areas | Temperate climates with moderate rainfall |
Introduction to Calcareous and Mesic Soils
Calcareous soils are characterized by high calcium carbonate content, leading to alkaline pH levels that influence nutrient availability and plant growth. Mesic soils exhibit moderate moisture conditions and balanced nutrient profiles, supporting diverse vegetation in temperate climates. Understanding the chemical and physical properties of calcareous versus mesic soils is essential for optimizing agricultural practices and ecosystem management.
Defining Calcareous Soil: Characteristics and Composition
Calcareous soil is defined by its high calcium carbonate content, often derived from underlying limestone or chalk, which results in an alkaline pH typically above 7.5. Characterized by good drainage and a tendency to retain nutrients like calcium and magnesium, calcareous soil often exhibits a gritty texture and supports plants adapted to alkaline environments. In contrast, mesic soils maintain moderate moisture levels and neutral pH, fostering diverse plant growth without the prominent calcium influence seen in calcareous soils.
Understanding Mesic Soil: Features and Structure
Mesic soil is characterized by moderate moisture content, supporting diverse plant life with balanced drainage and nutrient availability. Its structure typically includes a well-developed organic layer above a loamy or silty mineral layer, promoting optimal root growth and microbial activity. Unlike calcareous soil, which is rich in calcium carbonate and alkaline, mesic soil maintains a neutral pH that fosters wide-ranging ecosystem productivity.
Geographical Distribution of Calcareous vs Mesic Soils
Calcareous soils predominantly occur in arid and semi-arid regions, including parts of the Mediterranean basin, southwestern United States, and Middle Eastern deserts, where calcium carbonate accumulates from limited rainfall and high evaporation rates. Mesic soils are typically found in temperate regions with moderate precipitation, such as eastern North America and parts of Europe, supporting deciduous forests and grasslands. The distinct geographical distribution reflects the climatic conditions influencing soil formation processes, with calcareous soils thriving in drier zones and mesic soils developing under balanced moisture regimes.
Soil pH and Nutrient Availability Differences
Calcareous soil typically has a high pH ranging from 7.5 to 8.5, resulting from the presence of calcium carbonate, which limits the availability of micronutrients like iron, manganese, and phosphorus. In contrast, mesic soil generally exhibits a neutral to slightly acidic pH between 6 and 7, promoting optimal nutrient availability and fostering a balanced microbial activity. These pH differences significantly influence nutrient solubility and plant nutrient uptake, with calcareous soils often requiring amendments to correct micronutrient deficiencies.
Plant Adaptations in Calcareous vs Mesic Environments
Plants in calcareous soil often develop specialized root systems to cope with high pH and low nutrient availability, utilizing mechanisms like enhanced iron and phosphorus uptake. In mesic environments, plants adapt to moderate moisture and nutrient levels by diversifying root architecture and optimizing water use efficiency. These contrasting adaptations highlight evolutionary responses to soil chemistry and moisture conditions, influencing species distribution and ecosystem function.
Agricultural Implications: Crop Suitability and Soil Management
Calcareous soil, characterized by high calcium carbonate content and alkaline pH, supports crops like barley, legumes, and grapevines that tolerate alkaline conditions but may restrict micronutrient availability, necessitating soil amendments such as sulfur or chelated fertilizers. Mesic soil, with moderate moisture and balanced pH, offers versatile crop suitability including corn, wheat, and soybeans, promoting optimal nutrient cycling and microbial activity beneficial for plant growth. Effective soil management in calcareous soils involves mitigating calcium-induced nutrient deficiencies, while mesic soils require balanced irrigation and organic matter enhancement to maintain soil structure and fertility.
Environmental Impact and Ecosystem Function
Calcareous soil, rich in calcium carbonate, influences ecosystem function by promoting alkaline conditions that favor specific plant species and microbial communities, thereby affecting biodiversity and nutrient cycling. Mesic soil, characterized by moderate moisture levels and balanced nutrient availability, supports diverse ecosystems with stable plant growth and resilient habitats, enhancing carbon sequestration and water regulation. The environmental impact of calcareous soil often includes reduced soil acidity and altered soil chemistry, while mesic soil contributes to sustainable ecosystem productivity and improved soil health across temperate regions.
Challenges in Cultivating Calcareous and Mesic Soils
Calcareous soils, rich in calcium carbonate, pose challenges such as nutrient imbalances, particularly iron and zinc deficiencies, leading to poor crop uptake and stunted growth. Mesic soils, characterized by moderate moisture levels, face difficulties with water retention and drainage fluctuations that can stress root development and reduce yields. Managing pH levels, nutrient availability, and irrigation strategies are critical for optimizing cultivation in both soil types.
Summary: Choosing the Right Soil for Plant Growth
Calcareous soil, rich in calcium carbonate, offers an alkaline environment conducive to plants that thrive in high pH and well-drained conditions, such as lavender and olive trees. Mesic soil, characterized by moderate moisture and balanced nutrient levels, supports a wide variety of plants requiring consistent water availability and fertile conditions, including many deciduous trees and shrubs. Selecting soil based on specific plant requirements for pH, drainage, and moisture ensures optimal growth and health.
calcareous soil Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com