Centralization refers to the process where decision-making authority is concentrated at the top levels of an organization, enhancing consistency and control across all departments. This approach can streamline operations, improve resource allocation, and foster unified strategic direction. Discover how centralization impacts your organization's efficiency and adaptability by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
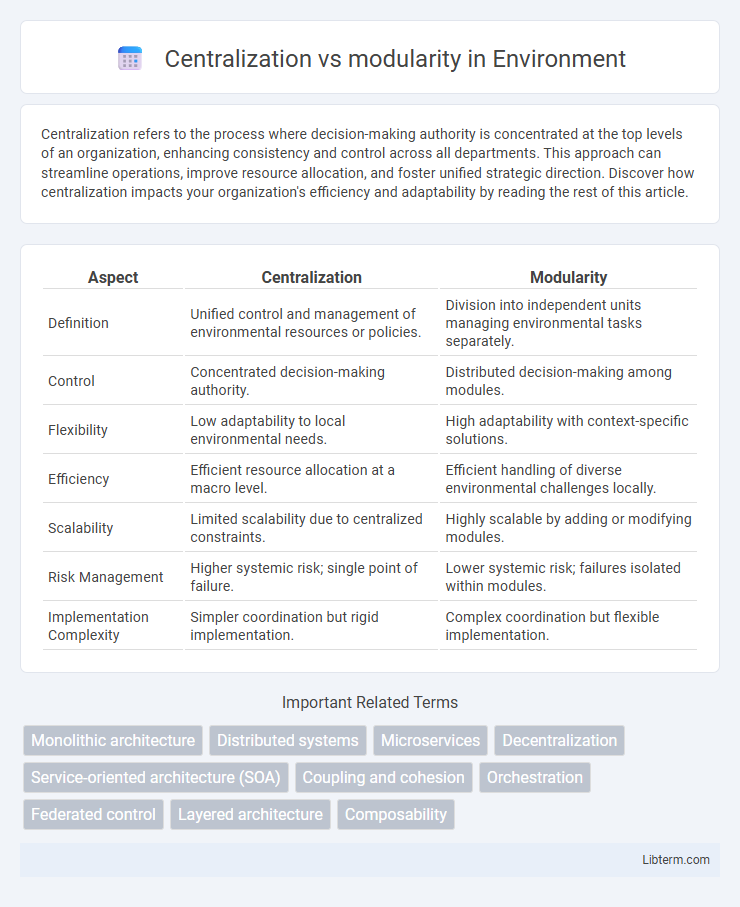
| Aspect | Centralization | Modularity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unified control and management of environmental resources or policies. | Division into independent units managing environmental tasks separately. |
| Control | Concentrated decision-making authority. | Distributed decision-making among modules. |
| Flexibility | Low adaptability to local environmental needs. | High adaptability with context-specific solutions. |
| Efficiency | Efficient resource allocation at a macro level. | Efficient handling of diverse environmental challenges locally. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability due to centralized constraints. | Highly scalable by adding or modifying modules. |
| Risk Management | Higher systemic risk; single point of failure. | Lower systemic risk; failures isolated within modules. |
| Implementation Complexity | Simpler coordination but rigid implementation. | Complex coordination but flexible implementation. |
Introduction to Centralization and Modularity
Centralization concentrates decision-making authority and control within a single, central point in an organization, enhancing consistency and streamlined coordination. Modularity, by contrast, divides systems into independent, interchangeable units, allowing flexibility, scalability, and easier maintenance. Both centralization and modularity impact organizational structure and efficiency, balancing control with adaptability.
Defining Centralization: Core Concepts
Centralization refers to the concentration of decision-making authority and control within a single, central unit or leadership body in an organization or system. Core concepts of centralization include a unified command structure, streamlined communication channels, and standardized procedures that enhance consistency and reduce redundancy. This approach often improves coordination and accountability but may limit flexibility and slow responsiveness to local needs.
Understanding Modularity in Systems
Modularity in systems refers to the decomposition of a complex system into smaller, manageable, and semi-independent units or modules that can be developed, tested, and maintained separately. This approach enhances flexibility, scalability, and ease of troubleshooting by isolating faults within individual modules, which contrasts with centralized systems where control and processes are concentrated in a single unit. Understanding modularity is crucial for designing efficient software architectures, manufacturing processes, and organizational structures that require adaptability and parallel development.
Historical Evolution: Centralized vs Modular Approaches
Centralized systems emerged early in organizational history, emphasizing hierarchical control and uniform decision-making to enhance efficiency and coordination. Over time, modularity gained traction, driven by technological advances and complex market demands, allowing independent components or units to evolve and adapt rapidly. This shift reflects a broader trend from rigid centralized control towards flexible, scalable modular architectures to balance stability with innovation.
Key Differences Between Centralization and Modularity
Centralization consolidates decision-making authority within a single point or a few top-level entities to ensure uniform control and consistency, while modularity divides a system into independent and interchangeable units to enhance flexibility and scalability. In centralized structures, communication flows vertically with tightly controlled processes, whereas modular systems promote horizontal interaction between autonomous modules that can evolve independently. Efficiency in centralized setups often hinges on streamlined oversight, whereas modularity prioritizes adaptability and rapid innovation through decentralized components.
Advantages of Centralized Structures
Centralized organizational structures enable streamlined decision-making by consolidating authority at higher management levels, resulting in consistent policies and efficient resource allocation. Enhanced control in centralized systems facilitates uniformity in procedures and faster implementation of strategic initiatives across departments. This structure reduces redundancy and simplifies communication channels, improving overall operational coherence and accountability.
Benefits of Modularity in Modern Systems
Modularity enhances scalability by breaking complex systems into independent, interchangeable components, facilitating easier updates and maintenance. It improves fault isolation, allowing individual modules to be tested and debugged without impacting the entire system's functionality. This approach fosters flexibility and innovation by enabling parallel development and integration of diverse technologies within modern software and hardware architectures.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Centralization often faces challenges such as reduced flexibility and slower decision-making due to concentrated authority, which can hinder responsiveness in dynamic environments. Modularity, while promoting adaptability and scalability, may encounter difficulties in coordination and integration across independent units, leading to potential inefficiencies and communication gaps. Both approaches require careful management of trade-offs related to control, complexity, and operational agility to optimize organizational performance.
Real-World Examples: Industry Applications
Centralization is evident in industries like banking, where centralized data management ensures uniform security protocols and compliance. In contrast, modularity dominates software development, as seen in microservices architectures that enable independent updates and scalability. Manufacturing sectors employ modular design for customizable production lines, enhancing flexibility and reducing downtime.
Choosing the Right Approach: Centralization or Modularity?
Choosing between centralization and modularity depends on an organization's size, complexity, and strategic goals. Centralization offers streamlined decision-making and consistency by consolidating authority, while modularity promotes flexibility and scalability through decentralized units that operate independently. Evaluating factors like operational efficiency, innovation capacity, and responsiveness to market changes helps determine the optimal balance between these two structural approaches.
Centralization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com