Integration streamlines your business processes by seamlessly connecting disparate systems and applications, enhancing efficiency and data consistency. It enables real-time data sharing and collaboration across departments, reducing errors and improving decision-making. Discover how effective integration can transform your operations by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
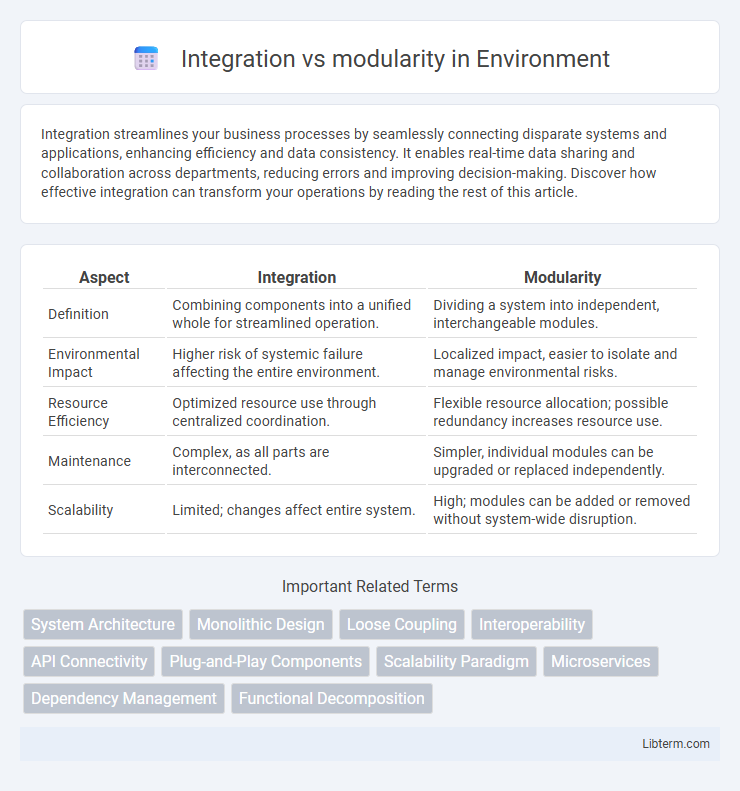
| Aspect | Integration | Modularity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining components into a unified whole for streamlined operation. | Dividing a system into independent, interchangeable modules. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher risk of systemic failure affecting the entire environment. | Localized impact, easier to isolate and manage environmental risks. |
| Resource Efficiency | Optimized resource use through centralized coordination. | Flexible resource allocation; possible redundancy increases resource use. |
| Maintenance | Complex, as all parts are interconnected. | Simpler, individual modules can be upgraded or replaced independently. |
| Scalability | Limited; changes affect entire system. | High; modules can be added or removed without system-wide disruption. |
Introduction to Integration and Modularity
Integration unifies system components to work seamlessly, enhancing overall functionality and efficiency. Modularity breaks down a system into independent, interchangeable units, promoting flexibility and easier maintenance. Both approaches balance complexity management, with integration emphasizing cohesion and modularity focusing on component isolation.
Defining Integration: Concepts and Benefits
Integration refers to the seamless connection of different systems, software, or components to function as a unified whole, enhancing data flow and operational efficiency. It enables real-time communication and collaboration across various platforms, reducing redundancies and minimizing errors. Benefits include improved decision-making speed, enhanced scalability, and streamlined business processes, which collectively boost organizational agility and competitive advantage.
Exploring Modularity: Principles and Advantages
Modularity emphasizes decomposing complex systems into smaller, interchangeable components, enhancing flexibility and maintainability. This design principle facilitates independent development and testing, reducing system-wide failures and enabling easier updates. Embracing modularity improves scalability and adaptability, crucial for evolving technological environments.
Key Differences Between Integration and Modularity
Integration combines multiple components or systems to function as a unified whole, enhancing coordination and reducing redundancy, while modularity emphasizes designing systems as independent, self-contained units that can be developed, tested, and maintained separately. Integration typically improves overall system performance by ensuring seamless interaction among modules, whereas modularity prioritizes flexibility, scalability, and ease of updates without affecting other parts. The key difference lies in integration's focus on interconnectedness and holistic operation, contrasting with modularity's focus on decoupling and independent functionality to accommodate change and customization.
Use Cases: When to Choose Integration
Integration is ideal for use cases requiring seamless data flow across multiple systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) or customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, where unified information enhances decision-making and operational efficiency. Businesses aiming to streamline workflows, reduce data silos, and ensure real-time updates benefit from integrated solutions that enable end-to-end process automation and centralized data management. Complex environments with interconnected applications and a need for consistent user experiences often demand integration over modularity to deliver cohesive functionality and maintain system integrity.
Use Cases: When Modularity is Preferred
Modularity is preferred in use cases requiring scalable and flexible system architectures, such as software development projects with evolving requirements or large teams working on independent components. It enhances maintainability by isolating functionalities into discrete modules, facilitating easier updates and debugging without impacting the entire system. This approach is especially beneficial in environments prioritizing rapid iteration, parallel development, and reuse of components across different projects.
Impact on System Scalability and Flexibility
Integration enhances system scalability by enabling seamless communication between components, facilitating faster data exchange and streamlined workflows. Modularity improves flexibility by isolating functions into independent units, allowing easier updates and customization without affecting the entire system. Balancing integration and modularity is essential for optimizing both scalability and adaptability in complex system architectures.
Cost Considerations: Integration vs Modularity
Integration often results in higher initial costs due to complex system design and tighter coupling of components, increasing development and maintenance expenses. Modularity reduces long-term costs by enabling independent updates, easier scalability, and lower risk of system-wide failures, enhancing cost efficiency. Choosing between integration and modularity depends on balancing upfront investment against flexibility and ongoing operational savings.
Challenges and Risks in Both Approaches
Integration challenges include data inconsistency, system complexity, and increased maintenance costs due to tightly coupled components. Modularity risks involve potential communication overhead, interface compatibility issues, and difficulties in managing dependencies among independently developed modules. Both approaches demand careful planning to balance flexibility, scalability, and system coherence to avoid operational inefficiencies and increased failure points.
Future Trends in System Architecture
Future trends in system architecture emphasize increased integration to enhance performance and reduce latency, while maintaining modularity to ensure scalability and flexibility in complex systems. Emerging technologies such as microservices and edge computing promote modular frameworks that can be seamlessly integrated through standardized APIs and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes. Advancements in AI-driven design tools are expected to optimize the balance between integration and modularity, enabling adaptive architectures that evolve with changing operational demands.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com