Composting transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil, reducing landfill impact and promoting sustainable gardening. This natural process enhances soil structure, retains moisture, and supports healthy plant growth. Discover how composting can benefit your garden and environment by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
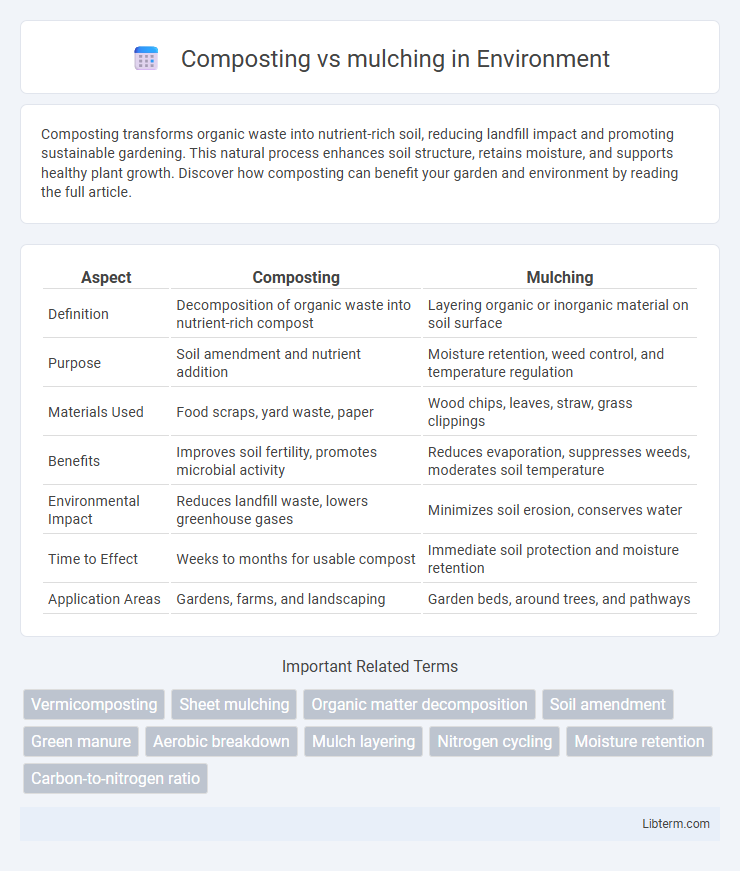
| Aspect | Composting | Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decomposition of organic waste into nutrient-rich compost | Layering organic or inorganic material on soil surface |
| Purpose | Soil amendment and nutrient addition | Moisture retention, weed control, and temperature regulation |
| Materials Used | Food scraps, yard waste, paper | Wood chips, leaves, straw, grass clippings |
| Benefits | Improves soil fertility, promotes microbial activity | Reduces evaporation, suppresses weeds, moderates soil temperature |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers greenhouse gases | Minimizes soil erosion, conserves water |
| Time to Effect | Weeks to months for usable compost | Immediate soil protection and moisture retention |
| Application Areas | Gardens, farms, and landscaping | Garden beds, around trees, and pathways |
Introduction to Composting and Mulching
Composting transforms organic waste such as kitchen scraps and yard debris into nutrient-rich humus that enhances soil health and fertility through microbial activity. Mulching involves applying a protective layer of materials like wood chips, straw, or shredded leaves on soil surfaces to regulate moisture, suppress weeds, and improve temperature stability. Both practices play crucial roles in sustainable gardening by recycling organic matter and promoting plant growth.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Composting is the biological process of decomposing organic waste into nutrient-rich humus through microbial activity, enhancing soil fertility and structure. Mulching involves the application of organic or inorganic materials on the soil surface to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate temperature. Both practices support sustainable gardening but differ fundamentally in purpose and method, with compost enriching soil internally and mulch protecting soil externally.
Key Differences Between Composting and Mulching
Composting transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich humus through aerobic decomposition, enhancing soil fertility and structure. Mulching involves spreading organic or inorganic materials on soil surfaces to conserve moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds without significantly altering soil composition. While compost integrates nutrients directly, mulch primarily acts as a protective layer that slowly breaks down over time.
Benefits of Composting
Composting enhances soil fertility by enriching it with essential nutrients and beneficial microorganisms that improve plant growth and resilience. It reduces organic waste in landfills, thereby lowering methane emissions and promoting environmental sustainability. Compost also improves soil structure, water retention, and aeration, leading to healthier ecosystems and increased agricultural productivity.
Benefits of Mulching
Mulching enhances soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation, which supports healthy plant growth and conserves water. It also suppresses weed growth, minimizing competition for nutrients and reducing the need for herbicides. Furthermore, mulching regulates soil temperature, providing insulation during extreme weather and promoting root development.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Composting breaks down organic waste into nutrient-rich humus, reducing landfill methane emissions and enhancing soil carbon sequestration, which mitigates climate change. Mulching conserves soil moisture, prevents erosion, and suppresses weeds, reducing the need for chemical herbicides that can harm ecosystems. Both practices promote sustainable waste management and improve soil health, but composting offers greater benefits in carbon cycling and greenhouse gas reduction.
Materials Suitable for Composting vs Mulching
Composting requires organic materials rich in nitrogen and carbon, such as vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings, and dry leaves, which break down to form nutrient-dense humus. Mulching involves using materials like straw, wood chips, bark, pine needles, and shredded leaves that decompose slowly to protect soil moisture and regulate temperature. While compost materials need a balance of green and brown components to decompose efficiently, mulch materials are selected primarily for their durability and ability to suppress weeds.
Steps to Start Composting at Home
Start composting at home by selecting a well-drained location with partial sunlight and gathering organic materials such as fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings, and dry leaves. Layer these materials in a compost bin, alternating between green nitrogen-rich items and brown carbon-rich items, then regularly turn the pile to aerate and speed up decomposition. Maintain moisture at the consistency of a damp sponge and avoid adding meat, dairy, or oily foods to prevent odors and pests.
How to Mulch Effectively in Your Garden
Mulching effectively in your garden involves applying a 2-4 inch layer of organic materials such as wood chips, straw, or shredded leaves around plants to retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate temperature. It is essential to keep mulch a few inches away from plant stems and tree trunks to prevent rot and pest issues. Regularly replenish mulch layers and monitor moisture levels to maximize soil health and plant growth.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden Needs
Choosing between composting and mulching depends on your garden's specific needs, soil condition, and plant types. Composting enriches soil with nutrients and improves structure by breaking down organic waste, making it ideal for long-term soil health and vegetable gardens. Mulching helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature, which benefits flower beds and established plants requiring moisture conservation.
Composting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com