Cover cropping improves soil health by reducing erosion, enhancing nutrient cycling, and increasing organic matter, which leads to higher crop yields. This sustainable agricultural practice also suppresses weeds, manages pests, and conserves moisture, benefiting your farm's long-term productivity. Discover how cover cropping can transform your soil and farming efficiency by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
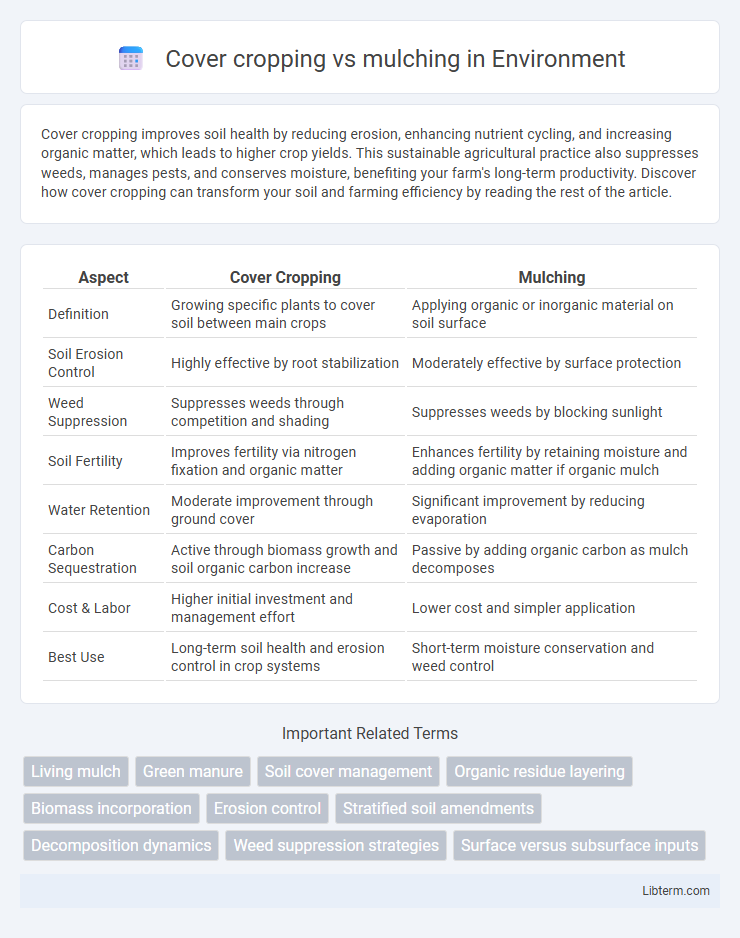
| Aspect | Cover Cropping | Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing specific plants to cover soil between main crops | Applying organic or inorganic material on soil surface |
| Soil Erosion Control | Highly effective by root stabilization | Moderately effective by surface protection |
| Weed Suppression | Suppresses weeds through competition and shading | Suppresses weeds by blocking sunlight |
| Soil Fertility | Improves fertility via nitrogen fixation and organic matter | Enhances fertility by retaining moisture and adding organic matter if organic mulch |
| Water Retention | Moderate improvement through ground cover | Significant improvement by reducing evaporation |
| Carbon Sequestration | Active through biomass growth and soil organic carbon increase | Passive by adding organic carbon as mulch decomposes |
| Cost & Labor | Higher initial investment and management effort | Lower cost and simpler application |
| Best Use | Long-term soil health and erosion control in crop systems | Short-term moisture conservation and weed control |
Introduction to Cover Cropping and Mulching
Cover cropping involves planting specific crops like clover or rye during off-season periods to improve soil health by enhancing nutrient cycling, reducing erosion, and suppressing weeds. Mulching uses organic or inorganic materials such as straw, wood chips, or plastic sheeting spread on the soil surface to conserve moisture, regulate soil temperature, and minimize weed growth. Both techniques promote sustainable agriculture by maintaining soil structure and fertility while supporting crop productivity.
Key Differences Between Cover Cropping and Mulching
Cover cropping involves planting specific crops such as clover or rye to improve soil health, enhance nutrient cycling, and reduce erosion, while mulching entails applying organic or inorganic materials like straw or plastic to suppress weeds and retain soil moisture. Cover crops actively grow and contribute biomass, fixing nitrogen and improving soil structure, whereas mulch serves primarily as a protective layer without direct nutrient contributions. The key difference lies in cover cropping's role in actively enriching soil biology versus mulching's function as a passive barrier to environmental stressors.
Soil Health Benefits: Cover Crops vs Mulches
Cover cropping enhances soil health by increasing organic matter, improving soil structure, and promoting beneficial microbial activity through root growth and residue decomposition. Mulching primarily protects soil from erosion, conserves moisture, and moderates soil temperature but offers limited direct nutrient contributions compared to cover crops. While both practices reduce weed pressure and soil compaction, cover crops provide superior long-term improvements in soil fertility and biological diversity.
Impact on Soil Erosion Control
Cover cropping significantly reduces soil erosion by creating a protective vegetative barrier that stabilizes the soil, improves water infiltration, and enhances organic matter content. Mulching serves as a physical shield that minimizes the impact of raindrops on the soil surface, reduces surface runoff, and maintains soil moisture levels. Both practices effectively control soil erosion, but cover cropping provides the added benefit of improving soil structure and fertility through root growth and organic residue.
Weed Suppression: Which Method Works Best?
Cover cropping excels at weed suppression by outcompeting weeds through dense plant growth and shading, reducing weed seed germination effectively. Mulching inhibits weed growth by physically blocking sunlight and creating a barrier, which slows weed emergence but may not prevent deep-rooted species as efficiently. Research indicates that integrating cover crops with organic mulches often provides the most comprehensive weed control by combining competitive growth with physical obstruction.
Moisture Retention: Mulch vs Cover Crops
Mulching creates a physical barrier that reduces soil evaporation and maintains consistent moisture levels, making it highly effective for immediate moisture retention. Cover crops enhance soil structure and organic matter over time, improving water infiltration and long-term moisture-holding capacity in the soil profile. Choosing between mulch and cover crops depends on whether short-term surface moisture conservation or sustained soil moisture improvement is the primary goal.
Nutrient Management and Soil Fertility
Cover cropping enhances nutrient management by fixing atmospheric nitrogen, increasing organic matter, and improving soil structure, which boosts soil fertility over time. Mulching conserves soil moisture and moderates soil temperature but provides limited direct nutrient inputs compared to cover crops. Integrating cover crops with mulching maximizes nutrient cycling and sustains long-term soil health.
Cost-Effectiveness and Labor Requirements
Cover cropping reduces expenses by naturally enhancing soil fertility and structure, minimizing the need for synthetic fertilizers, while requiring moderate labor for sowing and termination. Mulching offers immediate weed suppression and moisture retention benefits at a relatively low upfront cost but demands regular labor for application and replacement. Evaluating both practices involves balancing initial investment, ongoing maintenance labor, and long-term soil health benefits to achieve optimal cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Sustainability: Comparing Both Practices
Cover cropping enhances environmental sustainability by improving soil health, reducing erosion, and increasing biodiversity through living plant roots that fix nitrogen and support beneficial organisms. Mulching conserves soil moisture, moderates temperature, and suppresses weeds by providing a protective organic layer on the soil surface, which also contributes to carbon sequestration. Both practices play critical roles in sustainable agriculture by reducing chemical inputs and promoting resilient ecosystems, yet cover cropping offers more dynamic soil rehabilitation while mulching excels in immediate soil protection.
Choosing Between Cover Cropping and Mulching for Your Garden
Choosing between cover cropping and mulching depends on your garden's specific needs, soil health goals, and crop requirements. Cover cropping enhances soil fertility and structure by fixing nitrogen and increasing organic matter, making it ideal for nutrient-poor soils and long-term fertility improvement. Mulching controls weeds, retains moisture, and moderates soil temperature, providing immediate protection and conserving resources in established gardens.
Cover cropping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com