Non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels, are finite and deplete over time, while renewable resources like solar energy replenish naturally and continuously. Sustainable resources are managed to meet present needs without compromising future availability, and inexhaustible resources, including wind and sunlight, remain abundant regardless of human use. Understanding these resource categories will help you make informed decisions about energy consumption and environmental impact--read on to explore their significance in detail.
Table of Comparison
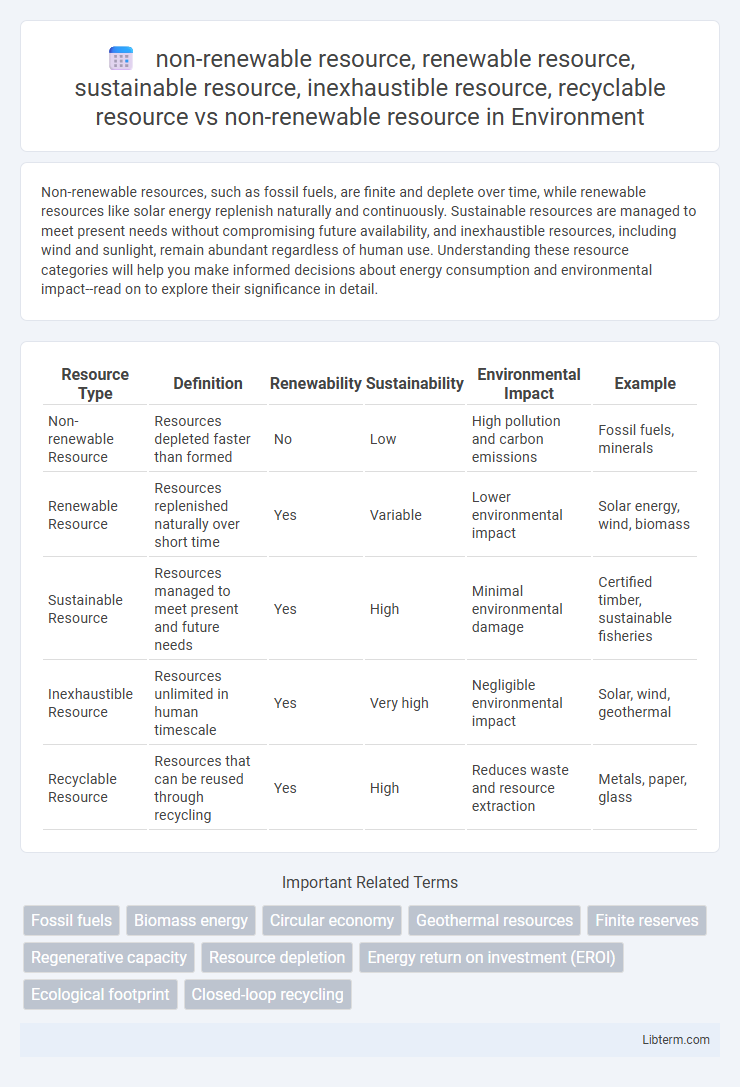
| Resource Type | Definition | Renewability | Sustainability | Environmental Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-renewable Resource | Resources depleted faster than formed | No | Low | High pollution and carbon emissions | Fossil fuels, minerals |
| Renewable Resource | Resources replenished naturally over short time | Yes | Variable | Lower environmental impact | Solar energy, wind, biomass |
| Sustainable Resource | Resources managed to meet present and future needs | Yes | High | Minimal environmental damage | Certified timber, sustainable fisheries |
| Inexhaustible Resource | Resources unlimited in human timescale | Yes | Very high | Negligible environmental impact | Solar, wind, geothermal |
| Recyclable Resource | Resources that can be reused through recycling | Yes | High | Reduces waste and resource extraction | Metals, paper, glass |
Understanding Resource Classifications: Key Definitions
Non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, are finite and deplete over time due to limited natural replenishment. Renewable resources, including solar energy and wind, regenerate naturally at a sustainable rate, ensuring continuous availability. Sustainable resources balance utilization and conservation to maintain ecosystem health, while inexhaustible resources, like sunlight, remain abundant regardless of consumption; recyclable resources can be reused to reduce dependence on non-renewable materials and minimize environmental impact.
Non-Renewable Resources: Characteristics and Examples
Non-renewable resources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite natural assets formed over millions of years that cannot be replenished within a human timescale, leading to eventual depletion. These resources possess characteristics like limited availability, high energy density, and significant environmental impact due to extraction and combustion. Unlike renewable resources like solar and wind energy, which regenerate naturally, non-renewable resources require careful management and substitution with sustainable or inexhaustible resources to minimize ecological damage and ensure long-term energy security.
Renewable Resources: Features and Significance
Renewable resources, such as solar energy, wind, and biomass, naturally replenish over short periods, making them vital for sustainable development and reducing dependence on finite non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas. These resources exhibit features including regeneration capacity, minimal environmental impact, and potential for continuous supply, essential for mitigating climate change and promoting energy security. Emphasizing renewable resources supports ecological balance and long-term economic stability by conserving non-renewable reserves and enabling efficient recycling practices within sustainable resource management frameworks.
Sustainable Resources: Balancing Use and Regeneration
Sustainable resources are managed to balance consumption with natural regeneration, ensuring long-term availability and minimizing environmental impact. Unlike non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels, which deplete finite reserves, sustainable resources emphasize renewable and recyclable materials that support ecosystem health. Effective stewardship of sustainable resources integrates efficient use, restoration efforts, and innovation to promote resilience within natural and human systems.
Inexhaustible Resources: Unlimited Natural Supplies
Inexhaustible resources, such as solar and wind energy, provide unlimited natural supplies that do not diminish over time, contrasting sharply with non-renewable resources like fossil fuels which are finite and deplete with use. Renewable and sustainable resources replenish naturally through ecological cycles, promoting environmental balance, while recyclable resources reduce waste by enabling material reuse, yet still depend on initial finite resources. Understanding the distinctions among these resource types emphasizes the importance of shifting towards inexhaustible resources to achieve long-term energy security and ecological sustainability.
Comparing Recyclable and Non-Renewable Resources
Recyclable resources are materials like metals and certain plastics that can be reprocessed and reused multiple times, reducing the need for extracting new raw materials, whereas non-renewable resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas are finite and deplete with use, leading to environmental degradation and resource scarcity. Unlike non-renewable resources, recyclable materials help conserve energy, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainable consumption patterns by minimizing waste. The efficient recycling of resources supports a circular economy and mitigates the environmental impact associated with the extraction and consumption of non-renewable resources.
Environmental Impacts of Resource Utilization
Non-renewable resources like fossil fuels cause significant environmental degradation through greenhouse gas emissions and habitat destruction, whereas renewable resources such as solar and wind energy offer cleaner alternatives with minimal ecological footprints. Sustainable resources involve managed utilization that maintains ecosystem balance, reducing long-term environmental damage, while inexhaustible resources like sunlight and wind remain perpetually available without depletion. Recyclable resources mitigate waste accumulation and conserve raw materials, contrasting with non-renewable resources that, once exhausted, lead to increased pollution and resource scarcity impacting biodiversity and climate stability.
Strategies for Enhancing Resource Sustainability
Strategies for enhancing resource sustainability focus on maximizing the use of renewable resources, promoting sustainable resource management, and improving recycling technologies to reduce reliance on non-renewable resources like fossil fuels and minerals. Implementing energy-efficient systems and encouraging the adoption of inexhaustible resources such as solar and wind power help decrease environmental impact and extend resource availability. Developing circular economy practices ensures recyclable resources are reused effectively, minimizing waste and conserving non-renewable resource reserves.
Technological Innovations in Resource Management
Technological innovations in resource management significantly enhance the efficient utilization of non-renewable resources by improving extraction methods and reducing waste. Renewable and inexhaustible resources benefit from advancements in energy storage and smart grid systems, promoting sustainable resource use. Recycling technologies further optimize resource cycles by converting recyclable materials into new products, decreasing dependency on finite non-renewable resources and supporting long-term environmental sustainability.
Future Perspectives on Responsible Resource Use
Future perspectives on responsible resource use emphasize maximizing renewable and sustainable resources like solar, wind, and biomass to reduce reliance on finite non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels and minerals. Integrating recyclable materials into production cycles minimizes environmental impact and preserves non-renewable reserves. Technological advancements and policy frameworks aim to balance resource consumption with ecosystem health, promoting inexhaustible resources for long-term ecological and economic stability.
non-renewable resource, renewable resource, sustainable resource, inexhaustible resource, recyclable Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com