A recyclable resource is any material that can be processed and used again, reducing waste and conserving natural resources. Properly managing recyclable materials like paper, plastic, glass, and metals helps lower environmental impact and supports sustainable living. Discover how effectively utilizing recyclable resources can benefit your community and the planet by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
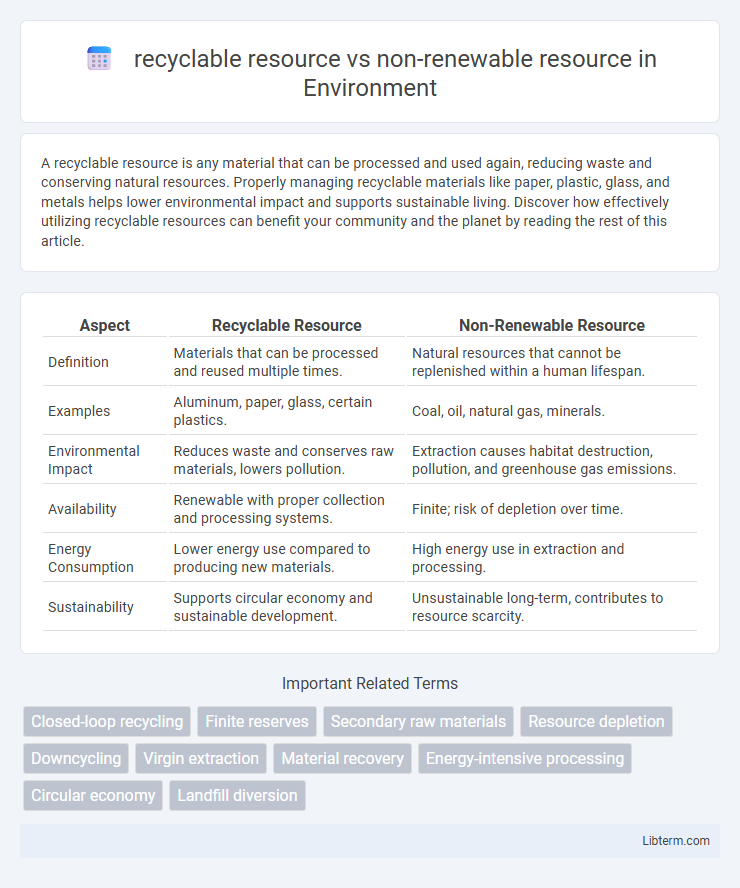
| Aspect | Recyclable Resource | Non-Renewable Resource |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Materials that can be processed and reused multiple times. | Natural resources that cannot be replenished within a human lifespan. |
| Examples | Aluminum, paper, glass, certain plastics. | Coal, oil, natural gas, minerals. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and conserves raw materials, lowers pollution. | Extraction causes habitat destruction, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Availability | Renewable with proper collection and processing systems. | Finite; risk of depletion over time. |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy use compared to producing new materials. | High energy use in extraction and processing. |
| Sustainability | Supports circular economy and sustainable development. | Unsustainable long-term, contributes to resource scarcity. |
Introduction to Recyclable and Non-Renewable Resources
Recyclable resources, such as metals, paper, and glass, can be processed and reused multiple times, reducing waste and conserving natural materials. Non-renewable resources, including fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite and deplete over time due to their slow formation rate. Understanding the distinction between these resource types is essential for sustainable resource management and environmental conservation.
Defining Recyclable Resources
Recyclable resources are materials that can be reprocessed and reused multiple times without significantly degrading their quality, such as metals, glass, paper, and certain plastics. These resources help reduce environmental impact by minimizing waste and conserving natural resources. Unlike non-renewable resources, which are finite and deplete over time, recyclable resources support sustainable consumption through continual recovery and reuse.
Characteristics of Non-Renewable Resources
Non-renewable resources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have finite reserves formed over millions of years and cannot be replenished within a human timeframe. Their extraction and consumption lead to depletion of natural stocks and often contribute to environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. These characteristics contrast with recyclable resources, which can be reused or regenerated more rapidly, reducing environmental impact and fostering sustainable resource management.
Examples of Common Recyclable Materials
Common recyclable materials include aluminum cans, paper, glass bottles, and certain plastics such as PET and HDPE. These materials can be processed and reused multiple times, reducing the need for extracting non-renewable resources like petroleum, coal, and natural gas. Recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy required to produce new aluminum from ore, highlighting the environmental and economic benefits of using recyclable resources.
Types of Non-Renewable Resources
Non-renewable resources consist primarily of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, along with minerals and metals like uranium and copper. These resources form over millions of years and cannot be replenished within a human timeframe, making their depletion a critical environmental concern. Unlike recyclable resources, non-renewable resources often require extensive extraction processes and generate significant pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Environmental Impact: Recyclable vs. Non-Renewable
Recyclable resources significantly reduce environmental impact by minimizing waste, conserving raw materials, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions during production processes. Non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, contribute to pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change due to their finite availability and extraction methods. Prioritizing recyclable resource use promotes sustainability and helps mitigate ecological degradation associated with non-renewable resource consumption.
Economic Benefits of Recycling Resources
Recycling recyclable resources such as metals, paper, and plastics significantly reduces the demand for non-renewable resources like fossil fuels and minerals, leading to substantial cost savings in raw material extraction and processing. This practice lowers energy consumption, decreases greenhouse gas emissions, and creates job opportunities in the recycling and manufacturing industries, enhancing economic resilience. Investing in recycling infrastructure promotes sustainable economic growth by conserving finite resources and reducing waste management expenses.
Challenges in Recycling and Resource Management
Recyclable resources face challenges such as contamination, sorting inefficiencies, and limited recycling infrastructure, leading to reduced material recovery rates and increased environmental impact. Non-renewable resource management struggles with depletion rates, environmental degradation from extraction, and difficulties in developing sustainable alternatives. Addressing these challenges requires advances in recycling technologies, improved waste management policies, and investment in renewable resource development to ensure long-term resource sustainability.
Strategies for Reducing Dependence on Non-Renewables
Implementing efficient recycling systems maximizes the reuse of recyclable resources, significantly lowering demand for non-renewable materials like fossil fuels and minerals. Promoting renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower reduces reliance on finite, non-renewable energy supplies. Enhancing energy efficiency in industries and consumer products also plays a crucial role in minimizing consumption of non-renewable resources.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Resource Use
Recyclable resources play a critical role in the future outlook for sustainable resource use by enabling circular economies that minimize waste and reduce extraction of finite materials. Non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, face depletion risks that drive innovation in renewable energy sources and material recycling technologies. Advancements in recycling efficiency and sustainable resource management are essential to balancing economic growth with environmental preservation and long-term resource availability.
recyclable resource Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com