Diffuse source pollution arises from multiple, often indistinct origins such as runoff from agricultural fields, urban areas, and atmospheric deposition, making it challenging to control. It significantly impacts water quality by introducing excess nutrients, sediments, and contaminants into rivers, lakes, and coastal waters. Explore the rest of this article to understand how diffuse source pollution affects ecosystems and what strategies can help mitigate its effects.
Table of Comparison
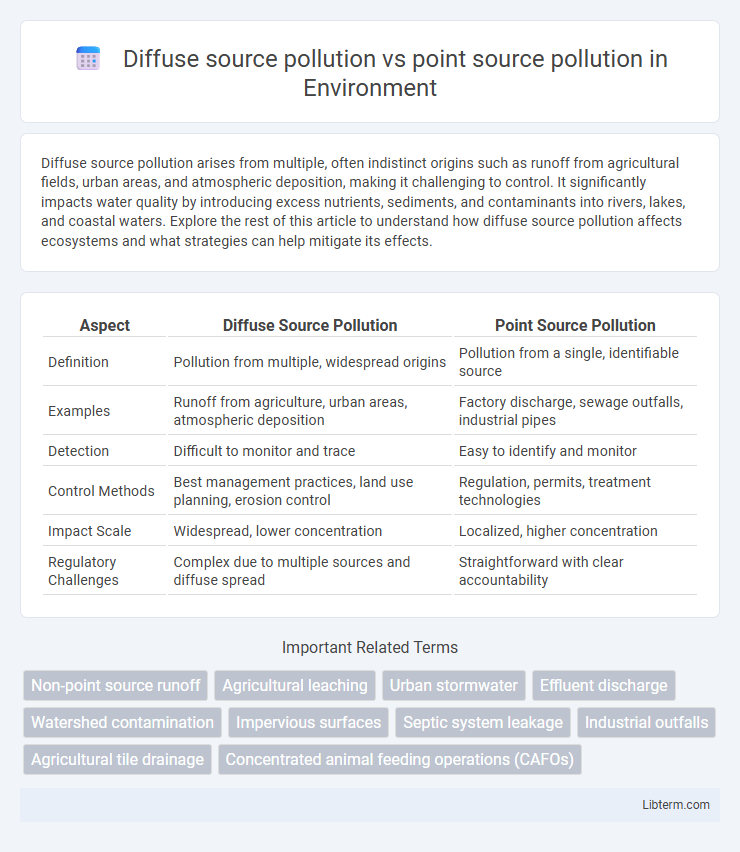
| Aspect | Diffuse Source Pollution | Point Source Pollution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pollution from multiple, widespread origins | Pollution from a single, identifiable source |
| Examples | Runoff from agriculture, urban areas, atmospheric deposition | Factory discharge, sewage outfalls, industrial pipes |
| Detection | Difficult to monitor and trace | Easy to identify and monitor |
| Control Methods | Best management practices, land use planning, erosion control | Regulation, permits, treatment technologies |
| Impact Scale | Widespread, lower concentration | Localized, higher concentration |
| Regulatory Challenges | Complex due to multiple sources and diffuse spread | Straightforward with clear accountability |
Introduction to Water Pollution Sources
Diffuse source pollution originates from widespread, non-specific areas such as agricultural runoff, urban stormwater, and atmospheric deposition, making it challenging to control and monitor. Point source pollution comes from identifiable, localized origins like industrial discharges, wastewater treatment plants, and sewage outfalls, allowing for targeted regulatory measures. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing effective water quality management and pollution mitigation strategies.
Defining Diffuse Source Pollution
Diffuse source pollution originates from multiple, scattered sources such as agricultural runoff, urban stormwater, and atmospheric deposition, making it difficult to trace and manage compared to point source pollution, which is discharged from a single, identifiable location like a factory or sewage treatment plant. This type of pollution introduces contaminants like nutrients, pesticides, and sediments into water bodies over large areas, leading to widespread environmental impacts such as eutrophication and habitat degradation. Effective control of diffuse source pollution requires integrated land-use management and best management practices across entire watersheds.
Understanding Point Source Pollution
Point source pollution originates from a single, identifiable location such as a factory discharge pipe or wastewater treatment plant outfall, making it easier to monitor and regulate. This type of pollution typically involves specific contaminants like heavy metals, chemicals, or pathogens directly entering water bodies. Effective management of point source pollution relies on permits, treatment technologies, and regulatory enforcement to prevent environmental damage.
Key Differences Between Diffuse and Point Source Pollution
Diffuse source pollution originates from multiple, scattered sources such as agricultural runoff or urban stormwater, making it difficult to identify and control. Point source pollution comes from a single, identifiable source like a factory discharge pipe or wastewater treatment plant, allowing for easier regulation and monitoring. The distinct nature of these pollution types affects management strategies, with point source pollution often addressed through permits and diffuse pollution requiring broader land-use planning and best management practices.
Common Examples of Diffuse Source Pollution
Diffuse source pollution originates from multiple, scattered sources, making it challenging to control and regulate compared to point source pollution, which comes from a single, identifiable location like a factory discharge pipe. Common examples of diffuse source pollution include agricultural runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides, urban stormwater runoff carrying oil, heavy metals, and sediments, and atmospheric deposition of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide. These pollutants collectively degrade water quality by increasing nutrient loads, causing eutrophication, and introducing toxic substances into aquatic ecosystems.
Typical Examples of Point Source Pollution
Typical examples of point source pollution include discharges from wastewater treatment plants, effluents from factories, and outflow pipes from oil refineries directly entering water bodies. These pollution sources are identifiable and localized, making regulation and monitoring more straightforward compared to diffuse source pollution. Point source pollutants often contain concentrated chemicals or pathogens that can severely impact aquatic ecosystems and human health.
Environmental Impacts of Diffuse and Point Source Pollution
Diffuse source pollution, resulting from widespread activities like agricultural runoff and urban stormwater, causes nutrient loading and sedimentation that degrade aquatic ecosystems and reduce biodiversity. Point source pollution, typically from identifiable sources such as factories and wastewater treatment plants, introduces concentrated toxins and heavy metals that can cause acute harm to water quality and aquatic life. Both types of pollution contribute to eutrophication, habitat disruption, and increased health risks, but diffuse pollution often poses greater challenges for regulation and remediation due to its dispersed origin.
Monitoring and Detection Methods
Monitoring point source pollution often relies on direct sampling and continuous sensors installed at discharge points, providing precise contaminant data from identifiable sources such as factories or wastewater treatment plants. Diffuse source pollution requires broader, landscape-level monitoring techniques including remote sensing, GIS mapping, and modeling to detect pollutant loads from multiple, non-point locations like agricultural runoff or urban stormwater. Advanced methods like bioindicator organisms and real-time sensor networks enhance detection accuracy for both pollution types, facilitating targeted mitigation strategies.
Prevention and Control Strategies
Prevention and control strategies for diffuse source pollution emphasize landscape management practices such as buffer strips, cover crops, and controlled use of fertilizers to reduce runoff and nutrient leaching across broad areas. Point source pollution control relies on regulatory measures including treatment of industrial discharge, improved wastewater treatment plants, and strict monitoring of effluent quality to directly limit contaminant release from identifiable sources. Implementing integrated watershed management with tailored interventions effectively minimizes both pollution types by addressing specific sources and diffuse contributions.
Future Challenges and Sustainable Solutions
Future challenges in addressing diffuse source pollution include managing widespread agricultural runoff and urban stormwater, which are harder to monitor and regulate compared to point source pollution that originates from identifiable facilities like factories or sewage treatment plants. Sustainable solutions emphasize implementing precision agriculture, constructing wetlands, and improving green infrastructure to reduce nutrient loading and chemical contaminants from non-point sources. Advances in real-time water quality monitoring and policy frameworks promoting integrated watershed management are critical for mitigating both diffuse and point source pollution effectively.
Diffuse source pollution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com