Rain drip refers to the slow, steady falling of individual water droplets from surfaces after rainfall or condensation. This natural occurrence can create soothing sounds and contribute to the ambiance of outdoor and indoor environments alike. Discover how understanding rain drips can enhance your appreciation of nature's subtle rhythms in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
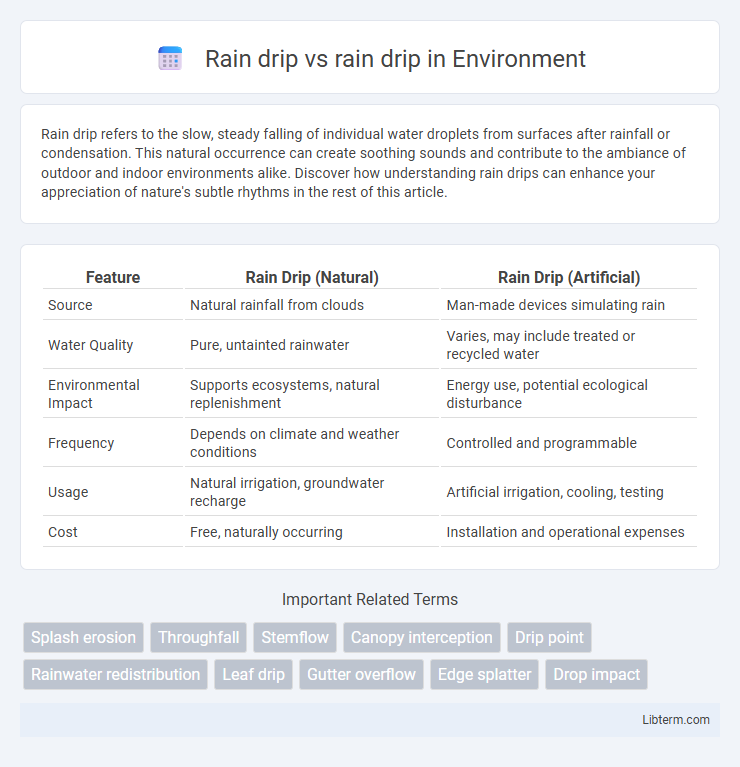
| Feature | Rain Drip (Natural) | Rain Drip (Artificial) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural rainfall from clouds | Man-made devices simulating rain |
| Water Quality | Pure, untainted rainwater | Varies, may include treated or recycled water |
| Environmental Impact | Supports ecosystems, natural replenishment | Energy use, potential ecological disturbance |
| Frequency | Depends on climate and weather conditions | Controlled and programmable |
| Usage | Natural irrigation, groundwater recharge | Artificial irrigation, cooling, testing |
| Cost | Free, naturally occurring | Installation and operational expenses |
Introduction to Rain Drip Systems
Rain drip systems offer efficient water management by directing rainwater from roofs to designated drainage areas, preventing erosion and structural damage. These systems use strategically placed gutters and downspouts to collect and channel runoff effectively, enhancing rainwater harvesting and landscape irrigation. Proper installation and maintenance of rain drip mechanisms optimize water flow and reduce the risk of water pooling or leaks around building foundations.
What is Rain Drip?
Rain drip refers to the slow, continuous dripping of water from edges of roofs, branches, or other surfaces after rainfall. This phenomenon occurs when accumulated rainwater gradually escapes due to gravity, often signaling poor drainage or inefficient gutter systems. Proper rain drip management is essential to prevent water damage to building foundations and maintain structural integrity.
Key Features of Rain Drip Systems
Rain drip systems feature precise water distribution mechanisms designed to deliver consistent moisture directly to plant roots, reducing water waste and promoting healthier growth. These systems often include adjustable emitters, pressure compensating valves, and UV-resistant tubing to ensure durability and efficient irrigation under various weather conditions. Key advantages include water conservation, minimized soil erosion, and customizable flow rates tailored to specific garden or agricultural needs.
Rain Drip vs Traditional Watering Methods
Rain drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots through a controlled drip system, minimizing evaporation and runoff, unlike traditional watering methods that often waste water through sprinklers or hoses. This precise delivery system enhances water efficiency by up to 70%, promotes healthier plant growth, and reduces weed proliferation by targeting only the desired areas. Compared to conventional watering, rain drip irrigation conserves water resources and lowers utility costs while improving soil moisture consistency.
Installation Process: Rain Drip vs Rain Drip
The installation process of Rain Drip vs Rain Drip mainly differs in their mounting and sealing techniques, with one model offering a more streamlined setup compatible with standard gutter systems, reducing labor time. Material quality impacts ease of installation, as durable components in the premium Rain Drip minimize adjustments during fitting, ensuring a secure and leak-proof attachment. Proper alignment and sealing are critical steps to prevent water damage, making precise measurements and weather-resistant adhesives essential for both systems.
Efficiency and Water Savings Comparison
RainDrip irrigation systems demonstrate superior efficiency by delivering water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional rain drip methods. This targeted watering approach results in significant water savings, often reducing consumption by up to 50% while maintaining optimal soil moisture levels. Efficient water distribution not only conserves resources but also promotes healthier plant growth through consistent hydration.
Maintenance Requirements of Rain Drip Systems
Rain drip systems require regular inspection and cleaning to prevent clogging and ensure efficient water drainage. Maintenance involves checking tubing for blockages, clearing debris from collection points, and replacing worn components promptly. Proper upkeep extends system lifespan and maintains optimal performance in managing roof runoff effectively.
Cost Analysis: Rain Drip Options
Rain drip systems vary significantly in cost depending on materials and installation complexity; premium copper rain drips can cost up to 30% more than standard aluminum options. Economical plastic rain drips are widely available but may require more frequent replacement, impacting long-term expenses. Choosing between rain drip types involves balancing initial investment against durability and maintenance requirements for optimal cost-efficiency.
Pros and Cons: Comparing Rain Drip Solutions
Rain drip systems effectively manage water runoff by directing rainwater away from structures, preventing foundation damage and soil erosion. These systems vary in design, with traditional rain drip traps offering simplicity and low cost, while advanced rain drip solutions provide enhanced durability and integrated filtration features. Choosing between options depends on factors like installation complexity, maintenance requirements, and budget constraints, with high-end rain drip models typically requiring less upkeep but demanding higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Rain Drip System for Your Landscape
Choosing the right rain drip system for your landscape involves assessing water pressure, soil type, and plant water needs to ensure efficient irrigation. High-quality rain drip emitters provide consistent water flow, reducing runoff and promoting healthy root growth by delivering moisture directly to the soil. Optimizing the placement and flow rate of rain drip systems minimizes water waste and supports sustainable landscaping practices.
Rain drip Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com