Depletable resources are natural materials that diminish over time as they are extracted and consumed, such as fossil fuels and minerals. Managing these finite resources sustainably is crucial to avoid exhaustion and environmental damage. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choices impact the future availability of these vital resources.
Table of Comparison
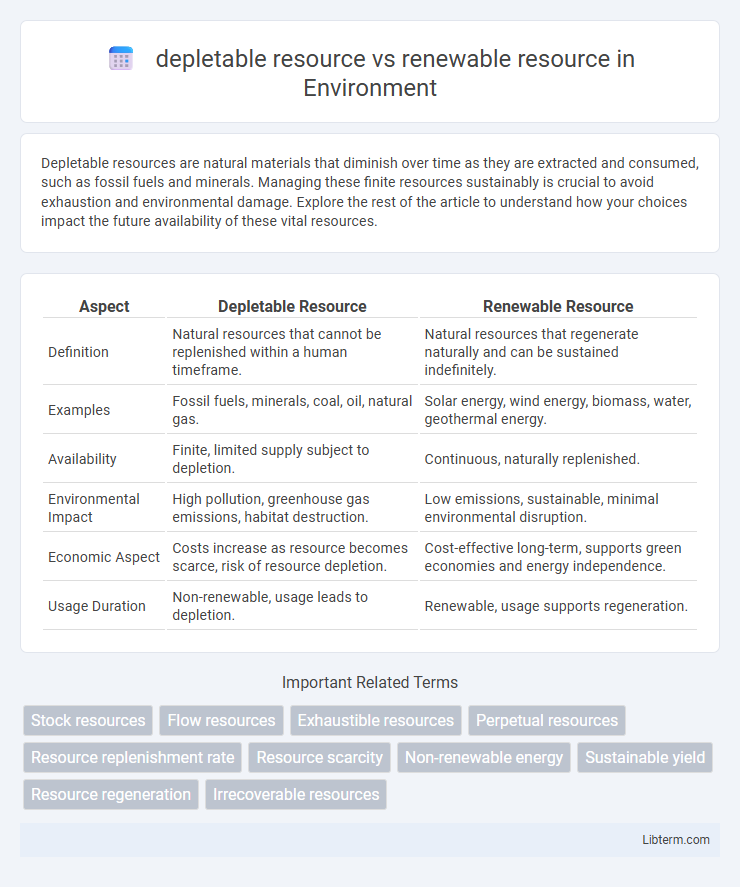
| Aspect | Depletable Resource | Renewable Resource |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural resources that cannot be replenished within a human timeframe. | Natural resources that regenerate naturally and can be sustained indefinitely. |
| Examples | Fossil fuels, minerals, coal, oil, natural gas. | Solar energy, wind energy, biomass, water, geothermal energy. |
| Availability | Finite, limited supply subject to depletion. | Continuous, naturally replenished. |
| Environmental Impact | High pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, habitat destruction. | Low emissions, sustainable, minimal environmental disruption. |
| Economic Aspect | Costs increase as resource becomes scarce, risk of resource depletion. | Cost-effective long-term, supports green economies and energy independence. |
| Usage Duration | Non-renewable, usage leads to depletion. | Renewable, usage supports regeneration. |
Understanding Depletable Resources
Depletable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, exist in finite quantities and cannot be replenished within a human timeframe once exhausted. Their extraction and consumption lead to permanent reduction, causing long-term environmental and economic impacts. Understanding depletable resources highlights the urgency of efficient management and the development of sustainable alternatives to mitigate resource scarcity.
What Are Renewable Resources?
Renewable resources are natural assets that regenerate and replenish over time through biological reproduction or other natural processes, making them sustainably available for continual use. Examples include solar energy, wind power, biomass, and hydropower, which contrast with depletable resources that diminish with consumption. Their renewable nature supports long-term environmental balance and reduces dependency on finite resources like fossil fuels and minerals.
Key Differences Between Depletable and Renewable Resources
Depletable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, are finite and diminish with continuous extraction, leading to eventual exhaustion. Renewable resources, including solar energy, wind power, and biomass, regenerate naturally over short periods and provide sustainable energy or material supply. The primary difference lies in renewability and sustainability, where renewable resources offer ongoing availability without depletion, contrasting with the limited lifespan of depletable resources.
Examples of Depletable Resources
Oil, coal, and natural gas are prominent examples of depletable resources, as their extraction reduces available reserves over time. These fossil fuels are finite and cannot be replenished on a human timescale once consumed. Minerals such as uranium and rare earth elements also fall under depletable resources due to their limited natural availability and slow formation rates.
Common Types of Renewable Resources
Common types of renewable resources include solar energy, wind power, hydroelectric energy, biomass, and geothermal energy, all of which naturally replenish over time. Unlike depletable resources such as fossil fuels and minerals that are finite and diminish with use, renewable resources provide sustainable options for long-term energy production. The widespread adoption of renewable resources helps reduce environmental impact and supports energy security.
Environmental Impact of Depletable Resources
Depletable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, cause significant environmental impact due to their finite availability and extraction processes that lead to habitat destruction, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. The excessive use of depletable resources accelerates climate change, contributes to biodiversity loss, and contaminates air and water systems. In contrast, renewable resources like solar and wind energy provide sustainable alternatives with minimal environmental degradation.
Sustainability Benefits of Renewable Resources
Renewable resources, such as solar energy, wind, and biomass, offer significant sustainability benefits by providing an endless supply of energy without depleting Earth's natural reserves. Their use reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigates climate change effects, and minimizes environmental degradation associated with fossil fuel extraction. Investing in renewable resources promotes long-term ecological balance and energy security, crucial for sustainable development.
Challenges in Transitioning to Renewable Resources
Transitioning from depletable resources like fossil fuels to renewable resources faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, technological limitations in energy storage and grid integration, and inconsistent energy supply due to weather variability. Infrastructure adjustments and policy reforms are required to support large-scale deployment of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources. Overcoming these obstacles is critical for achieving sustainable energy systems and reducing carbon emissions.
Resource Management Strategies
Effective resource management strategies for depletable resources focus on sustainable extraction rates, conservation practices, and technological innovation to minimize environmental impact and extend resource availability. Renewable resource management emphasizes regeneration capacity, implementing practices such as reforestation, sustainable fishing quotas, and renewable energy utilization to maintain ecological balance. Integrating monitoring systems and adaptive management enhances resource stewardship by aligning extraction and usage with natural replenishment rates.
The Future of Resource Utilization: Depletable vs. Renewable
The future of resource utilization hinges on balancing depletable resources like fossil fuels and minerals with renewable resources such as solar energy, wind power, and biomass. Efficient management of depletable resources is critical to delay exhaustion while accelerating investment in renewable technologies reduces environmental impact and supports sustainable growth. Transitioning to renewable resources promotes resilience against scarcity and fosters long-term energy security essential for future generations.
depletable resource Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com