Halophytic plants thrive in environments with high salt concentrations, such as coastal marshes and salt flats, by adapting specialized mechanisms to manage salt uptake and water retention. These salt-tolerant species play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance and preventing soil salinization. Discover how understanding halophytic vegetation can enhance your knowledge of sustainable land management in the following article.
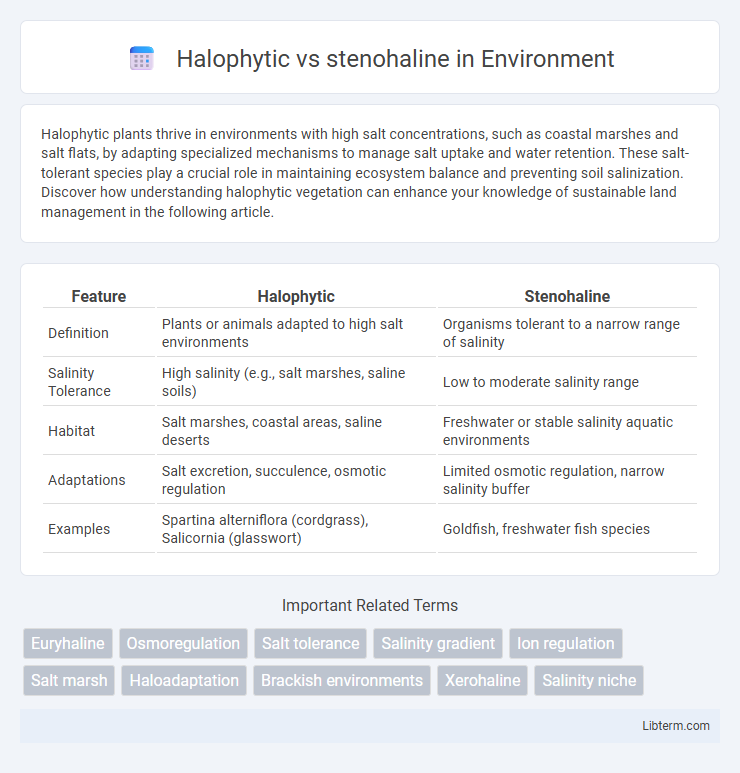
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Halophytic | Stenohaline |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants or animals adapted to high salt environments | Organisms tolerant to a narrow range of salinity |
| Salinity Tolerance | High salinity (e.g., salt marshes, saline soils) | Low to moderate salinity range |
| Habitat | Salt marshes, coastal areas, saline deserts | Freshwater or stable salinity aquatic environments |
| Adaptations | Salt excretion, succulence, osmotic regulation | Limited osmotic regulation, narrow salinity buffer |
| Examples | Spartina alterniflora (cordgrass), Salicornia (glasswort) | Goldfish, freshwater fish species |
Introduction to Halophytic and Stenohaline Organisms
Halophytic organisms are specialized plants adapted to thrive in high-salinity environments such as salt marshes and coastal regions, utilizing physiological mechanisms to regulate salt intake and water balance. Stenohaline organisms, on the other hand, possess a narrow tolerance for salinity fluctuations, restricting their habitat to environments with stable salinity levels, often freshwater or marine systems with minimal salinity change. Understanding these categories highlights the ecological adaptations and survival strategies of organisms in diverse saline habitats.
Defining Halophytes: Salt-Tolerant Adaptations
Halophytes are salt-tolerant plants adapted to thrive in high-salinity environments such as salt marshes, mangroves, and saline soils, demonstrating physiological and structural mechanisms like salt excretion glands and succulence for water retention. In contrast, stenohaline species can only tolerate narrow salinity ranges, limiting their distribution to less variable aquatic or terrestrial habitats. Understanding halophytic adaptations aids in ecological restoration and agricultural development in saline-prone regions.
Understanding Stenohaline Species: Sensitivity to Salinity
Stenohaline species exhibit a narrow salinity tolerance, surviving only within specific salinity ranges typically between 10 to 30 ppt, making them highly sensitive to changes in salinity levels. Unlike halophytic organisms adapted to saline environments through specialized salt regulation mechanisms, stenohaline species lack such extensive osmoregulatory adaptations, resulting in vulnerability to salinity fluctuations. Understanding the physiological limitations of stenohaline species aids in predicting their distribution and survival in estuarine and coastal habitats impacted by salinity variability.
Physiological Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance
Halophytic plants utilize specialized physiological mechanisms such as ion compartmentalization, osmotic adjustment, and salt excretion through salt glands to maintain cellular homeostasis under high salinity conditions. In contrast, stenohaline organisms exhibit limited physiological plasticity, lacking efficient ion regulation and osmolyte synthesis, which restricts their survival to narrow salinity ranges. The ability of halophytes to control ion transporters and accumulate compatible solutes like proline and glycine betaine is critical for osmotic balance and protection against ionic toxicity.
Ecological Niches and Habitat Preferences
Halophytic plants thrive in high-salinity environments such as salt marshes, coastal lagoons, and saline soils by adapting physiological mechanisms to manage salt stress. In contrast, stenohaline species occupy habitats with stable, low salinity levels, including freshwater ecosystems and estuaries, due to their narrow salinity tolerance. These ecological niche preferences influence species distribution, community structure, and resilience to environmental stressors in aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
Comparative Adaptations: Halophytes vs. Stenohaline Organisms
Halophytes exhibit specialized adaptations such as salt excretion glands and succulence to survive in high-salinity environments, while stenohaline organisms maintain narrow salinity tolerances and rely on efficient osmoregulatory mechanisms to prevent cellular damage. Halophytes accumulate compatible solutes like proline and glycine betaine to balance osmotic stress, whereas stenohaline species often possess selective ion transporters to stabilize intracellular ion concentrations. These contrasting strategies highlight the evolutionary divergence between salt-tolerant plants and salinity-sensitive aquatic organisms in managing ionic and osmotic stress.
Evolutionary Significance of Salinity Adaptation
Halophytic plants exhibit evolutionary adaptations enabling survival in high-salinity environments through specialized salt-excreting glands and osmoprotectant accumulation, contrasting with stenohaline species that maintain narrow salinity tolerance due to limited genetic plasticity. The divergence between halophytes and stenohalines represents a key evolutionary response to saline stress, showcasing genetic and physiological mechanisms that enhance ion homeostasis and cellular hydration under salt-induced osmotic pressure. This adaptive evolution in halophytes facilitates niche specialization, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem stability in saline habitats.
Impact of Salinity Changes on Species Distribution
Halophytic plants thrive in high salinity environments, showing adaptive traits that allow them to maintain cellular function despite salt stress, while stenohaline species possess narrow salinity tolerance ranges and often face distribution limitations as salinity levels fluctuate. Changes in salinity can lead to shifts in habitat suitability, driving halophytic species to expand into increasingly saline areas and causing stenohaline organisms to retract or face population declines. Salinity gradients directly influence community composition and ecosystem dynamics, with halophytes playing a critical role in stabilizing saline habitats where stenohaline species cannot survive.
Role in Ecosystems and Environmental Interactions
Halophytic plants thrive in high-salinity environments, playing a crucial role in stabilizing saline soils and supporting unique coastal and estuarine ecosystems by providing habitat and preventing erosion. Stenohaline organisms, restricted to narrow salinity ranges, serve as sensitive indicators of environmental change and maintain ecological balance within their stable aquatic habitats. The contrasting adaptations of halophytes and stenohalines underscore their importance in sustaining biodiversity and regulating nutrient cycles in variable salinity conditions.
Future Research and Applications in Salinity Studies
Future research on halophytic plants focuses on their genetic mechanisms for salt tolerance, aiming to enhance crop resilience in saline environments. Stenohaline species serve as bioindicators in assessing the impact of salinity fluctuations on biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Advanced genomic and physiological studies on both halophytic and stenohaline organisms could lead to innovative biotechnological applications for sustainable agriculture in salt-affected soils.
Halophytic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com