Terpenes and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are aromatic compounds found in plants that significantly influence flavor, aroma, and therapeutic properties. These substances play a crucial role in essential oils, contributing to their potency and effects on human health. Discover how understanding these compounds can enhance your appreciation and use of natural extracts by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
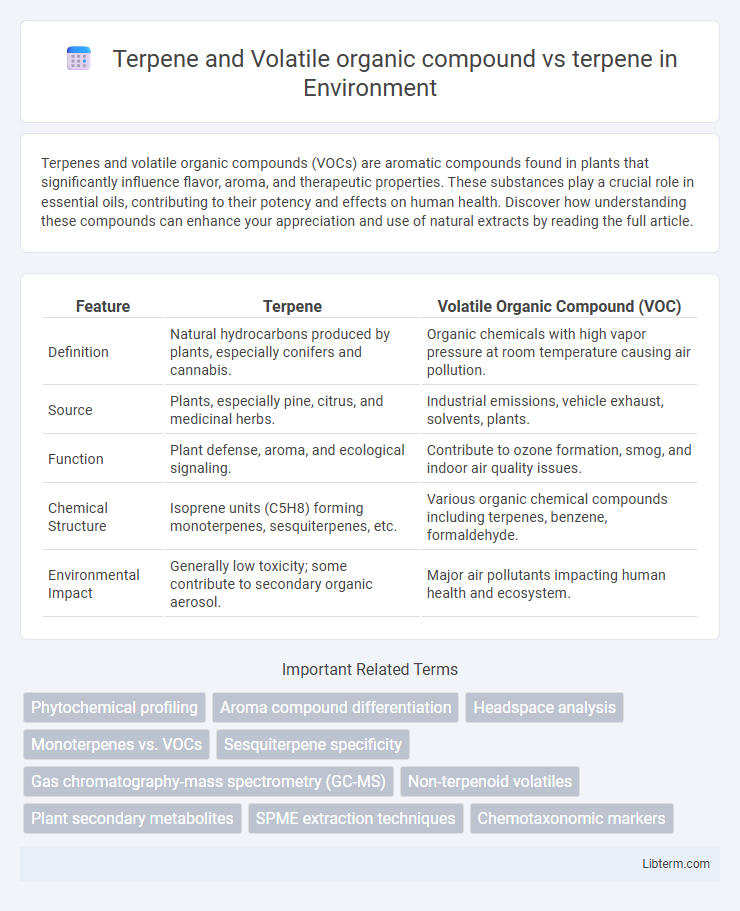
| Feature | Terpene | Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural hydrocarbons produced by plants, especially conifers and cannabis. | Organic chemicals with high vapor pressure at room temperature causing air pollution. |
| Source | Plants, especially pine, citrus, and medicinal herbs. | Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, solvents, plants. |
| Function | Plant defense, aroma, and ecological signaling. | Contribute to ozone formation, smog, and indoor air quality issues. |
| Chemical Structure | Isoprene units (C5H8) forming monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, etc. | Various organic chemical compounds including terpenes, benzene, formaldehyde. |
| Environmental Impact | Generally low toxicity; some contribute to secondary organic aerosol. | Major air pollutants impacting human health and ecosystem. |
Introduction to Terpenes and Volatile Organic Compounds
Terpenes are a large class of organic compounds produced by plants and some insects, known for their strong aromas and roles in plant defense. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) include terpenes but also encompass a broader range of carbon-based chemicals that easily vaporize at room temperature, contributing to air quality and scent profiles. Understanding the distinction between terpenes as specific VOCs clarifies their unique ecological functions and applications in industries like aromatherapy and perfumery.
Defining Terpenes: Nature and Function
Terpenes are a diverse class of organic compounds produced by plants, especially conifers, responsible for their aromatic qualities and defense mechanisms. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) encompass a broader category that includes terpenes along with other substances released into the air, contributing to environmental and atmospheric chemistry. Unlike general VOCs, terpenes specifically function in ecological interactions such as attracting pollinators and deterring herbivores, underscoring their critical role in nature.
Understanding Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are a broad category of carbon-based chemicals that easily evaporate at room temperature, encompassing substances like terpenes, aldehydes, and ketones. Terpenes, a specific type of VOC, are naturally occurring hydrocarbons produced by plants, responsible for distinct aromas and potential therapeutic effects. Understanding VOCs involves recognizing their roles in air quality, environmental impact, and sensory properties, with terpenes being key contributors to both fragrance and atmospheric chemistry.
Key Differences: Terpenes vs Volatile Organic Compounds
Terpenes are a specific class of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) primarily produced by plants, characterized by their distinct aromatic properties and roles in plant defense and attraction. VOCs encompass a broad category of organic chemicals, including terpenes, that readily vaporize at room temperature and contribute to air quality and atmospheric reactions. Key differences lie in terpenes being naturally occurring biogenic VOCs with specific molecular structures based on isoprene units, whereas VOCs include a wide range of natural and synthetic chemicals with diverse chemical structures and environmental impacts.
Chemical Structures and Classification
Terpenes are a specific class of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) characterized by their isoprene (C5H8) units arranged in repeating patterns, forming structures like monoterpenes (C10H16) and sesquiterpenes (C15H24). VOCs encompass a broader category of organic chemicals that readily vaporize at room temperature, including terpenes, alcohols, aldehydes, and esters, distinguished by diverse chemical structures and functional groups. The classification of terpenes is based on the number of isoprene units and their cyclization patterns, whereas VOCs are categorized by volatility and chemical composition rather than a specific structural motif.
Sources and Natural Occurrence
Terpenes are a diverse class of hydrocarbons primarily produced by plants, especially conifers, citrus fruits, and aromatic herbs, responsible for their distinctive scents and flavors. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) encompass a broader category that includes terpenes as well as other compounds like aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols emitted by many natural sources such as vegetation, soil microbes, and aquatic systems. Terpenes stand out as specifically biosynthesized secondary metabolites, whereas VOCs can arise from both biogenic and anthropogenic sources, influencing atmospheric chemistry and natural ecosystem interactions.
Therapeutic and Industrial Applications
Terpenes, a class of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), exhibit significant therapeutic properties such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial effects utilized in aromatherapy and pharmaceutical formulations. Industrial applications leverage terpenes as natural solvents, flavorings, and fragrances in cosmetics, food production, and bio-based plastics, highlighting their biodegradability and eco-friendly advantages. Compared to general VOCs, terpenes present lower toxicity and greater functional versatility, making them preferable in both medical treatments and sustainable manufacturing processes.
Health and Environmental Impacts
Terpenes and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) both significantly impact health and the environment by contributing to indoor and outdoor air pollution, potentially causing respiratory issues and allergic reactions. While terpenes are natural VOCs emitted by plants and are commonly used in aromatherapy and cleaning products, they can react with nitrogen oxides to form secondary pollutants like ozone, exacerbating smog in urban areas. Controlled use and proper ventilation reduce adverse health effects and environmental damage linked to terpene-based products and other VOC emissions.
Detection and Analysis Methods
Terpenes, a class of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), are typically detected and analyzed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) due to its high sensitivity and specificity for separating complex mixtures. Proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS) and solid-phase microextraction (SPME) coupled with GC-MS enhance the detection of terpenes by enabling real-time monitoring and non-destructive sample preparation. Advanced analytical techniques prioritize terpene profiling to distinguish them from other VOCs by targeting their unique molecular fragments and retention times.
Future Trends in Terpene and VOC Research
Future trends in terpene and volatile organic compound (VOC) research emphasize advanced analytical techniques such as proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS) and two-dimensional gas chromatography (GCxGC) for enhanced detection and quantification. Emerging studies focus on the biosynthetic pathways of terpenes and their roles in plant communication, environmental impact, and pharmaceutical applications. Integration of machine learning algorithms enables predictive modeling of terpene and VOC emissions, facilitating innovations in sustainable agriculture and green chemistry.
Terpene and Volatile organic compound Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com