Tidal marshes are coastal wetlands flooded and drained by tidal waters, serving as vital habitats for diverse plant and animal species. They play a crucial role in shoreline protection, water filtration, and carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change impacts. Discover how these ecosystems support biodiversity and enhance your understanding of their environmental significance in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
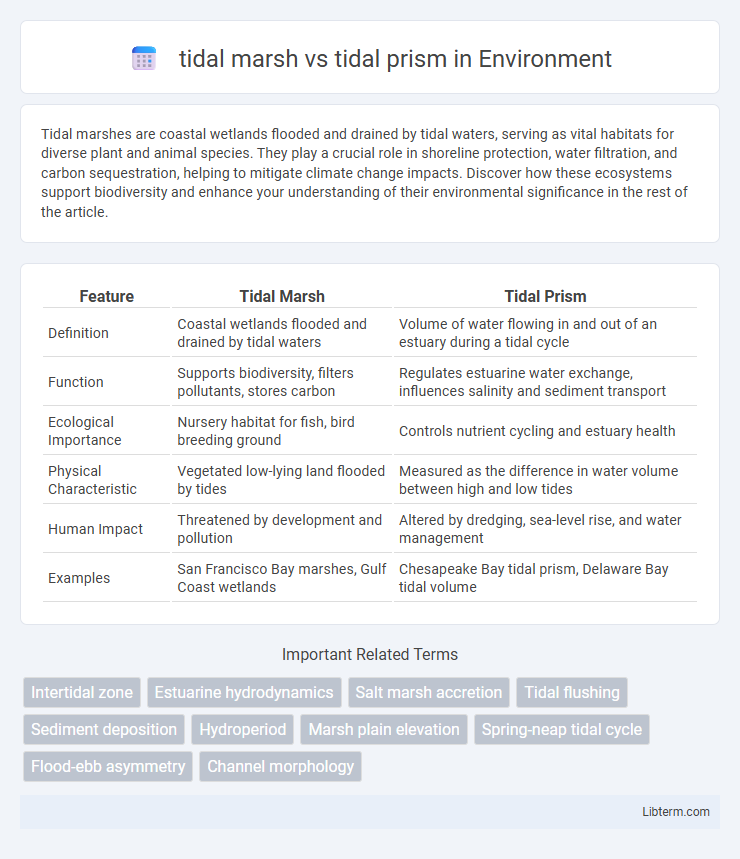
| Feature | Tidal Marsh | Tidal Prism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coastal wetlands flooded and drained by tidal waters | Volume of water flowing in and out of an estuary during a tidal cycle |
| Function | Supports biodiversity, filters pollutants, stores carbon | Regulates estuarine water exchange, influences salinity and sediment transport |
| Ecological Importance | Nursery habitat for fish, bird breeding ground | Controls nutrient cycling and estuary health |
| Physical Characteristic | Vegetated low-lying land flooded by tides | Measured as the difference in water volume between high and low tides |
| Human Impact | Threatened by development and pollution | Altered by dredging, sea-level rise, and water management |
| Examples | San Francisco Bay marshes, Gulf Coast wetlands | Chesapeake Bay tidal prism, Delaware Bay tidal volume |
Introduction to Tidal Marshes and Tidal Prism
Tidal marshes are coastal wetlands flooded and drained by tidal waters, providing essential habitats for diverse plant and animal species while acting as natural buffers against storm surges. The tidal prism represents the volume of water that flows in and out of an estuary or tidal basin with each tidal cycle, influencing sediment transport and marsh stability. Understanding the interaction between tidal marshes and tidal prism is crucial for coastal management and ecological restoration.
Defining Tidal Marsh: Characteristics and Functions
Tidal marshes are coastal wetlands flooded and drained by tidal waters, characterized by salt-tolerant vegetation such as Spartina alterniflora and Juncus species. These ecosystems serve crucial functions including nutrient cycling, sediment trapping, and providing habitat for diverse wildlife, particularly migratory birds and estuarine fish. The tidal prism, the volume of water exchanged during a tidal cycle, influences the hydrodynamics and sediment distribution that shape the morphology and ecological health of tidal marshes.
Understanding Tidal Prism: Concepts and Calculations
Tidal prism refers to the total volume of water that flows in and out of a tidal marsh during a tidal cycle, playing a crucial role in nutrient exchange and sediment transport. It is calculated by measuring the difference between high tide and low tide water volumes within the marsh's boundaries. Understanding tidal prism helps in predicting marsh health, managing coastal erosion, and designing effective restoration projects in tidal marsh ecosystems.
Formation and Evolution of Tidal Marshes
Tidal marsh formation depends on the balance between sediment deposition and tidal prism, which is the volume of water exchanged during tidal cycles. A larger tidal prism increases sediment transport capacity, promoting marsh accretion and elevation gain essential for marsh sustainability. Over time, changes in tidal prism influence marsh evolution by altering sediment dynamics, vegetation patterns, and habitat complexity.
The Role of Tidal Prism in Estuarine Dynamics
Tidal prism, the volume of water exchanged between high and low tides, is crucial in shaping estuarine hydrodynamics, sediment transport, and nutrient cycling. It influences the extent and health of tidal marshes by regulating salinity gradients, sediment deposition, and habitat availability for estuarine flora and fauna. Understanding tidal prism variability helps predict marsh resilience and the overall ecological functioning of estuarine systems.
Ecological Significance of Tidal Marshes
Tidal marshes serve as crucial coastal ecosystems that provide habitat for diverse wildlife, support nutrient cycling, and act as natural buffers against storm surges and flooding. The tidal prism, which is the volume of water exchanged between high and low tides, directly influences the health and ecological function of these marshes by regulating water flow, sediment transport, and salinity levels. Maintaining a balanced tidal prism is essential for sustaining the biodiversity and resilience of tidal marsh ecosystems.
How Tidal Prism Influences Sediment Transport
Tidal prism, the volume of water flowing in and out of a tidal marsh during the tidal cycle, significantly influences sediment transport by controlling the strength and extent of tidal currents. Larger tidal prisms generate stronger tidal flows that enhance the capacity to mobilize and redistribute sediments within the marsh, promoting sediment deposition and marsh accretion. This dynamic interaction shapes the morphology and ecological resilience of tidal marshes by regulating sediment supply and distribution patterns.
Human Impacts on Tidal Marshes and Tidal Prism
Human impacts on tidal marshes include land reclamation, pollution, and altered water flow, which reduce habitat quality and biodiversity. Changes in the tidal prism, the volume of water exchanged during tidal cycles, result from dredging, construction, and sea-level rise, disrupting sediment transport and nutrient exchange. These alterations impair marsh resilience, diminish flood protection, and increase vulnerability to coastal erosion and habitat loss.
Comparative Analysis: Tidal Marsh vs Tidal Prism
Tidal marshes serve as crucial coastal ecosystems characterized by their vegetation and sediment accumulation, whereas tidal prism refers to the volume of water exchanged during tidal cycles within an estuary or inlet. Comparing these, tidal marshes influence the tidal prism by modulating water flow and sediment deposition, which impacts nutrient cycling and habitat sustainability. Understanding the interaction between tidal marshes and tidal prism is essential for managing coastal resilience and mitigating erosion in estuarine environments.
Future Trends in Tidal Marsh and Tidal Prism Research
Future trends in tidal marsh research emphasize the integration of high-resolution remote sensing and machine learning to monitor marsh resilience and carbon sequestration under climate change scenarios. Emerging studies on tidal prism increasingly focus on its role in estuarine hydrodynamics and sediment transport, enhancing predictive models for coastal flooding and habitat restoration. Advancements in coupled ecological-hydrodynamic models are expected to improve understanding of feedback mechanisms between tidal marsh vegetation and tidal prism dynamics.
tidal marsh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com