A watershed is a land area that channels rainfall and snowmelt to creeks, streams, and rivers, eventually flowing into larger bodies of water. Proper management of your watershed is essential to maintaining water quality and preventing flooding. Explore the rest of the article to learn how watersheds impact ecosystems and what you can do to protect them.
Table of Comparison
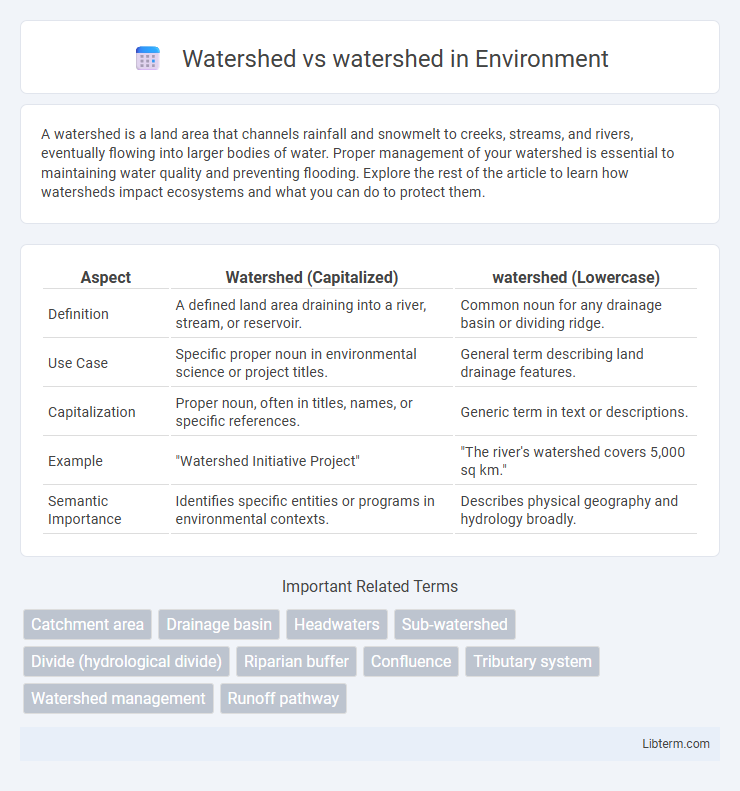
| Aspect | Watershed (Capitalized) | watershed (Lowercase) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A defined land area draining into a river, stream, or reservoir. | Common noun for any drainage basin or dividing ridge. |
| Use Case | Specific proper noun in environmental science or project titles. | General term describing land drainage features. |
| Capitalization | Proper noun, often in titles, names, or specific references. | Generic term in text or descriptions. |
| Example | "Watershed Initiative Project" | "The river's watershed covers 5,000 sq km." |
| Semantic Importance | Identifies specific entities or programs in environmental contexts. | Describes physical geography and hydrology broadly. |
Definition of Watershed: Geography vs. Hydrology
In geography, a watershed refers to a ridge or elevated area that separates different drainage basins, effectively dividing the flow of surface water towards distinct oceanic or river systems. Hydrology defines a watershed as an area of land where all precipitation collects and drains off into a common outlet, such as a river, bay, or other body of water, emphasizing the flow and accumulation of water. The geographic perspective highlights physical boundaries, while the hydrological view centers on water flow and catchment dynamics.
Watershed: Scientific Perspective
Watershed in scientific terms refers to a land area that channels rainfall and snowmelt to creeks, streams, and rivers, ultimately leading to outflow points such as reservoirs, bays, or the ocean. It functions as a crucial hydrological unit, influencing water quality, ecosystem health, and regional hydrodynamics, with factors like topography, soil composition, and vegetation playing significant roles in its function. Understanding Watershed dynamics enables effective water resource management, flood control, and environmental conservation strategies based on data such as drainage patterns, runoff coefficients, and sediment transport.
Watershed: Cultural and Figurative Context
Watershed in a cultural and figurative context signifies a critical turning point or moment of significant change, often marking a division between two distinct phases. This metaphorical use originates from the geographical term watershed, which denotes a ridge dividing different drainage basins but extends to describe pivotal events in history, careers, or social movements. Recognizing a watershed moment implies acknowledging an irreversible shift with lasting impact on subsequent developments.
Historical Evolution of the Term "Watershed
The term "watershed" historically evolved from its original British English usage describing a critical geographical divide or ridge separating drainage basins, to a broader North American context that also signifies a drainage basin or catchment area itself. Early cartographic and hydrological studies in the 18th and 19th centuries primarily emphasized watershed as a physical boundary that directs water flow, influencing land management and territorial delineation. Over time, scientific advancements and environmental planning expanded the semantic scope of "watershed," integrating ecological and management perspectives beyond its strict topographical meaning.
Differences Between Watershed (Hydrological) and Watershed (Turning Point)
Watershed in hydrology refers to an area of land where all precipitation drains into a common water body, playing a critical role in water resource management and ecosystem health. Watershed as a turning point signifies a decisive moment or event that leads to significant change or development in a process, situation, or individual's life. The primary difference lies in their contexts: hydrological watershed pertains to physical geography and environmental science, while watershed as a metaphor relates to temporal shifts in history, personal growth, or progress.
Global Usage: Watershed in British vs. American English
In British English, "watershed" commonly refers to a critical turning point or boundary in time, especially in media regulation where it marks the hour when adult content becomes permissible for broadcast. In American English, "watershed" primarily denotes a drainage basin or land area where all precipitation collects and drains into a common outlet, such as a river or lake. The difference in usage highlights the term's semantic shift, with British English emphasizing temporal or figurative significance, while American English stresses geographic and environmental context.
Importance of Watersheds in Environmental Management
Watersheds play a critical role in environmental management by regulating water flow, maintaining water quality, and supporting biodiversity within ecosystems. The term "Watershed" often refers to larger, significant hydrological units essential for regional planning and conservation efforts, while "watershed" can denote smaller drainage basins impacting local water systems. Effective management of both scales ensures sustainable water resources, mitigates flood risks, and preserves habitats vital for ecosystem resilience.
Watershed Moments: Metaphorical Significance
Watershed moments symbolize critical turning points that signify irreversible change, originating from the geographical definition of a watershed where water divides and flows into distinct basins. In metaphorical contexts, these moments represent pivotal decisions or events that redefine trajectories in personal lives, history, or culture. Recognizing a watershed moment helps understand the profound impact of transformation, emphasizing shifts that permanently alter outcomes or directions.
Watershed Boundaries and Their Determination
Watershed boundaries, also known as drainage divides, define the geographic limits within which all precipitation converges to a single outlet such as a river or lake. Determination of watershed boundaries relies on topographic data, including digital elevation models (DEMs), to delineate ridgelines and flow paths using GIS hydrology tools. Accurate watershed boundary mapping is essential for water resource management, flood control, and environmental conservation planning.
Conclusion: Clarifying the Dual Meanings of Watershed
Watershed" as a geographical term refers to a land area that channels rainfall and streams to a common outlet, crucial for managing water resources and environmental planning. In contrast, "watershed" in a figurative sense signifies a critical turning point or moment of significant change in history, personal lives, or progress. Clarifying these dual meanings enhances communication in environmental science and everyday discourse by preventing ambiguity and emphasizing context-specific interpretations.
Watershed Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com