Hedgerows serve as vital ecological corridors that support diverse wildlife and enhance landscape connectivity. They play an essential role in soil stabilization and help in reducing wind erosion, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. Discover how maintaining and managing your hedgerows can benefit biodiversity and land health in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
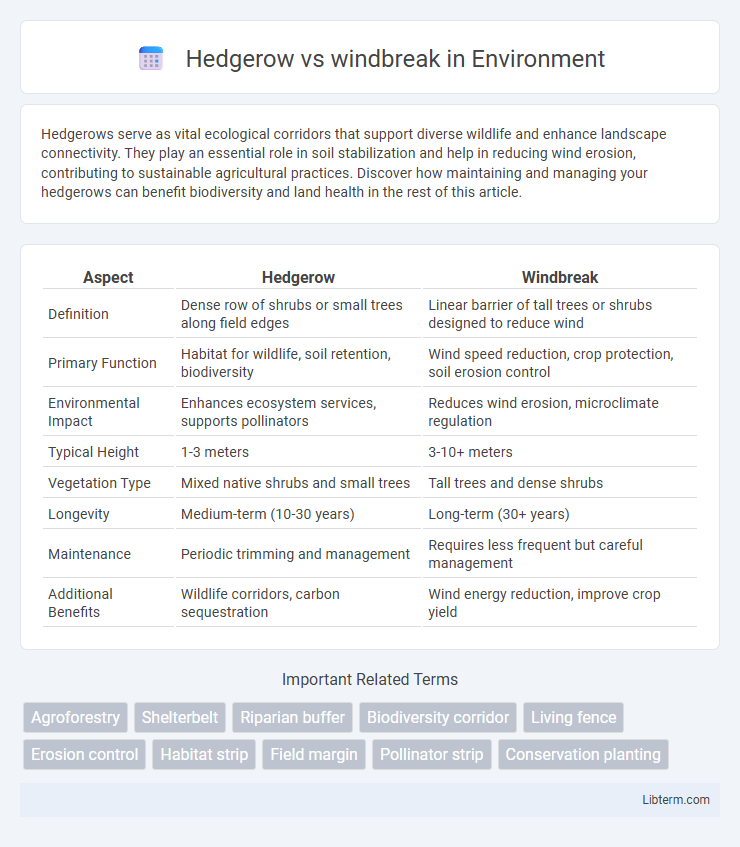
| Aspect | Hedgerow | Windbreak |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dense row of shrubs or small trees along field edges | Linear barrier of tall trees or shrubs designed to reduce wind |
| Primary Function | Habitat for wildlife, soil retention, biodiversity | Wind speed reduction, crop protection, soil erosion control |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances ecosystem services, supports pollinators | Reduces wind erosion, microclimate regulation |
| Typical Height | 1-3 meters | 3-10+ meters |
| Vegetation Type | Mixed native shrubs and small trees | Tall trees and dense shrubs |
| Longevity | Medium-term (10-30 years) | Long-term (30+ years) |
| Maintenance | Periodic trimming and management | Requires less frequent but careful management |
| Additional Benefits | Wildlife corridors, carbon sequestration | Wind energy reduction, improve crop yield |
Introduction to Hedgerows and Windbreaks
Hedgerows and windbreaks are both natural vegetative barriers designed to provide environmental benefits such as reducing soil erosion, enhancing biodiversity, and protecting crops from wind damage. Hedgerows consist of dense rows of shrubs and trees planted closely together to create habitat corridors, while windbreaks are typically single or multiple rows of trees or shrubs arranged to reduce wind speed across agricultural fields. Understanding the structural differences and ecological functions of hedgerows versus windbreaks is essential for effective landscape management and conservation practices.
Definition and Key Differences
A hedgerow is a dense line of shrubs or trees planted closely together primarily to form a living fence, enhance biodiversity, and provide habitat for wildlife. A windbreak, also called a shelterbelt, is a strategically spaced row of trees or shrubs designed specifically to reduce wind speed and protect soil, crops, or buildings from wind damage. Key differences include the planting density and primary function: hedgerows emphasize ecological benefits and boundary marking, while windbreaks focus on aerodynamic protection and microclimate improvement.
Historical Uses and Development
Hedgerows have been historically utilized in Europe since the Iron Age as boundary markers, livestock barriers, and sources of firewood, shaping agricultural landscapes for centuries. Windbreaks originated primarily in North America in the 19th century to protect crops from wind erosion and improve microclimates for farming. Both practices evolved through selective planting of native trees and shrubs, reflecting regional environmental and cultural needs in land management.
Ecological Benefits of Hedgerows
Hedgerows provide significant ecological benefits by enhancing biodiversity, offering habitat corridors for wildlife, and supporting pollinators essential for agriculture. They improve soil health through nutrient cycling and reduce erosion more effectively than traditional windbreaks by stabilizing the soil with diverse root systems. Unlike simple windbreaks, hedgerows contribute to carbon sequestration and help maintain ecological balance in agricultural landscapes.
Environmental Impact of Windbreaks
Windbreaks reduce soil erosion by blocking wind, thereby preserving topsoil and promoting healthier ecosystems. They enhance biodiversity by providing habitats for birds, insects, and small mammals, contributing to greater environmental stability. Windbreaks also improve microclimates, leading to lower energy consumption for heating and cooling in adjacent agricultural and residential areas.
Design and Plant Selection Considerations
Hedgerow design emphasizes dense, multi-layered plantings with native shrubs and small trees to enhance biodiversity, soil stabilization, and wildlife habitat. Windbreak planning prioritizes taller, spaced tree rows, often conifers and fast-growing species, to effectively reduce wind speed and protect crops or structures. Both require site-specific soil and climate evaluations to optimize plant health and functional performance.
Agricultural Advantages and Crop Protection
Hedgerows provide essential habitat for beneficial insects and birds, enhancing biodiversity and natural pest control while stabilizing soil and reducing erosion in agricultural fields. Windbreaks primarily reduce wind speed, lowering evapotranspiration rates and protecting crops from physical damage and drought stress, thereby improving yield stability. Combining hedgerows with windbreaks maximizes crop protection by offering both ecological benefits and microclimate regulation critical for sustainable farming systems.
Biodiversity and Wildlife Support
Hedgerows provide dense, multi-layered habitats rich in native flora, promoting greater biodiversity and serving as crucial corridors for wildlife movement and nesting. Windbreaks, typically composed of fewer species and structured primarily for wind protection, support less diverse wildlife but offer essential shelter for certain bird and insect populations. Both structures enhance ecosystem services, yet hedgerows contribute more significantly to sustaining complex ecological networks and supporting species-rich environments.
Maintenance and Long-Term Management
Hedgerows require regular trimming and selective pruning to maintain plant health and encourage dense growth, which helps sustain wildlife habitats and pest control functions. Windbreaks typically need less frequent maintenance but involve periodic inspection and replacement of damaged or diseased trees to ensure continued effectiveness in reducing wind speed and protecting crops. Long-term management of hedgerows emphasizes biodiversity with varied species composition, while windbreaks focus on structural integrity and uniformity for optimal wind protection over time.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Land
Hedgerows offer dense, multi-species vegetation that enhances biodiversity and provides habitat while windbreaks use rows of trees or shrubs designed primarily to reduce wind speed and protect soil erosion. When choosing the right solution for your land, consider factors such as climate, soil type, and desired ecological benefits: hedgerows suit areas needing habitat support, while windbreaks excel in protecting crops and reducing wind damage. Evaluating land goals and local environmental conditions ensures optimal selection between hedgerow and windbreak systems for sustainable land management.
Hedgerow Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com