Landfilling is a common waste management method where solid waste is buried to minimize environmental impact and promote decomposition over time. Proper landfill design includes lining systems and leachate collection to prevent contamination of soil and groundwater. Explore the rest of the article to learn how landfilling impacts your environment and what sustainable alternatives exist.
Table of Comparison
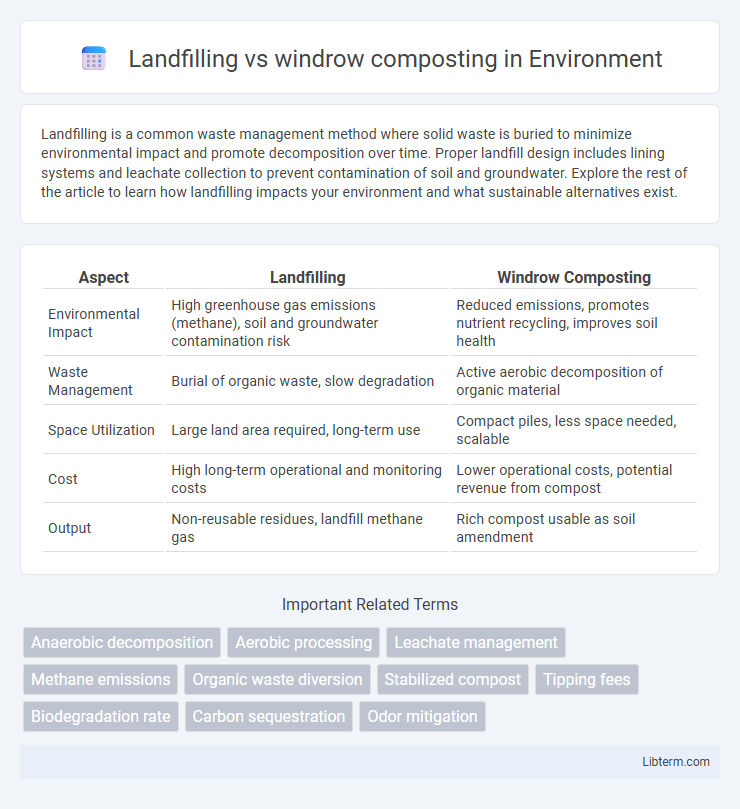
| Aspect | Landfilling | Windrow Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | High greenhouse gas emissions (methane), soil and groundwater contamination risk | Reduced emissions, promotes nutrient recycling, improves soil health |
| Waste Management | Burial of organic waste, slow degradation | Active aerobic decomposition of organic material |
| Space Utilization | Large land area required, long-term use | Compact piles, less space needed, scalable |
| Cost | High long-term operational and monitoring costs | Lower operational costs, potential revenue from compost |
| Output | Non-reusable residues, landfill methane gas | Rich compost usable as soil amendment |
Introduction to Waste Management Methods
Landfilling involves the controlled burial of solid waste in designated sites, minimizing environmental exposure but often leading to methane emissions and long-term land use. Windrow composting aerates organic waste by piling it into rows, enabling microbial decomposition that produces nutrient-rich compost while reducing landfill dependency. Choosing between landfilling and windrow composting impacts waste volume, greenhouse gas emissions, and soil amendment potential in sustainable waste management strategies.
Understanding Landfilling: Process and Impacts
Landfilling involves burying waste in engineered sites designed to isolate refuse from the environment, where organic materials decompose anaerobically, producing methane--a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. This process often leads to long-term environmental concerns such as leachate generation, groundwater contamination, and significant space consumption. Compared to windrow composting, landfilling offers limited nutrient recovery and higher ecological risks due to slower organic matter decomposition and methane emissions.
What is Windrow Composting?
Windrow composting is an aerobic process where organic waste is piled into long, narrow rows called windrows that are regularly turned to promote oxygen flow and microbial activity. This method accelerates decomposition, producing nutrient-rich compost suitable for soil amendment and reducing landfill waste volumes. Compared to landfilling, windrow composting minimizes methane emissions and supports sustainable waste management by converting biodegradable materials into valuable organic fertilizer.
Landfilling: Environmental Effects
Landfilling generates significant environmental impacts through methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change, and leachate production that can contaminate soil and groundwater. The anaerobic decomposition in landfills slows organic waste breakdown, prolonging environmental hazards compared to windrow composting, which promotes aerobic microbial activity and reduces methane release. Improperly managed landfills also occupy large land areas and pose long-term risks to ecosystem health and biodiversity.
Windrow Composting: Environmental Benefits
Windrow composting reduces landfill waste by diverting organic materials from anaerobic decomposition, which significantly lowers methane emissions. This process enhances soil health through nutrient-rich compost that improves soil structure and moisture retention, promoting sustainable agriculture. Moreover, windrow composting helps recycle carbon and nitrogen, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Cost Comparison: Landfilling vs Windrow Composting
Landfilling typically incurs higher long-term costs due to tipping fees, transportation, and environmental compliance expenses, averaging around $50 to $100 per ton. Windrow composting presents a more cost-effective alternative, with operational costs ranging between $20 and $40 per ton, driven by lower energy requirements and potential revenue from compost sales. The economic benefits of windrow composting are enhanced by reduced landfill tipping fees and decreased greenhouse gas emissions, making it a financially and environmentally preferable waste management option.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Comparative Analysis
Landfilling generates significant methane emissions due to anaerobic decomposition of organic waste, contributing substantially to greenhouse gas (GHG) levels. Windrow composting, by promoting aerobic microbial activity, substantially reduces methane emissions while producing CO2, which has a lower global warming potential. Comparative analyses reveal windrow composting can lower overall GHG emissions by 30-70% compared to landfilling, highlighting its effectiveness as a sustainable waste management strategy.
Resource Recovery and Soil Health
Landfilling traps organic waste in anaerobic conditions, leading to methane emissions and minimal resource recovery, whereas windrow composting promotes aerobic decomposition, producing nutrient-rich compost that enhances soil structure and fertility. Windrow composting accelerates organic matter breakdown, returning essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to the soil, improving water retention and microbial activity. Efficient resource recovery through windrow composting supports sustainable waste management and soil health restoration, reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers and decreasing landfill volumes.
Practical Considerations: Site, Scale, and Regulations
Landfilling requires extensive land area and must comply with strict environmental regulations related to leachate management and methane emissions, making site selection critical to minimize groundwater contamination and odor issues. Windrow composting, often suitable for medium-scale operations, necessitates well-drained land with adequate space for turning equipment and must adhere to regulations governing odor control, pathogen reduction, and runoff management. Both methods demand careful assessment of local zoning laws, proximity to residential areas, and available infrastructure to ensure sustainable and compliant waste management.
Future Trends in Organic Waste Disposal
Future trends in organic waste disposal emphasize a shift from traditional landfilling to windrow composting due to increasing environmental regulations and the demand for sustainable waste management solutions. Windrow composting offers enhanced carbon sequestration, nutrient recovery, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to landfilling, aligning with global climate goals. Technological advancements in aeration and microbial inoculation are expected to further optimize windrow composting efficiency and scalability.
Landfilling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com