Anthropogenic factors refer to environmental changes caused directly or indirectly by human activities, such as pollution, deforestation, and urbanization, significantly impacting ecosystems and climate patterns. Understanding these influences is crucial for developing effective sustainability strategies to mitigate negative effects on natural resources. Explore the rest of this article to learn how your actions contribute to anthropogenic changes and what steps you can take to promote environmental stewardship.
Table of Comparison
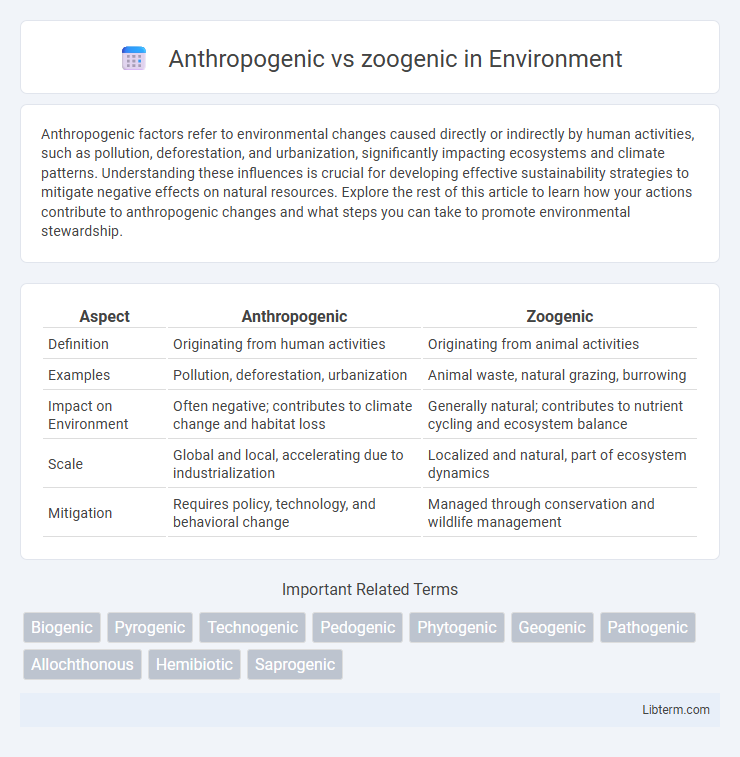
| Aspect | Anthropogenic | Zoogenic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Originating from human activities | Originating from animal activities |
| Examples | Pollution, deforestation, urbanization | Animal waste, natural grazing, burrowing |
| Impact on Environment | Often negative; contributes to climate change and habitat loss | Generally natural; contributes to nutrient cycling and ecosystem balance |
| Scale | Global and local, accelerating due to industrialization | Localized and natural, part of ecosystem dynamics |
| Mitigation | Requires policy, technology, and behavioral change | Managed through conservation and wildlife management |
Introduction to Anthropogenic and Zoogenic Origins
Anthropogenic origins refer to environmental and ecological changes caused directly by human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, and industrial emissions that significantly alter natural ecosystems. Zoogenic origins focus on biological and ecological impacts driven by animal activities, including livestock grazing, wildlife migration, and the introduction of invasive species. Understanding these distinct sources is crucial for developing targeted environmental management and conservation strategies.
Defining Anthropogenic Factors
Anthropogenic factors refer to environmental changes directly caused by human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, pollution, and industrialization, significantly impacting ecosystems and climate. These factors contrast with zoogenic influences, which arise from animal behaviors and populations affecting habitats. Understanding anthropogenic factors is essential for addressing human-driven environmental challenges and promoting sustainable development.
Understanding Zoogenic Processes
Zoogenic processes refer to natural biological activities driven by animals that influence ecosystems, such as nutrient cycling through grazing, burrowing, and waste deposition. Understanding zoogenic contributions is pivotal for ecosystem management and biodiversity conservation, as these processes regulate soil structure, plant growth, and food web dynamics. Distinguishing zoogenic impacts from anthropogenic influences helps in assessing human effects on environmental health and developing sustainable mitigation strategies.
Key Differences Between Anthropogenic and Zoogenic Impacts
Anthropogenic impacts originate from human activities such as urbanization, industrialization, and deforestation, leading to pollution, habitat loss, and climate change, whereas zoogenic impacts result from animal behaviors like grazing, trampling, and burrowing, influencing soil compaction and vegetation dynamics. Key differences include the scale and permanence of effects, with anthropogenic impacts often causing widespread, long-term alterations, while zoogenic impacts are typically localized and cyclical. Understanding these distinctions is critical for effective environmental management and conservation strategies.
Examples of Anthropogenic Influences on the Environment
Anthropogenic influences on the environment include deforestation, urbanization, and industrial pollution, which contribute to habitat loss and climate change. Activities such as fossil fuel combustion release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, accelerating global warming. In contrast, zoogenic factors involve natural animal behaviors and populations impacting ecosystems, but the scale and intensity are far less compared to human-driven changes.
Zoogenic Effects in Ecosystem Dynamics
Zoogenic effects play a critical role in ecosystem dynamics by influencing nutrient cycling, seed dispersal, and habitat modification through animal activities. Herbivores regulate plant community structure by selective grazing, while predators control prey populations, maintaining ecological balance. Scavengers contribute to decomposition processes, enhancing soil fertility and promoting biodiversity within habitats.
Human Activities vs. Animal Contributions
Human activities such as industrial emissions, deforestation, and agriculture significantly contribute to environmental changes by releasing greenhouse gases and pollutants. Animal contributions, including methane production from ruminants and waste decomposition, play a natural role in the carbon and nitrogen cycles but are relatively minor compared to anthropogenic impacts. Understanding the scale and sources of these emissions is crucial for developing effective climate mitigation strategies.
Measurement and Assessment Methods
Measurement and assessment methods for anthropogenic emissions often rely on remote sensing technologies, atmospheric inversion models, and emission inventories to quantify human-induced pollutants such as CO2 and methane. Zoogenic sources are evaluated using tracer gases, direct animal activity monitoring, and stable isotope analysis to distinguish biological methane emissions from livestock and wildlife. Combining high-resolution spatial data with temporal sampling allows for more accurate differentiation and quantification of anthropogenic versus zoogenic contributions to greenhouse gas fluxes.
Environmental and Ecological Implications
Anthropogenic factors, driven by human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and urbanization, significantly alter ecosystems by disrupting natural habitats and biodiversity, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Zoogenic influences, originating from animal activities like grazing, burrowing, and nutrient cycling, play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance and soil health but can also contribute to habitat degradation when populations are imbalanced. Understanding the differential environmental and ecological impacts of anthropogenic versus zoogenic processes is crucial for developing targeted conservation and management strategies that support sustainable ecosystem functions.
Future Perspectives and Sustainable Solutions
Anthropogenic impacts, driven by industrialization and urbanization, significantly alter ecosystems, demanding future perspectives centered on reducing carbon emissions and adopting green technologies. Zoogenic influences, including wildlife behavior and disease transmission, require sustainable solutions that integrate habitat conservation and biodiversity management to maintain ecological balance. Emphasizing interdisciplinary approaches and innovative policies ensures resilience against environmental degradation caused by both human and animal activities.
Anthropogenic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com