A megabyte (MB) is a standard unit of digital information used to measure data storage capacity, equivalent to approximately one million bytes. It plays a crucial role in understanding file sizes, memory capacity, and data transfer limits in computers, smartphones, and other digital devices. Explore this article to learn how a megabyte impacts your digital experience and why it matters in everyday technology.
Table of Comparison
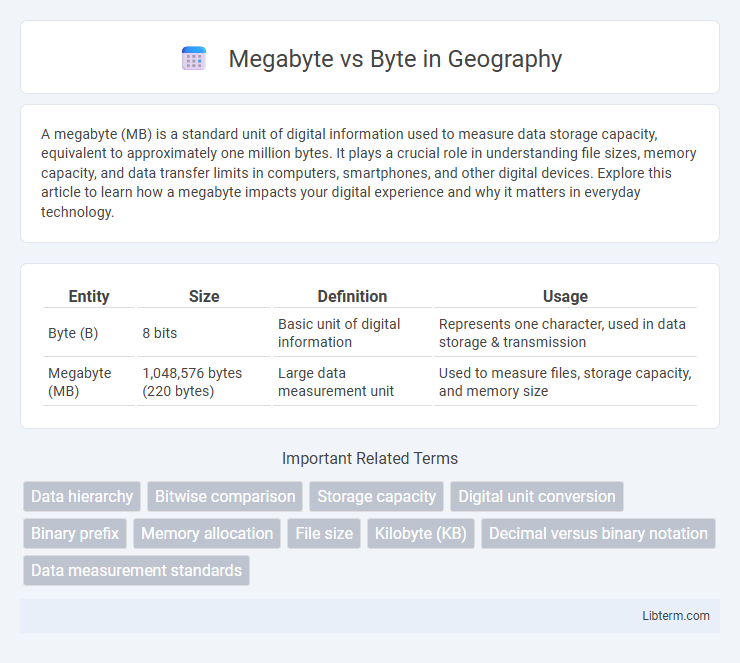
| Entity | Size | Definition | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Byte (B) | 8 bits | Basic unit of digital information | Represents one character, used in data storage & transmission |
| Megabyte (MB) | 1,048,576 bytes (220 bytes) | Large data measurement unit | Used to measure files, storage capacity, and memory size |
Understanding Bytes and Megabytes
A byte consists of 8 bits and represents the basic unit of digital information used to encode a single character, such as a letter or number. A megabyte (MB) equals 1,048,576 bytes, making it a larger measure ideal for quantifying file sizes like images, videos, and software applications. Understanding the difference between bytes and megabytes is crucial for accurate data storage calculations and efficient digital resource management.
Definition of a Byte
A byte is a fundamental unit of digital information storage, typically representing eight bits, which can encode a single character such as a letter, digit, or symbol. It serves as the basic addressable element in computer memory, enabling the combination of binary data into meaningful values. Understanding the definition of a byte is essential for grasping larger data measurements, including megabytes, which equal one million bytes or 1,048,576 bytes in binary terms.
What is a Megabyte?
A megabyte (MB) is a unit of digital information storage equivalent to 1,048,576 bytes or 2^20 bytes, often used to measure file sizes and data capacity in computers and digital devices. It is larger than a byte, which represents a single unit of data or character in computing. The megabyte serves as a practical scale for quantifying medium-sized digital content such as images, audio files, and software applications.
Byte vs Megabyte: Key Differences
A byte consists of 8 bits and serves as the basic unit of data storage, whereas a megabyte (MB) equals 1,048,576 bytes (2^20 bytes) in binary terms or 1,000,000 bytes in decimal measurement. Bytes measure small data amounts like characters, while megabytes quantify larger files such as images or documents. Understanding the byte versus megabyte scale is crucial for accurately assessing digital storage capacity and data transfer rates.
Conversion: How Many Bytes in a Megabyte?
One megabyte (MB) is equal to 1,048,576 bytes when using the binary system (1 MB = 1024^2 bytes), commonly applied in computer science for memory and storage. In contrast, the decimal system used in data transfer rates defines 1 megabyte as 1,000,000 bytes, emphasizing the difference in units depending on context. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately interpreting file sizes and storage capacities in various digital devices and software.
Storage Capacity: Byte vs Megabyte
A byte consists of 8 bits and represents the smallest unit of storage in digital systems, capable of holding a single character or symbol. A megabyte (MB) equals 1,048,576 bytes (2^20 bytes) in binary measurement, commonly used to quantify file sizes, memory capacities, and storage devices. Understanding the difference between bytes and megabytes is crucial for evaluating data storage requirements, as megabytes provide a more practical scale for handling large amounts of digital information.
Real-World Examples of Bytes and Megabytes
A byte represents a single character of data, such as a letter or number, making it the fundamental unit of digital information storage. Megabytes, equivalent to approximately one million bytes, are commonly used to measure the size of digital files like high-resolution photos, MP3 songs, or short video clips. For instance, a typical 3-minute MP3 audio file may consume around 3 to 5 megabytes, while a plain text email message might only require a few kilobytes, showcasing practical differences in data scale.
Importance of Megabytes in Digital Storage
Megabytes (MB) represent a crucial unit of digital storage, measuring data in increments of approximately one million bytes, which allows for efficient handling of files such as high-resolution images, audio, and documents. Compared to bytes, which store a single character of text, megabytes enable the storage and transfer of significantly larger data volumes essential for modern computing and multimedia applications. Understanding the importance of megabytes helps optimize memory usage and improve system performance in devices ranging from smartphones to large-scale servers.
Byte and Megabyte in Data Transfer
A Byte consists of 8 bits and is the fundamental unit for data storage and transfer, representing a single character such as a letter or number. A Megabyte (MB) equals 1,048,576 Bytes in binary measurement (2^20) and is commonly used to quantify larger data transfers, such as files, images, or application data. Data transfer speeds and capacities are often measured in Megabytes per second (MB/s) to indicate the amount of data transmitted in larger, more practical units compared to individual Bytes.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bytes and Megabytes
A megabyte (MB) is equal to 1,048,576 bytes, often used to measure file sizes and storage capacity in digital devices. Bytes represent the smallest unit of digital data storage, typically storing a single character, while megabytes are used for larger data volumes like images, audio, and software. Frequently asked questions often address the difference in size, usage contexts, and conversion formulas between bytes and megabytes for data management and transfer.
Megabyte Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com