The Alps boast breathtaking landscapes, rich biodiversity, and world-renowned ski resorts, making them a top destination for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. Vibrant alpine villages offer a unique cultural experience combined with modern amenities. Discover how the Alps can inspire your next adventure by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
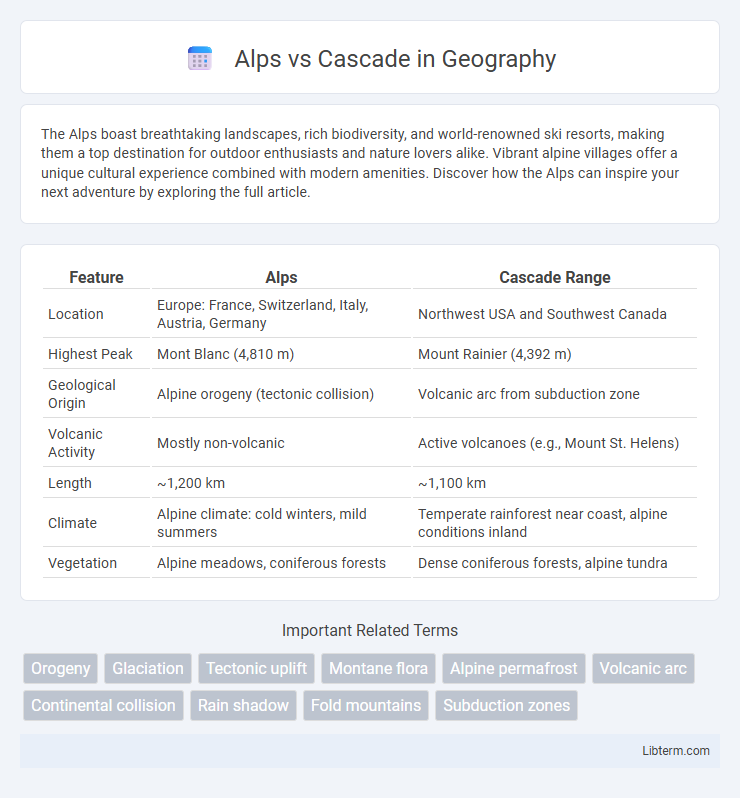
| Feature | Alps | Cascade Range |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Europe: France, Switzerland, Italy, Austria, Germany | Northwest USA and Southwest Canada |
| Highest Peak | Mont Blanc (4,810 m) | Mount Rainier (4,392 m) |
| Geological Origin | Alpine orogeny (tectonic collision) | Volcanic arc from subduction zone |
| Volcanic Activity | Mostly non-volcanic | Active volcanoes (e.g., Mount St. Helens) |
| Length | ~1,200 km | ~1,100 km |
| Climate | Alpine climate: cold winters, mild summers | Temperate rainforest near coast, alpine conditions inland |
| Vegetation | Alpine meadows, coniferous forests | Dense coniferous forests, alpine tundra |
Introduction: Comparing the Alps and the Cascades
The Alps, Europe's highest and most extensive mountain range, span eight countries and feature iconic peaks like Mont Blanc at 4,810 meters. The Cascade Range, located in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, is known for its volcanic peaks such as Mount Rainier at 4,392 meters and Mount St. Helens. Both mountain ranges offer unique geological features, diverse ecosystems, and significant cultural and recreational importance.
Geographic Location and Extent
The Alps span across eight European countries, including France, Switzerland, Italy, and Austria, covering roughly 1,200 kilometers in length. In contrast, the Cascade Range extends approximately 1,100 kilometers through the Pacific Northwest of North America, predominantly in the United States and Canada. The Alps' elevation peaks at Mont Blanc (4,808 meters), while the Cascade Range features prominent volcanic summits like Mount Rainier (4,392 meters).
Geological Origins and Formation
The Alps formed about 65 million years ago through the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, resulting in intense folding and uplift of sedimentary rock layers. The Cascade Range, in contrast, is primarily a volcanic arc created by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate beneath the North American Plate, with active volcanoes like Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier. These contrasting geological processes highlight the Alps' fold-mountain origins versus the Cascades' volcanic formation linked to Pacific Plate subduction.
Climate and Weather Patterns
The Alps experience a temperate climate characterized by cold, snowy winters and mild summers, with significant precipitation due to moist air masses from the Mediterranean and Atlantic. In contrast, the Cascade Range has a more varied climate, with wet, cool conditions on the western slopes caused by Pacific Ocean weather systems, and drier, warmer conditions on the eastern slopes due to a rain shadow effect. Seasonal snowpack in both ranges is critical for regional water supplies, but the Alps generally have heavier and more consistent snowfall compared to the Cascade Mountains.
Iconic Peaks and Landmarks
The Alps feature iconic peaks such as Mont Blanc, the highest in Western Europe at 4,808 meters, and the Matterhorn, known for its distinctive pyramid shape. In contrast, the Cascade Range boasts notable landmarks like Mount Rainier, an active stratovolcano rising to 4,392 meters, and Mount St. Helens, famous for its 1980 volcanic eruption. Both mountain ranges attract climbers and nature enthusiasts due to their unique geological features and stunning landscapes.
Flora and Fauna Diversity
The Alps, spanning Europe, host a diverse range of flora including edelweiss, alpine roses, and larch forests, supporting fauna such as ibex, chamois, and golden eagles. The Cascade Range in North America boasts rich biodiversity with species like Douglas fir, western red cedar, and giant sequoia, alongside wildlife including black bears, mountain lions, and spotted owls. Both mountain ranges exemplify unique ecosystems shaped by their climates, elevations, and geological histories, contributing to their distinct flora and fauna diversity.
Outdoor Activities and Adventure Sports
The Alps offer a vast range of outdoor activities including skiing, snowboarding, mountaineering, and paragliding, making it a premier destination for alpine sports enthusiasts. The Cascade Range is known for its rugged terrain ideal for hiking, rock climbing, mountain biking, and backcountry skiing, providing diverse adventure opportunities in both Washington and Oregon. Both mountain ranges feature extensive trail systems, challenging peaks, and extreme sports events that attract adventure seekers worldwide.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The Alps boast a rich cultural heritage deeply intertwined with centuries-old traditions, languages, and historic trade routes that shaped European identity and art. In contrast, the Cascade Range reflects Indigenous histories and early exploration that influenced settlement patterns in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Both mountain ranges serve as symbolic landmarks, preserving distinct cultural narratives essential to their regional histories.
Tourism Infrastructure and Accessibility
The Alps feature an extensive tourism infrastructure with over 1,200 ski resorts, comprehensive lift systems, and well-developed hiking trails, accessible via major European airports such as Zurich and Geneva. In contrast, the Cascade Range offers fewer but rapidly developing recreational facilities, with key access points including Seattle-Tacoma International Airport and Portland International Airport. Both regions provide diverse outdoor activities, but the Alps have a more established network of accommodations, guided tours, and public transportation connecting popular destinations.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Similarities
The Alps and Cascades both feature prominent mountainous landscapes shaped by tectonic activity, yet the Alps are primarily composed of older, metamorphic rock formations, while the Cascades are known for active volcanic peaks. Both mountain ranges support diverse ecosystems with alpine flora and fauna, but the Alps experience a more extensive influence of glaciation compared to the Cascades. Despite their geological and climatic differences, both ranges serve as crucial water sources and popular destinations for outdoor recreation and mountaineering.
Alps Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com