Sirocco is a powerful Mediterranean wind originating from the Sahara Desert, known for bringing hot, dry air and dust storms to Southern Europe. This weather phenomenon impacts climate patterns, agriculture, and daily life across affected regions by causing temperature spikes and reduced air quality. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the sirocco influences your environment and what measures can be taken to adapt.
Table of Comparison
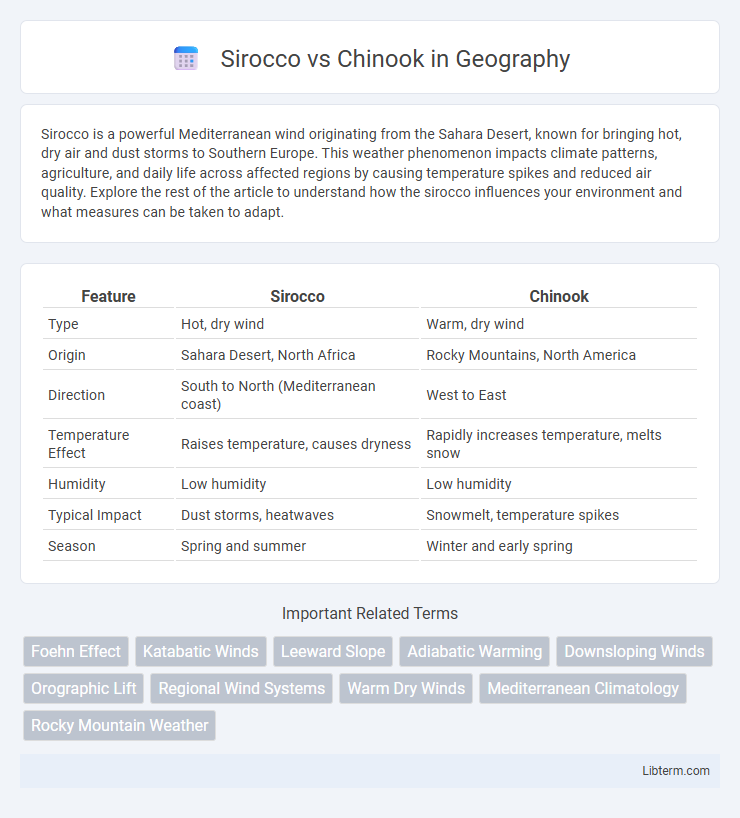
| Feature | Sirocco | Chinook |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Hot, dry wind | Warm, dry wind |
| Origin | Sahara Desert, North Africa | Rocky Mountains, North America |
| Direction | South to North (Mediterranean coast) | West to East |
| Temperature Effect | Raises temperature, causes dryness | Rapidly increases temperature, melts snow |
| Humidity | Low humidity | Low humidity |
| Typical Impact | Dust storms, heatwaves | Snowmelt, temperature spikes |
| Season | Spring and summer | Winter and early spring |
Introduction to Sirocco and Chinook Winds
Sirocco and Chinook winds are notable atmospheric phenomena with distinct origins and effects. The Sirocco is a hot, dry wind that originates from the Sahara Desert, sweeping across the Mediterranean region and often bringing dust and high temperatures. In contrast, the Chinook wind is a warm, moist wind descending the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains in North America, known for rapid temperature increases and melting snow.
Origins and Geographic Distribution
The Sirocco wind originates from the Sahara Desert, blowing across North Africa and affecting Southern Europe, particularly the Mediterranean Basin, including Italy, Greece, and the Balkans. The Chinook wind develops east of the Rocky Mountains in North America, impacting regions such as Alberta, Montana, and surrounding areas with warm, dry air descending from the mountains. Both winds significantly influence local climates, with the Sirocco carrying hot, dry sand and the Chinook causing rapid temperature increases in winter.
Meteorological Mechanisms
The Sirocco and Chinook winds differ primarily in their meteorological mechanisms; the Sirocco originates from warm, dry air masses over the Sahara Desert, driven by intense low-pressure systems over the Mediterranean, causing hot, dusty conditions in southern Europe. In contrast, the Chinook results from moist Pacific air ascending the windward side of the Rocky Mountains, shedding precipitation, then rapidly descending the leeward slopes as warm, dry air due to adiabatic compression. This process leads to significant temperature increases and drying effects typical of Chinook events in western North America.
Seasonal Patterns and Occurrence
Sirocco winds typically occur in the spring and fall across the Mediterranean, originating from the Sahara Desert and driving hot, dry conditions northward. Chinook winds predominantly affect the Rocky Mountain region during winter and early spring, resulting from warm, moist Pacific air descending the eastern slopes and causing rapid temperature increases. Both wind systems exhibit distinct seasonal patterns tied to geographical and atmospheric dynamics, influencing regional climate and weather events.
Temperature and Humidity Effects
Sirocco winds typically raise temperatures significantly, often exceeding 30degC, and bring dry, low-humidity air from the Sahara Desert, leading to arid conditions. In contrast, Chinook winds cause rapid temperature increases, sometimes by 20degC within hours, while simultaneously reducing humidity by promoting the evaporation of moisture on the leeward side of mountains. Both winds dramatically alter local climates but differ in origin and their respective impacts on moisture levels and temperature fluctuations.
Impacts on Local Climate
Sirocco and Chinook winds both significantly affect local climate by altering temperature and humidity levels; the Sirocco carries hot, dry air from the Sahara Desert, causing heatwaves and drought conditions in Southern Europe. In contrast, the Chinook wind brings warm, moist air down the eastern slopes of the Rockies in North America, leading to rapid snowmelt and temperature spikes. These winds influence agriculture, water resources, and weather patterns in their respective regions.
Economic and Environmental Consequences
The Sirocco and Chinook winds impact economies differently due to their contrasting effects on agriculture and energy consumption; the Sirocco often causes crop damage and increases cooling costs, whereas the Chinook can benefit agriculture by rapidly melting snow and reducing heating demand. Environmentally, the Sirocco carries dust and pollutants from the Sahara, worsening air quality and soil erosion, while the Chinook promotes quicker snowmelt runoff that can lead to both beneficial early water availability and increased flood risks. Understanding these winds' economic and environmental consequences is crucial for regional planning in affected areas such as the Mediterranean Basin for the Sirocco and the Rocky Mountain region for the Chinook.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The Sirocco wind, originating from the Sahara Desert, holds significant cultural importance in Mediterranean societies, often symbolizing both peril and fertility in folklore and traditional practices. In contrast, the Chinook wind of North America plays a crucial role in Indigenous cultures and settler histories, associated with rapid seasonal weather changes that impact agriculture and daily life. Both winds have shaped local customs, oral histories, and even architectural adaptations, reflecting their deep-rooted influence on human settlement and cultural identity.
Health and Safety Considerations
Sirocco winds, characterized by hot, dry air often carrying dust and allergens, can exacerbate respiratory issues and trigger allergies, posing health risks to sensitive individuals. In contrast, Chinook winds bring sudden temperature rises and rapid snowmelt but are generally less hazardous for respiratory health, although their abrupt changes can affect conditions like arthritis and migraines. Both wind types require awareness of environmental impacts on human health, with Sirocco demanding precautions against air quality deterioration and Chinook necessitating monitoring for weather-induced physical stress.
Comparative Summary: Sirocco vs Chinook
Sirocco winds originate from the Sahara, carrying hot, dry air into Southern Europe, while Chinook winds descend the eastern slopes of the Rockies, bringing warm, moist air to the Pacific Northwest. Sirocco typically causes temperature spikes and dusty conditions, contrasting sharply with Chinook's rapid snowmelt and temperature rise due to moist air warming adiabatically. Both winds influence local climates significantly, but Sirocco impacts mainly Mediterranean regions and Chinook affects mountainous areas in North America.
Sirocco Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com