Human-environment interaction explores how people adapt to, modify, and depend on their natural surroundings, influencing ecosystems and climate patterns. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing sustainable practices that balance societal needs with environmental stewardship. Discover how this relationship shapes your world and what steps you can take by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
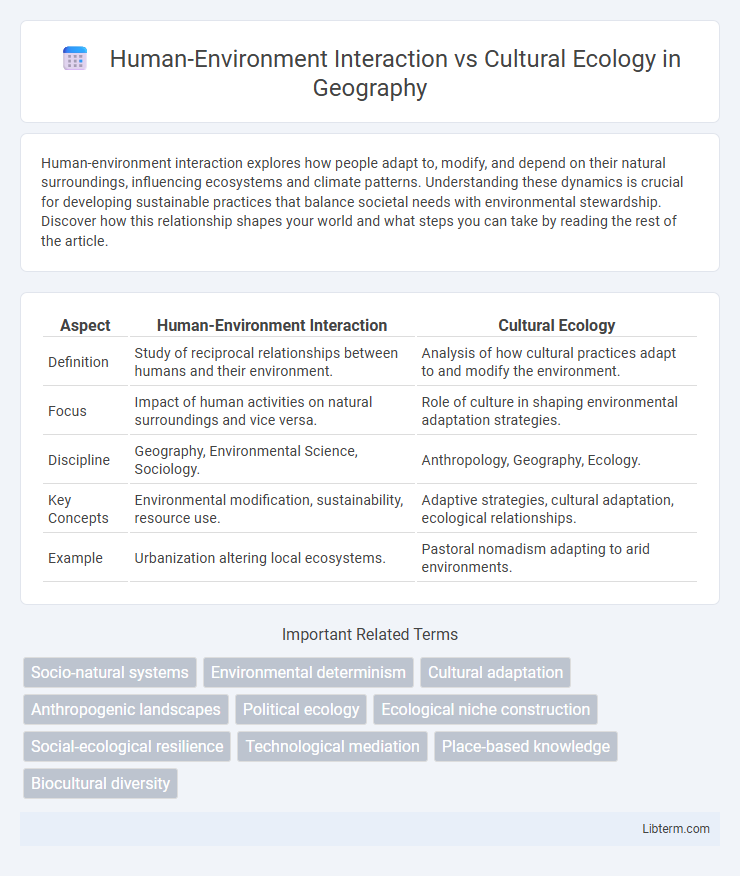
| Aspect | Human-Environment Interaction | Cultural Ecology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of reciprocal relationships between humans and their environment. | Analysis of how cultural practices adapt to and modify the environment. |
| Focus | Impact of human activities on natural surroundings and vice versa. | Role of culture in shaping environmental adaptation strategies. |
| Discipline | Geography, Environmental Science, Sociology. | Anthropology, Geography, Ecology. |
| Key Concepts | Environmental modification, sustainability, resource use. | Adaptive strategies, cultural adaptation, ecological relationships. |
| Example | Urbanization altering local ecosystems. | Pastoral nomadism adapting to arid environments. |
Introduction to Human-Environment Interaction and Cultural Ecology
Human-Environment Interaction examines how humans adapt to, modify, and depend on their environment, emphasizing the reciprocal relationships shaping both natural and built landscapes. Cultural Ecology focuses on how cultural beliefs and practices influence human-environment relationships, analyzing how societies use knowledge, technology, and social organization to interact sustainably with their surroundings. Both frameworks contribute to understanding the complex dynamics between human cultures and environmental systems, highlighting adaptation, resource management, and environmental impact.
Defining Human-Environment Interaction
Human-Environment Interaction refers to the dynamic relationship between humans and their physical surroundings, emphasizing how human activities modify natural environments and how environmental conditions influence human life. This concept explores adaptive behaviors, resource use, and environmental impacts within specific geographies. Cultural Ecology, in contrast, analyzes how cultural beliefs and practices shape and are shaped by ecological systems, focusing on the link between culture and environmental adaptation.
Understanding Cultural Ecology
Cultural ecology examines the ways human cultures adapt to and modify their environments through technology, social organization, and belief systems. It analyzes the dynamic relationships between cultural practices and environmental conditions, emphasizing the reciprocal influence between humans and their surroundings. Understanding cultural ecology provides insights into sustainable resource management and the cultural factors shaping ecological resilience.
Historical Development of Both Concepts
Human-Environment Interaction emerged from early geographic studies emphasizing the reciprocal relationships between humans and their natural surroundings, with foundational contributions from scholars like Carl Sauer in the early 20th century. Cultural Ecology, developed primarily by Julian Steward in the mid-20th century, introduced a more systematic analysis of how cultural practices adapt to environmental constraints and opportunities over time. Both concepts evolved through interdisciplinary research, shaping contemporary understandings of how societies influence and are influenced by their ecological contexts.
Key Theoretical Differences
Human-Environment Interaction explores how human activities affect and are affected by the natural environment, emphasizing reciprocal relationships and the consequences of human actions on ecological systems. Cultural Ecology focuses on the ways cultural beliefs, practices, and technologies shape human adaptations to environmental challenges, highlighting cultural determinants in ecological relationships. The key theoretical difference lies in Human-Environment Interaction's emphasis on bidirectional impacts between humans and nature, while Cultural Ecology centers on cultural adaptations as drivers of environmental management and resource use.
Similarities and Overlapping Areas
Human-Environment Interaction and Cultural Ecology both explore the reciprocal relationships between humans and their natural surroundings, emphasizing how cultural practices influence environmental use and modification. Both fields examine adaptation strategies, resource management, and the impact of human activities on ecosystems, highlighting the dynamic and interdependent nature of cultural and ecological systems. Overlapping areas include studying sustainable development, environmental adaptation, and the role of cultural beliefs in shaping environmental decisions.
Case Studies: Applications in Real-World Contexts
Human-environment interaction examines how human activities shape and are shaped by the natural environment, illustrated in case studies like deforestation in the Amazon and urbanization in coastal cities. Cultural ecology focuses on the adaptive strategies cultures develop to live sustainably within specific ecosystems, as seen in the traditional agricultural practices of the Andean highlands and water management systems of the Navajo people. These case studies highlight the dynamic relationship between cultural practices and environmental challenges, demonstrating how societies respond to climate variability and resource limitations through innovation and resilience.
Role in Environmental Management and Policy
Human-environment interaction explores how people adapt to and modify their surroundings, emphasizing the reciprocal relationship between human activities and environmental changes for sustainable resource use. Cultural ecology studies how cultural beliefs and practices shape environmental management, highlighting the importance of traditional knowledge and social institutions in ecosystem conservation. Both frameworks inform environmental policy by integrating scientific data with cultural values to promote adaptive management strategies that address ecological challenges.
Influence on Contemporary Environmental Thought
Human-Environment Interaction examines the reciprocal relationship between humans and their surroundings, emphasizing how human activities modify natural landscapes and ecosystems, influencing sustainability practices. Cultural Ecology explores how cultural beliefs and social systems shape environmental adaptation strategies, providing insight into the diverse ways societies respond to ecological challenges. Both frameworks significantly impact contemporary environmental thought by promoting an integrated understanding of ecological dynamics and human cultural factors, guiding policy development and conservation efforts.
Future Directions in Human-Environment Research
Future directions in human-environment research emphasize integrating advanced spatial analysis and big data to deepen understanding of adaptive strategies within cultural ecology frameworks. Researchers prioritize examining how technological innovation and climate change reshape human-environment interactions, fostering resilience in diverse socio-ecological systems. Emphasis on interdisciplinary approaches enhances predictive models to guide sustainable resource management and policy development.
Human-Environment Interaction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com