Partition systems maximize space efficiency and privacy in both residential and commercial environments through versatile design options. They offer customizable materials including glass, wood, and metal, adapting to various aesthetic and functional needs while improving acoustic insulation and workflow. Discover how the right partition can transform your space by exploring the full details in the article.
Table of Comparison
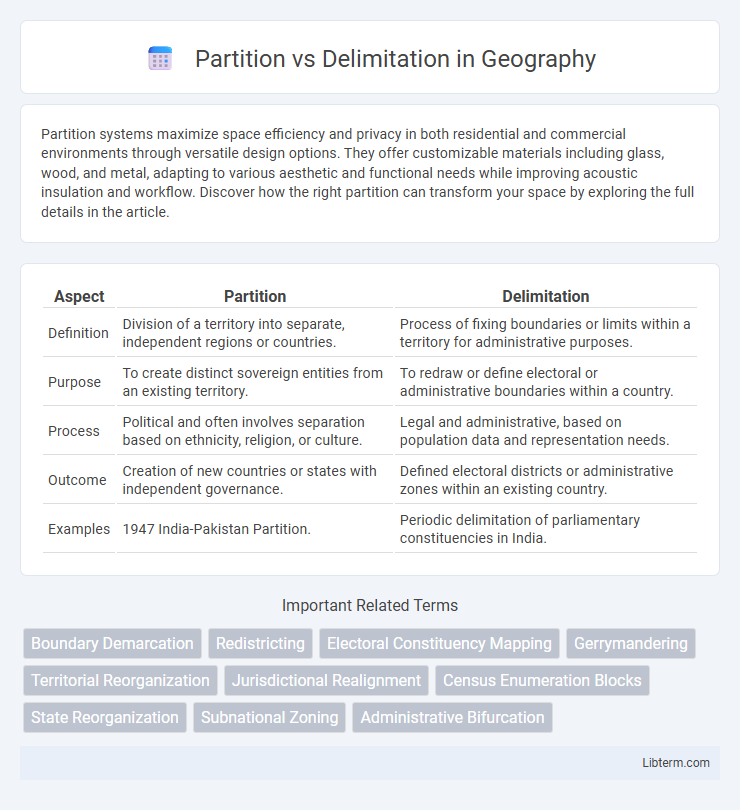
| Aspect | Partition | Delimitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Division of a territory into separate, independent regions or countries. | Process of fixing boundaries or limits within a territory for administrative purposes. |
| Purpose | To create distinct sovereign entities from an existing territory. | To redraw or define electoral or administrative boundaries within a country. |
| Process | Political and often involves separation based on ethnicity, religion, or culture. | Legal and administrative, based on population data and representation needs. |
| Outcome | Creation of new countries or states with independent governance. | Defined electoral districts or administrative zones within an existing country. |
| Examples | 1947 India-Pakistan Partition. | Periodic delimitation of parliamentary constituencies in India. |
Introduction to Partition and Delimitation
Partition involves dividing a geographical or political entity into distinct parts, often based on administrative, ethnic, or cultural boundaries to create separate governance units. Delimitation refers to the precise drawing or fixing of boundaries, commonly used in defining electoral constituencies or territorial limits through legal and cartographic methods. Both processes play critical roles in political geography by shaping representation, resource allocation, and territorial sovereignty.
Defining Partition: Meaning and Historical Context
Partition refers to the process of dividing a territory or country into distinct political or administrative units, often involving significant demographic and cultural shifts. Historically, notable partitions include the Partition of India in 1947, which resulted in the creation of India and Pakistan and triggered massive population displacement and conflict. This event exemplifies how partition is more than a boundary change; it profoundly reshapes national identities and geopolitical landscapes.
What is Delimitation? Core Concepts Explained
Delimitation refers to the precise process of establishing boundaries, typically in political geography, to define the limits of territorial areas such as countries, states, or electoral districts. It involves drawing detailed maps and legal documentation to mark these boundaries clearly, facilitating governance and administrative functions. The core concept centers on legally and cartographically defining borders to avoid disputes and ensure clear jurisdictional authority.
Key Differences Between Partition and Delimitation
Partition divides a territory or resource into distinct, separate parts often resulting in physical or political boundaries, whereas delimitation involves defining or marking the precise limits of those boundaries legally or cartographically. Partition typically leads to the establishment of independent entities or zones, while delimitation serves as a technical process for clarifying borderlines within existing territories. The key difference lies in partition creating new separations, and delimitation specifying exact border points within agreed frameworks.
Historical Examples: Partition vs Delimitation
The Partition of India in 1947, which resulted in the creation of India and Pakistan, exemplifies partition as a political division based on religious demographics, leading to massive population displacements and violence. In contrast, the delimitation of electoral boundaries in post-apartheid South Africa involved redrawing constituencies to ensure fair political representation without altering sovereign territories. These historical examples highlight Partition as a division creating new states or territories, whereas delimitation is a boundary adjustment within existing political frameworks to optimize governance or representation.
Political and Legal Implications
Partition often involves dividing a territory into separate political entities, usually along ethnic, religious, or cultural lines, which can lead to significant legal challenges regarding sovereignty and governance frameworks. Delimitation focuses on legally defining and marking boundaries between existing political units or jurisdictions, crucial for maintaining clarity in electoral districts, resource allocation, and dispute resolution. Both processes carry profound political implications, potentially affecting national unity, minority rights, and international relations depending on the methods and agreements used.
Societal Impact and Demographic Changes
Partition often results in abrupt societal upheaval, causing mass displacement, ethnic tensions, and long-lasting demographic shifts as populations migrate or are forcibly relocated. Delimitation, involving boundary adjustments through legal or political processes, tends to produce more controlled demographic outcomes with less immediate social disruption. Both impact societal structures, but partition triggers intense identity conflicts and refugee crises, whereas delimitation primarily influences electoral representation and resource distribution.
Partition and Delimitation in Contemporary Politics
Partition and delimitation serve distinct roles in contemporary politics, with partition referring to the division of a state or territory into separate political entities, often leading to sovereignty changes or new national boundaries. Delimitation involves the precise drawing or redrawing of boundaries within a political entity, typically for electoral purposes, to ensure fair representation based on demographic changes. Both processes significantly influence political stability, identity politics, and governance by reshaping territorial and electoral landscapes.
Challenges and Controversies Involved
Partition and delimitation often trigger disputes due to divergent political interests, ethnic identities, and historical claims, complicating consensus on boundary definitions. Challenges include managing population displacement, ensuring minority rights, and addressing resource allocation, which frequently lead to prolonged conflicts and legal battles. Controversies intensify when international laws clash with local aspirations, resulting in contested sovereignties and ongoing geopolitical instability.
Conclusion: Weighing the Effects and Importance
Partition causes division by creating distinct boundaries, often leading to long-term geopolitical conflicts and social fragmentation. Delimitation focuses on defining clear boundaries through legal or administrative processes, promoting clarity and reducing disputes. Understanding their effects is crucial for policymakers to balance territorial integrity with peaceful coexistence.
Partition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com