Combining elements effectively enhances the overall functionality and aesthetic appeal of any project. Consider how integrating diverse components can streamline processes and yield innovative results. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for successful combination in your endeavors.
Table of Comparison
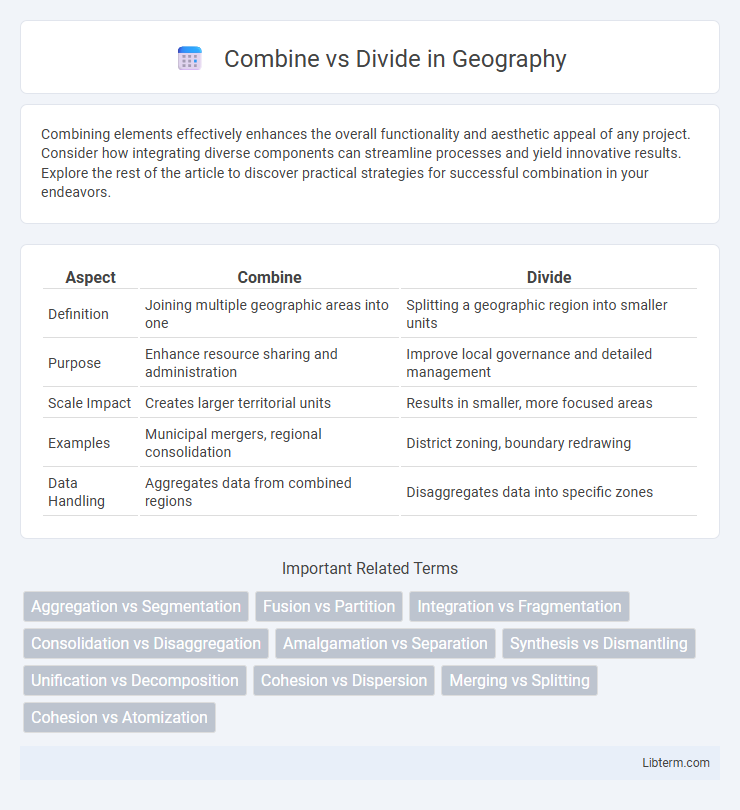
| Aspect | Combine | Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Joining multiple geographic areas into one | Splitting a geographic region into smaller units |
| Purpose | Enhance resource sharing and administration | Improve local governance and detailed management |
| Scale Impact | Creates larger territorial units | Results in smaller, more focused areas |
| Examples | Municipal mergers, regional consolidation | District zoning, boundary redrawing |
| Data Handling | Aggregates data from combined regions | Disaggregates data into specific zones |
Understanding the Concepts: Combine and Divide
Combine and Divide represent fundamental arithmetic operations essential for quantitative reasoning. Combining refers to the process of joining two or more quantities to form a larger amount, often represented by addition or multiplication. Dividing involves partitioning a total quantity into equal parts or groups, symbolized by division, which helps in understanding ratios, fractions, and proportional distribution.
Historical Perspectives on Combining and Dividing
Historical perspectives on combining and dividing trace back to ancient civilizations where early societies used aggregation and partitioning for resource management and trade. The Babylonians developed sophisticated systems for combining quantities in their cuneiform tablets, while ancient Egyptians employed division in grain distribution among workers. These foundational mathematical operations evolved alongside cultural advancements, influencing economic, architectural, and scientific practices throughout history.
Key Differences Between Combining and Dividing
Combining involves merging multiple elements into a single entity, enhancing unity and overall cohesion, whereas dividing separates a whole into distinct parts to simplify analysis or allocation. The key difference lies in their purpose: combining aims to unify and integrate resources or concepts, while dividing focuses on segregation and distribution. These processes impact decision-making by either consolidating data for holistic insight or partitioning information for targeted management.
Benefits of Combining Resources
Combining resources enhances efficiency by pooling expertise, technology, and capital, leading to economies of scale and reduced costs. It fosters innovation through diverse perspectives and shared knowledge, accelerating problem-solving and product development. Greater resource integration improves market competitiveness, enabling organizations to expand reach and strengthen stakeholder value.
Challenges in Dividing Assets
Dividing assets during a split often presents significant challenges, including accurately valuing diverse property types, navigating complex legal frameworks, and ensuring equitable distribution among parties. Disputes frequently arise over sentimental versus monetary worth, complicating negotiations and prolonging resolution. Addressing these obstacles requires careful documentation, expert appraisals, and clear communication to minimize conflict and financial loss.
Applications in Mathematics and Science
Combine and divide serve fundamental roles in mathematics and science, with combine operations often involving addition or merging of elements to form a whole, such as summing data sets or uniting chemical compounds. Divide processes entail partitioning quantities into equal or specified parts, crucial for understanding ratios, proportions, and molecular distributions in experiments. Mastery of these operations enables accurate problem-solving across statistical analysis, physics problem formulations, and biological quantification.
Real-world Examples of Combining and Dividing
Combining and dividing are fundamental operations used in various real-world situations, such as cooking recipes where ingredients are combined to create a dish or when dividing a pizza into equal slices for sharing. In construction, combining materials like cement, sand, and water form concrete, whereas dividing tasks among workers increases efficiency. Financial management also illustrates these concepts by combining different sources of income to calculate total earnings and dividing expenses to create a budget.
Psychological Impacts: Unity vs. Separation
Combining elements fosters psychological unity, enhancing feelings of togetherness, cooperation, and shared identity that promote mental well-being and resilience. Dividing, on the other hand, can trigger perceptions of separation, isolation, and conflict, often leading to stress, anxiety, and diminished social cohesion. Understanding the psychological impacts of unity versus separation is critical for improving interpersonal relationships and group dynamics.
Combine vs. Divide in Business Strategies
Combine strategies in business integrate resources, markets, or product lines to achieve economies of scale, expand market share, and foster innovation through synergies. Divide strategies focus on segmenting operations, markets, or business units to improve focus, efficiency, and risk management by isolating underperforming assets or tailoring approaches to specific customer needs. Understanding when to combine for growth versus divide for specialization is crucial for optimizing business performance and competitive advantage.
Future Trends: The Balance Between Integration and Segregation
Future trends in data management emphasize a strategic balance between combining and dividing datasets to optimize analytics and storage efficiency. Hybrid models leverage the integration of diverse data sources while maintaining essential segregation for security and compliance, enabling enhanced machine learning outcomes and real-time decision-making. Advances in AI-driven data orchestration tools facilitate dynamic switching between combined and divided states, adapting to evolving business needs and regulatory landscapes.
Combine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com