Oasis refers to fertile areas in deserts where water is available, supporting vegetation and wildlife. These natural havens provide crucial resources for travelers and inhabitants, offering relief from arid conditions and enabling sustainable agriculture. Discover how these lifelines transform harsh landscapes and support ecosystems by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
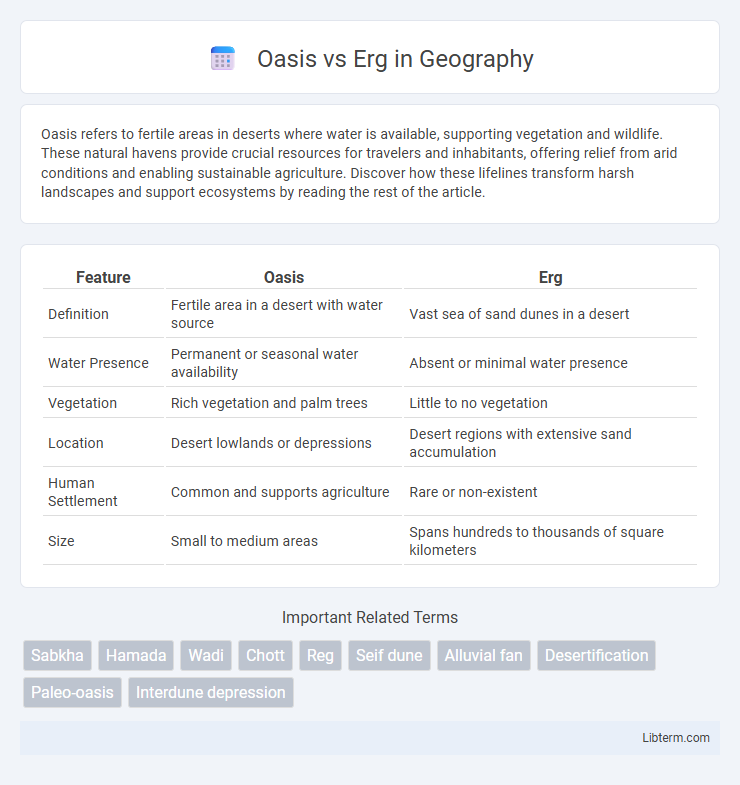
| Feature | Oasis | Erg |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fertile area in a desert with water source | Vast sea of sand dunes in a desert |
| Water Presence | Permanent or seasonal water availability | Absent or minimal water presence |
| Vegetation | Rich vegetation and palm trees | Little to no vegetation |
| Location | Desert lowlands or depressions | Desert regions with extensive sand accumulation |
| Human Settlement | Common and supports agriculture | Rare or non-existent |
| Size | Small to medium areas | Spans hundreds to thousands of square kilometers |
Introduction to Oases and Ergs
Oases and ergs represent distinct desert landscapes with contrasting features; oases are fertile areas in deserts where water from underground springs or aquifers supports vegetation and human habitation, serving as vital life sources in arid regions. Ergs, also known as sand seas, are vast expanses of wind-swept dunes formed by loose, shifting sand that create extreme, barren environments with minimal vegetation. Understanding the ecological and geological differences between oases and ergs is crucial for studying desert ecosystems and resource management.
Defining Oases: Lifelines in the Desert
Oases are fertile areas in deserts where water from underground springs or aquifers reaches the surface, creating a crucial habitat for plants, animals, and human settlements. Unlike ergs, which are vast expanses of wind-swept sand dunes, oases provide stable sources of water and vegetation essential for sustaining life in arid environments. These lifelines support agriculture, trade routes, and biodiversity, making them vital ecological and cultural hubs in desert landscapes.
Ergs Explained: Seas of Sand
Ergs, also known as seas of sand, are vast expanses of shifting sand dunes covering thousands of square kilometers in desert regions, forming some of the most extreme and dynamic landscapes on Earth. Unlike oases, which are fertile spots with water supporting vegetation and life, ergs consist primarily of loose sand shaped by wind into extensive dune fields with minimal to no vegetation. These sand seas play a critical role in desert ecology and climate, influencing sandstorms and acting as reservoirs of sand that reshape desert terrains over time.
Geographic Distribution: Where Oases and Ergs Are Found
Oases are predominantly found in desert regions such as the Sahara, Arabian, and Gobi deserts, where underground water sources create fertile areas amidst arid landscapes. Ergs, expansive sand dune fields, are characteristic of vast desert interiors like the Sahara in North Africa and the Rub' al Khali on the Arabian Peninsula. While oases serve as isolated pockets of vegetation and habitation, ergs cover extensive areas, shaping the geography of some of the world's largest deserts.
Formation Processes of Oases vs Ergs
Oases form through natural groundwater accumulation where water surfaces in arid regions, supporting vegetation and human habitation. Ergs develop from vast wind-blown sand deposits shaped by aeolian processes, creating extensive dune fields with minimal moisture. The contrasting formation processes highlight oases as hydrological phenomena reliant on subsurface aquifers, while ergs result from sediment transport and deposition driven by wind dynamics.
Role in Ecosystems: Biodiversity Comparison
Oases serve as critical biodiversity hotspots, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna adapted to water-rich environments within otherwise arid deserts. Ergs, vast sand dune fields, host specialized organisms such as xerophytic plants and desert-adapted insects, but exhibit significantly lower species diversity due to harsher, drier conditions. The contrasting microhabitats of oases contribute disproportionately to regional ecosystem productivity and biodiversity conservation compared to the relatively barren ergs.
Human Settlement and Survival: Oases vs Ergs
Oases provide critical freshwater sources supporting permanent human settlements, agriculture, and trade routes in arid regions, enabling sustained survival and community development. Ergs, vast sandy deserts with shifting dunes, lack reliable water and vegetation, making them inhospitable for long-term habitation and forcing nomadic or transient lifestyles. The presence of oases transforms otherwise barren landscapes into viable habitats, while ergs challenge human resilience due to extreme scarcity of resources.
Economic Importance: Agriculture, Tourism, and Resources
Oases sustain local economies by providing fertile land for agriculture, supporting cultivation of date palms, fruits, and vegetables essential for food security and trade in arid regions. Erg areas, characterized by vast sand dunes, have limited agricultural potential but attract tourism through unique desert landscapes for activities like dune bashing and cultural experiences. Both oases and ergs contribute to resource extraction, with oases offering groundwater for irrigation while ergs hold mineral deposits such as gypsum and hydrocarbons, playing roles in regional economic development.
Climate Adaptations: Flora and Fauna in Oases & Ergs
Oases support diverse flora such as date palms, reeds, and grasses adapted to stable water sources, while fauna includes species like migratory birds, amphibians, and small mammals reliant on vegetation and water availability. Ergs, vast sandy deserts with shifting dunes, harbor specialized xerophytic plants and hardy animals like desert lizards, scorpions, and insects adapted to extreme aridity and temperature fluctuations. These climate adaptations highlight the contrasting ecosystems where oases provide microhabitats with sustained moisture, whereas ergs challenge survival through scarcity of water and harsh environmental conditions.
Oases and Ergs in Culture and History
Oases have historically served as vital cultural hubs and trade centers in desert regions, supporting agriculture and human settlement for millennia. Ergs, vast sand dune seas, shaped nomadic cultures by influencing migration patterns and survival strategies in harsh desert environments. The differing landscapes of oases and ergs profoundly impacted the development of civilizations in arid zones, with oases enabling sustained communities and ergs embodying the challenges of desert life.
Oasis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com