Facies and biozones provide critical information in geology for interpreting Earth's history through sedimentary rocks and fossil distribution. Facies represent distinctive rock characteristics indicating specific depositional environments, while biozones are intervals defined by unique fossil assemblages used for biostratigraphic correlation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can apply facies and biozones in geological studies and fossil analysis.
Table of Comparison
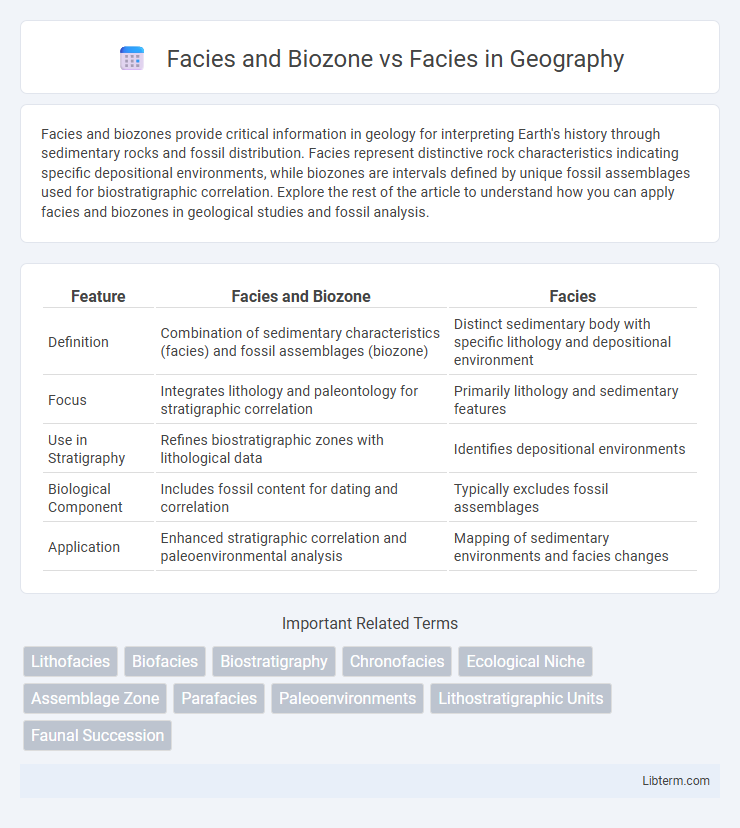
| Feature | Facies and Biozone | Facies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of sedimentary characteristics (facies) and fossil assemblages (biozone) | Distinct sedimentary body with specific lithology and depositional environment |
| Focus | Integrates lithology and paleontology for stratigraphic correlation | Primarily lithology and sedimentary features |
| Use in Stratigraphy | Refines biostratigraphic zones with lithological data | Identifies depositional environments |
| Biological Component | Includes fossil content for dating and correlation | Typically excludes fossil assemblages |
| Application | Enhanced stratigraphic correlation and paleoenvironmental analysis | Mapping of sedimentary environments and facies changes |
Understanding Facies: Definition and Importance
Facies are distinct bodies of sediment with specific characteristics reflecting particular depositional environments, essential for interpreting geological history. Biozones represent intervals defined by fossil content, aiding in biostratigraphic correlation but do not directly describe sedimentary processes like facies do. Understanding facies provides critical insights into past depositional settings, sediment dynamics, and basin evolution, fundamental for reservoir characterization and paleoenvironmental reconstruction.
What is a Biozone? Key Concepts Explained
A biozone is a stratigraphic interval defined by the presence and range of specific fossil taxa, serving as a critical tool for biostratigraphic correlation and dating sedimentary layers. Unlike facies, which represent the depositional environment and sediment characteristics of a rock unit, biozones focus on paleontological data to establish relative geological time frameworks. Understanding biozones enables geologists to link fossil assemblages to specific geological periods, enhancing the resolution of stratigraphic and paleoenvironmental interpretations.
Relationship Between Facies and Biozones
Facies represent distinct rock units characterized by specific sedimentary features, while biozones are intervals defined by the presence of particular fossil assemblages. The relationship between facies and biozones lies in their complementary roles for interpreting depositional environments and stratigraphic correlations; facies provide environmental context, whereas biozones offer biostratigraphic age constraints. Integrating facies analysis with biozone distributions enhances the resolution of paleoenvironmental reconstructions and improves geological correlation accuracy across different regions.
Facies vs Biozone: Key Differences
Facies represent the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of sedimentary rocks, reflecting depositional environments, while biozones are stratigraphic intervals defined by the presence or abundance of specific fossil taxa. The primary distinction lies in facies emphasizing environmental conditions and lithology, whereas biozones focus on biostratigraphy and temporal correlations using fossil assemblages. Facies can vary laterally within the same biozone, making them crucial for interpreting paleoenvironmental changes, whereas biozones provide a framework for relative dating and correlation across regions.
Methods for Identifying Facies in Sedimentary Rocks
Identifying facies in sedimentary rocks relies on detailed analysis of lithology, sedimentary structures, fossil content, and stratigraphic relationships. Techniques such as petrographic microscopy, geochemical assays, and sedimentological logging help delineate facies based on depositional environment characteristics. Biozone correlation enhances facies interpretation by integrating biostratigraphic data, improving paleoenvironmental reconstructions and facilitating more precise facies boundaries.
Biozone Identification Techniques in Stratigraphy
Biozone identification techniques in stratigraphy rely heavily on fossil content within sedimentary layers, distinguishing biozones by unique assemblages of index fossils rather than solely lithological characteristics typical of facies analysis. While facies focus on depositional environments and sedimentological features, biozones prioritize paleontological data, using quantitative methods such as range charts, cluster analysis, and statistical biofacies modeling to delineate stratigraphic intervals. These specialized techniques allow precise correlation and temporal resolution by integrating biostratigraphy with sedimentological insights, enhancing stratigraphic frameworks beyond conventional facies interpretation.
Integrated Stratigraphic Analysis: Facies and Biozones Together
Integrated stratigraphic analysis combines facies and biozone data to enhance paleoenvironmental interpretations and improve chronological resolution in sedimentary sequences. Facies represent distinct depositional environments characterized by lithology and sedimentary structures, while biozones define stratigraphic intervals based on fossil assemblages and biostratigraphic markers. The joint analysis of facies and biozones allows for precise correlation of sedimentary units, facilitating more accurate reconstructions of basin evolution and refining stratigraphic frameworks.
Case Studies: Facies and Biozone Correlation
Case studies on facies and biozone correlation reveal significant insights into paleoenvironmental reconstruction by integrating lithofacies characteristics with fossil assemblages for precise stratigraphic zoning. The correlation of facies and biozones allows for detailed identification of depositional environments and temporal changes, enhancing the resolution of sedimentary basin analysis. Examples from carbonate platform successions demonstrate how combined facies-biozone frameworks improve the interpretation of sea-level fluctuations and biodiversity patterns.
Importance of Facies and Biozone Differentiation in Petroleum Geology
Facies and biozone differentiation is crucial in petroleum geology for accurately characterizing depositional environments and correlating stratigraphic units, which directly impact reservoir quality prediction. Facies analysis provides insights into sedimentary environments, while biozones, based on fossil assemblages, enable precise chronological correlation essential for identifying potential hydrocarbon-bearing intervals. Integrating facies and biozone data enhances subsurface geological models, optimizing exploration and production strategies.
Future Trends in Facies and Biozone Research
Future trends in facies and biozone research emphasize integrating high-resolution stratigraphic data with advanced geochemical and paleontological techniques to enhance depositional environment interpretations and improve biostratigraphic correlations. Emerging methods such as machine learning and isotopic analyses are driving precise facies modeling and refined biozone classification, enabling better predictions of reservoir quality and paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Collaborative multidisciplinary approaches are expected to bridge gaps between sedimentology and biostratigraphy, fostering innovative frameworks for understanding sedimentary basins and facilitating resource exploration.
Facies and Biozone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com