Albedo measures the reflectivity of a surface, indicating how much sunlight it reflects back into space rather than absorbing it. High albedo surfaces like ice and snow help regulate Earth's temperature by reflecting solar energy, while darker surfaces absorb more heat, impacting climate patterns. Discover how albedo influences environmental changes and what it means for your understanding of global warming in the full article.
Table of Comparison
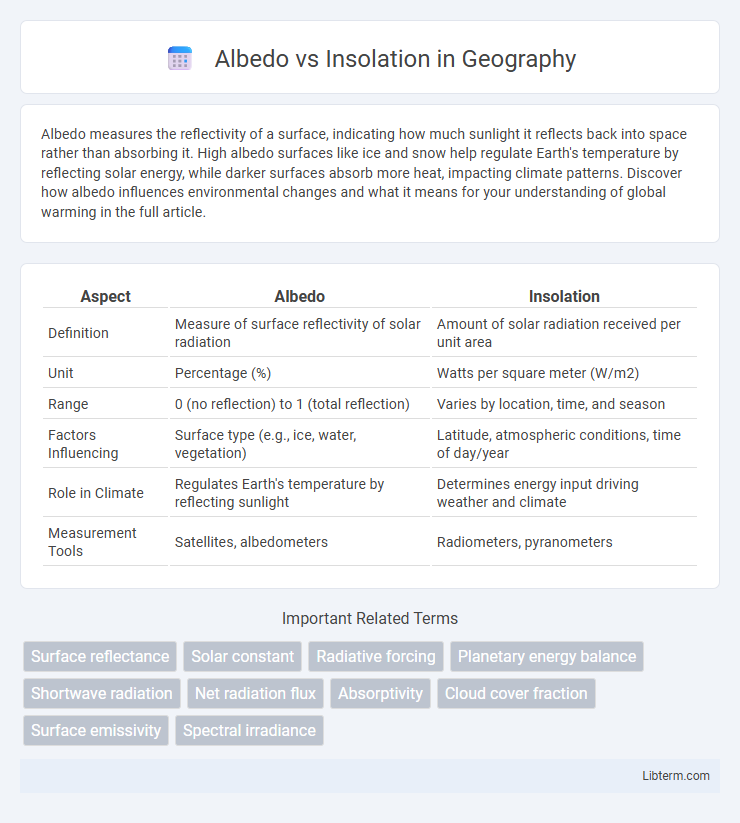
| Aspect | Albedo | Insolation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of surface reflectivity of solar radiation | Amount of solar radiation received per unit area |
| Unit | Percentage (%) | Watts per square meter (W/m2) |
| Range | 0 (no reflection) to 1 (total reflection) | Varies by location, time, and season |
| Factors Influencing | Surface type (e.g., ice, water, vegetation) | Latitude, atmospheric conditions, time of day/year |
| Role in Climate | Regulates Earth's temperature by reflecting sunlight | Determines energy input driving weather and climate |
| Measurement Tools | Satellites, albedometers | Radiometers, pyranometers |
Understanding Albedo: Definition and Importance
Albedo is the measure of a surface's reflectivity, expressed as a percentage of incoming solar radiation that is reflected back into space. High albedo surfaces, such as ice and snow, play a crucial role in regulating Earth's temperature by reflecting more insolation and reducing heat absorption. Understanding albedo is essential for climate models because it directly influences energy balance and global warming projections.
What is Insolation? Key Concepts Explained
Insolation refers to the amount of solar radiation energy received on a given surface area during a given time, typically measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). It plays a crucial role in Earth's energy balance by determining how much solar energy reaches the surface, influencing climate and weather patterns. Understanding insolation involves key concepts such as solar angle, atmospheric absorption, and Earth's axial tilt, all affecting the intensity and distribution of solar radiation.
How Albedo Influences Earth’s Climate System
Albedo, the measure of Earth's surface reflectivity, significantly influences the planet's energy balance by determining how much solar radiation is reflected back into space versus absorbed. Surfaces with high albedo, such as ice caps and snow, reflect a large portion of insolation, helping to cool the Earth, while low albedo surfaces like oceans and forests absorb more solar energy, contributing to warming. Variations in albedo due to changing land use, ice melt, and cloud cover directly impact climate feedback mechanisms, thus playing a critical role in global temperature regulation and climate change dynamics.
Factors Affecting Albedo Levels
Albedo levels are primarily influenced by surface characteristics such as color, texture, and composition, with lighter surfaces like snow and ice reflecting more solar radiation compared to darker surfaces like oceans and forests. Seasonal changes, vegetation cover, and land use also play significant roles in altering albedo by modifying the reflectivity of the Earth's surface. Atmospheric conditions, including cloud cover and aerosol presence, further affect the amount of solar energy reflected back into space, impacting overall insolation received at the surface.
The Role of Insolation in Global Temperature
Insolation, the solar radiation received by Earth, plays a critical role in determining global temperature by supplying the primary energy source that heats the planet's surface. Variations in insolation, influenced by Earth's orbit and axial tilt, drive seasonal temperature changes and long-term climate patterns. While albedo affects how much solar energy is reflected back into space, insolation fundamentally controls the energy input that powers atmospheric and oceanic circulation, ultimately shaping global temperature dynamics.
Albedo vs Insolation: Key Differences
Albedo measures the reflectivity of a surface, expressed as a percentage of incoming solar radiation reflected back into space, while insolation quantifies the total solar radiation energy received per unit area over a specific time, usually measured in watts per square meter. A high albedo indicates more solar radiation is reflected, reducing the amount of insolation absorbed by the Earth's surface, which directly influences local and global temperature patterns. Understanding the relationship between albedo and insolation is crucial for climate modeling, as variations affect energy balance, surface temperature, and atmospheric dynamics.
Interactions Between Albedo and Insolation
Albedo influences the amount of solar radiation reflected by Earth's surface, directly affecting insolation levels that reach the ground for heating. Surfaces with high albedo, such as ice and snow, reflect a significant portion of insolation, reducing heat absorption and cooling the local climate. Changes in insolation due to seasonal or geographic variations modify the effectiveness of albedo, creating feedback loops that impact global energy balance and climate patterns.
Real-World Examples: Albedo and Insolation in Action
Light-colored surfaces, such as snow-covered regions in Antarctica, exhibit high albedo by reflecting a significant portion of solar insolation, thereby reducing heat absorption. In contrast, dark urban areas with asphalt roads absorb more insolation due to their low albedo, contributing to the urban heat island effect. These real-world examples demonstrate how albedo directly influences the amount of solar energy retained by different environments.
Human Impact on Albedo and Insolation
Human activities significantly alter Earth's albedo through deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion, which reduce reflective surfaces like ice and vegetation, leading to increased absorption of solar radiation. This decrease in albedo enhances insolation, intensifying local and global warming by trapping more heat in the atmosphere. Furthermore, the increased carbon emissions from fossil fuels contribute to atmospheric changes that affect insolation patterns, altering the balance of incoming and outgoing solar energy.
Albedo and Insolation: Implications for Climate Change
Albedo, the measure of surface reflectivity, significantly influences Earth's energy balance by determining how much solar radiation (insolation) is reflected versus absorbed. Variations in albedo, such as the decline of polar ice caps, reduce reflectivity and increase insolation absorption, exacerbating global warming. Understanding the interplay between albedo and insolation is crucial for accurately modeling climate change impacts and predicting future temperature trends.
Albedo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com