The atmosphere is a complex mixture of gases that surrounds Earth, playing a vital role in sustaining life by regulating temperature and protecting from harmful solar radiation. Its layers, including the troposphere and stratosphere, support weather patterns and the ozone layer. Discover how understanding the atmosphere can enhance your awareness of environmental changes by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
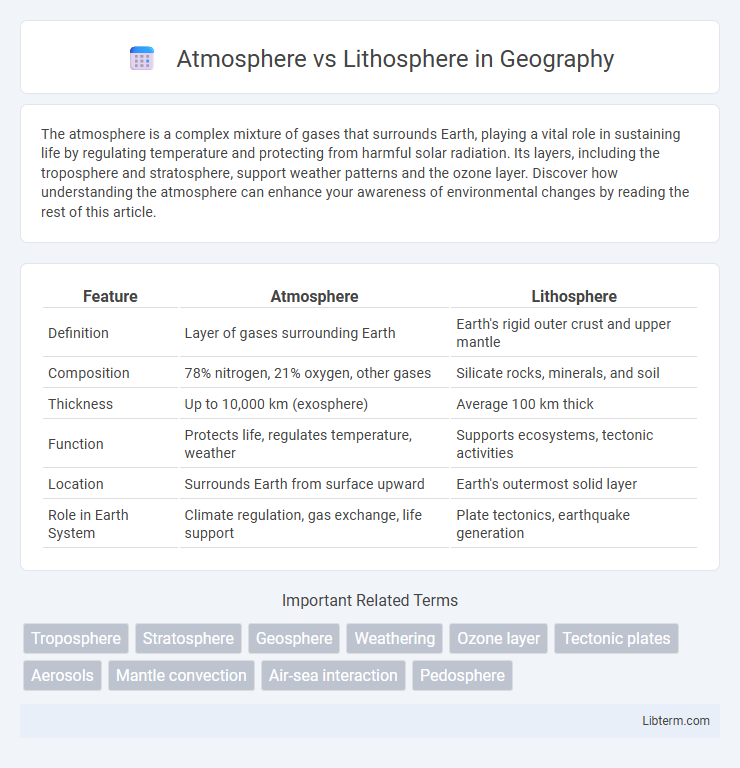
| Feature | Atmosphere | Lithosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layer of gases surrounding Earth | Earth's rigid outer crust and upper mantle |
| Composition | 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, other gases | Silicate rocks, minerals, and soil |
| Thickness | Up to 10,000 km (exosphere) | Average 100 km thick |
| Function | Protects life, regulates temperature, weather | Supports ecosystems, tectonic activities |
| Location | Surrounds Earth from surface upward | Earth's outermost solid layer |
| Role in Earth System | Climate regulation, gas exchange, life support | Plate tectonics, earthquake generation |
Introduction to Atmosphere and Lithosphere
The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding Earth, composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), essential for sustaining life and regulating climate. The lithosphere consists of the rigid outer shell of the Earth, including the crust and upper mantle, forming tectonic plates that shape the planet's surface through geological processes. Both the atmosphere and lithosphere interact dynamically, influencing weather patterns, erosion, and volcanic activity.
Defining the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding Earth, consisting primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), which supports life by providing essential air for respiration and regulating temperature through the greenhouse effect. It extends from the Earth's surface up to about 10,000 kilometers, including distinct layers such as the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Unlike the lithosphere, which comprises the rigid outer shell of the Earth including the crust and upper mantle, the atmosphere is a dynamic and fluid envelope critical for weather, climate, and protecting the planet from harmful solar radiation.
Defining the Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost layer of the Earth, comprising the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, extending roughly 100 kilometers deep. It forms the solid foundation beneath the atmosphere, which consists of the gases enveloping the planet, primarily nitrogen and oxygen. The lithosphere interacts with the atmosphere through geological processes such as volcanic eruptions and tectonic activity, influencing climatic and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Atmosphere and Lithosphere
The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding Earth, primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), essential for supporting life and climate regulation. The lithosphere is the rigid outer shell of Earth, encompassing the crust and upper mantle, responsible for tectonic activity and formation of landforms. Unlike the atmosphere's gaseous state, the lithosphere consists of solid rock and minerals, influencing geological processes such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Composition and Structure Comparison
The atmosphere consists primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases, arranged in layers such as the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. The lithosphere is the rigid outer shell of Earth, composed of the crust and upper mantle, made up of silicate minerals like oxygen, silicon, aluminum, and iron. While the atmosphere is a gaseous envelope surrounding Earth, the lithosphere is a solid, rocky layer that forms the tectonic plates.
Functions and Roles in Earth's Systems
The atmosphere regulates Earth's climate by controlling temperature and weather patterns, facilitating gas exchange essential for life, and protecting organisms from harmful solar radiation. The lithosphere provides a solid foundation for terrestrial ecosystems, supports nutrient cycling through rock weathering, and drives tectonic activity that shapes Earth's surface and influences seismic events. Together, these systems interact to maintain planetary stability, enabling diverse biological and geological processes critical to Earth's sustainability.
Interactions Between Atmosphere and Lithosphere
The interactions between the atmosphere and lithosphere drive critical Earth systems such as weathering, erosion, and volcanic activity. Atmospheric conditions like temperature, wind, and precipitation directly influence lithospheric processes by shaping soil formation and sediment transport. Volcanic eruptions release gases and particles into the atmosphere, impacting climate and air quality, exemplifying the dynamic exchange between these two Earth spheres.
Importance for Life on Earth
The atmosphere regulates temperature and provides essential gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, crucial for respiration and photosynthesis, sustaining life on Earth. The lithosphere offers a stable surface for organisms to live and grow, supplies minerals and nutrients necessary for biological processes, and supports ecosystems through soil formation. Interaction between the atmosphere and lithosphere drives weather patterns and nutrient cycles, maintaining Earth's habitability.
Human Impact on Atmosphere vs Lithosphere
Human activities release pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing climate change, ozone depletion, and air quality degradation, which directly affect ecosystems and human health. On the lithosphere, intensive agriculture, deforestation, mining, and urbanization contribute to soil erosion, habitat loss, and land degradation, reducing biodiversity and altering natural landforms. Both atmospheric pollution and lithospheric exploitation disrupt the balance of Earth's systems, intensifying environmental challenges like global warming and desertification.
Conclusion: Significance of Understanding Both Spheres
Understanding both the atmosphere and lithosphere is crucial for comprehending Earth's complex systems and their interactions. The atmosphere regulates climate and weather patterns essential for life, while the lithosphere provides the solid foundation supporting terrestrial ecosystems and human infrastructure. Integrating knowledge of these spheres enables better environmental management, natural disaster prediction, and sustainable resource use.
Atmosphere Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com