A global city is a major urban center that serves as a hub for international finance, culture, and political influence, driving economic growth worldwide. These cities connect diverse populations and industries, shaping global trends and innovation. Discover how your city ranks and what makes a global city truly transformative in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
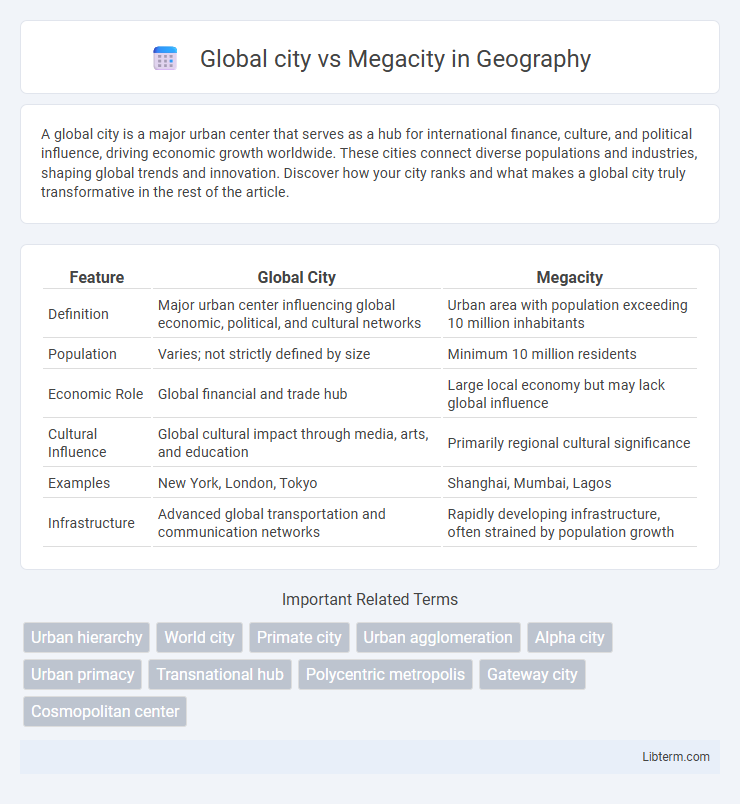
| Feature | Global City | Megacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Major urban center influencing global economic, political, and cultural networks | Urban area with population exceeding 10 million inhabitants |
| Population | Varies; not strictly defined by size | Minimum 10 million residents |
| Economic Role | Global financial and trade hub | Large local economy but may lack global influence |
| Cultural Influence | Global cultural impact through media, arts, and education | Primarily regional cultural significance |
| Examples | New York, London, Tokyo | Shanghai, Mumbai, Lagos |
| Infrastructure | Advanced global transportation and communication networks | Rapidly developing infrastructure, often strained by population growth |
Introduction to Global Cities and Megacities
Global cities are major urban centers that play a crucial role in the global economy due to their influence in finance, culture, and politics, often serving as hubs for international trade and multinational corporations. Megacities, defined by populations exceeding 10 million, emphasize scale and density rather than economic power or global influence, commonly facing challenges such as infrastructure strain and urban sprawl. Both concepts highlight different dimensions of urbanization, with global cities emphasizing connectivity and economic dominance, while megacities focus on demographic size and rapid growth.
Defining Global Cities: Characteristics and Examples
Global cities serve as pivotal nodes in the global economic network, characterized by advanced infrastructure, financial markets, and a high concentration of multinational corporations. Key examples include New York, London, and Tokyo, each exhibiting cultural influence, political power, and connectivity that extend beyond national borders. Unlike megacities, which are defined primarily by population size exceeding 10 million, global cities emphasize economic integration and global impact.
Understanding Megacities: Features and Growth
Megacities are urban areas with populations exceeding 10 million, characterized by rapid growth, infrastructural challenges, and diverse economies. Unlike global cities that serve as centers of worldwide finance, culture, and politics, megacities primarily demonstrate intense demographic expansion and urban sprawl. Understanding megacities involves analyzing their social dynamics, resource management, and environmental impacts caused by accelerated urbanization.
Economic Influence: Global Cities vs Megacities
Global cities such as New York, London, and Tokyo exert immense economic influence through their roles as financial hubs, hosting major stock exchanges, multinational corporations, and international organizations that shape global markets. Megacities like Mumbai, Sao Paulo, and Cairo primarily drive large-scale domestic economies, characterized by vast populations and rapid urbanization but have less direct impact on global economic policies. The economic power of global cities lies in their connectivity and innovation ecosystems, whereas megacities contribute through extensive labor markets and growing consumer bases.
Urban Infrastructure and Connectivity
Global cities feature highly developed urban infrastructure with advanced transportation networks, including international airports, extensive public transit systems, and integrated communication technologies that facilitate global business and cultural exchange. Megacities, characterized by populations exceeding 10 million, often struggle with infrastructure challenges such as overcrowded transit systems, inadequate road networks, and insufficient utility services, impacting connectivity and quality of life. Investments in smart infrastructure and sustainable urban planning are crucial for both city types to enhance mobility, reduce congestion, and support economic growth.
Cultural Impact and Diversity
Global cities, such as New York and London, serve as cultural hubs by attracting diverse populations, fostering innovation, and influencing worldwide arts, fashion, and media trends. Megacities, characterized by populations exceeding 10 million, like Mumbai and Tokyo, exhibit immense cultural diversity but often face challenges in integrating multicultural communities cohesively. The cultural impact of global cities is marked by their role in shaping global cultural flows, whereas megacities primarily reflect vast demographic heterogeneity and localized cultural expressions.
Governance and International Relations
Global cities like New York and London wield significant influence in international relations through robust governance frameworks that facilitate economic diplomacy and transnational cooperation. Megacities, defined primarily by population size such as Mumbai or Lagos, often face governance challenges including infrastructure strain and limited political autonomy, which impact their ability to engage effectively on a global stage. The governance capacity of global cities supports strategic partnerships and policy innovation, positioning them as pivotal nodes in global networks compared to megacities where internal governance complexities may hinder such roles.
Challenges: Sustainability and Urban Planning
Global cities and megacities face significant challenges in sustainability and urban planning due to their rapidly increasing populations and economic activities. Limited green spaces, inefficient public transportation systems, and high energy consumption contribute to environmental degradation and strain on infrastructure in both city types. Implementing integrated urban planning strategies and investing in sustainable technologies are critical for managing pollution, waste, and resource allocation effectively.
Case Studies: Notable Global Cities and Megacities
Tokyo exemplifies a megacity with a population exceeding 37 million, showcasing vast urban sprawl and complex infrastructure challenges. London, as a notable global city, excels in international finance, culture, and political influence, serving as a major economic hub. Mumbai represents a megacity facing rapid population growth and significant socio-economic disparities, while New York City combines characteristics of both, balancing global connectivity with diverse urban dynamics.
Future Trends: Urbanization and Global Impact
Future trends in urbanization indicate megacities will expand rapidly, with populations surpassing 10 million, driving significant infrastructure demands and environmental challenges. Global cities will evolve as strategic hubs of finance, technology, and cultural influence, shaping international economic networks and innovation ecosystems. The interplay between megacity growth and global city functions will redefine urban governance, sustainability efforts, and global interconnectedness in the coming decades.
Global city Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com