A primate city dominates a country's urban hierarchy by being significantly larger and more influential than any other city in the nation. This city often serves as the cultural, economic, and political hub, concentrating resources and opportunities that shape national development. Discover how primate cities impact your country's growth and urban planning in the following article.
Table of Comparison
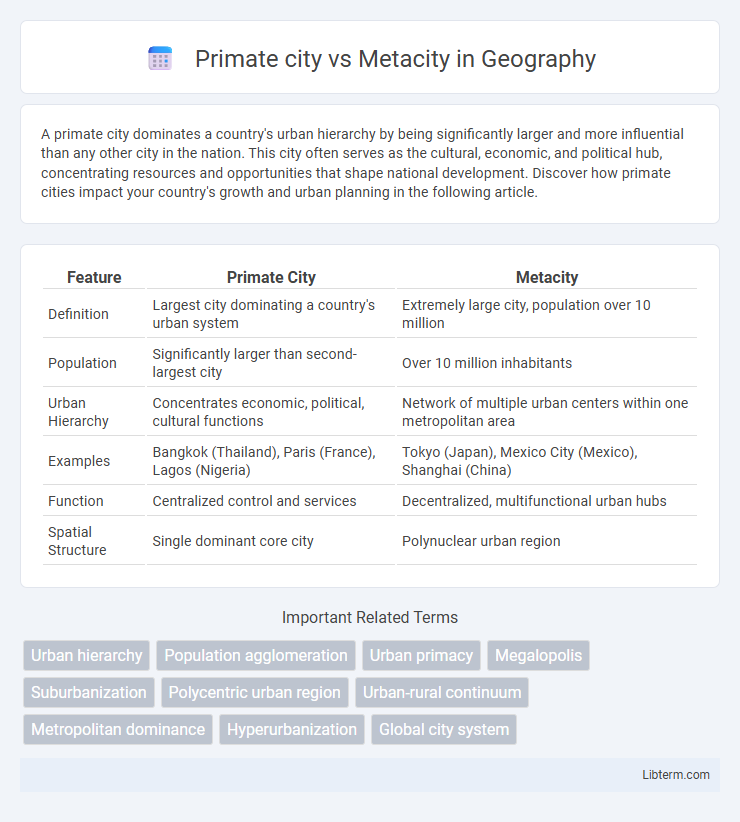
| Feature | Primate City | Metacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Largest city dominating a country's urban system | Extremely large city, population over 10 million |
| Population | Significantly larger than second-largest city | Over 10 million inhabitants |
| Urban Hierarchy | Concentrates economic, political, cultural functions | Network of multiple urban centers within one metropolitan area |
| Examples | Bangkok (Thailand), Paris (France), Lagos (Nigeria) | Tokyo (Japan), Mexico City (Mexico), Shanghai (China) |
| Function | Centralized control and services | Decentralized, multifunctional urban hubs |
| Spatial Structure | Single dominant core city | Polynuclear urban region |
Introduction to Urban Hierarchies
Primate cities dominate a country's urban hierarchy by significantly surpassing other cities in population and economic influence, often centralizing political, cultural, and financial functions. In contrast, metacities represent extensive, multi-nodal urban regions with populations exceeding 20 million, characterized by integrated economic activities and infrastructure across several large cities or urban zones. Understanding these distinctions helps in analyzing spatial organization, resource distribution, and urban planning challenges within national and global urban systems.
Defining Primate Cities
A primate city is a country's largest urban center, significantly exceeding the size and economic influence of other cities within the same nation, often dominating national culture, politics, and commerce. Unlike a metacity, which refers to a vast metropolitan area with multiple interconnected cities and extensive infrastructure, a primate city concentrates population and resources disproportionately in a single urban hub. Examples include Bangkok in Thailand and Paris in France, where the primate city shapes the country's demographic and economic landscape.
Understanding Metacities
Metacities are vast urban areas with populations exceeding 20 million inhabitants, characterized by complex infrastructures and diverse economic activities, unlike primate cities which dominate a country's urban hierarchy with a single leading city. Understanding metacities involves analyzing their polycentric structures, where multiple urban centers coexist, offering decentralized governance, varied cultural landscapes, and extensive connectivity. These sprawling regions pose unique challenges in urban planning, transportation, and sustainability, requiring integrated strategies to manage rapid growth and resource demands effectively.
Key Characteristics of Primate Cities
Primate cities exhibit a dominant size and influence compared to other cities within the same country, often housing a disproportionate proportion of the national population and economic activities. These cities serve as the political, cultural, and economic hubs, concentrating resources, infrastructure, and services that overshadow secondary urban centers. In contrast to metacities, which emphasize vast urban sprawl and global connectivity, primate cities are characterized by their centralized primacy and pivotal role in national identity and governance.
Distinctive Features of Metacities
Metacities exhibit vast population sizes exceeding 20 million inhabitants and possess extensive urban sprawl that integrates multiple metropolitan areas into one continuous urban region. They are characterized by complex socio-economic networks, diversified industries, and advanced infrastructure supporting multimodal transportation systems and high-density living. Unlike primate cities, which dominate a country's urban hierarchy, metacities function as polycentric hubs with multiple central business districts and cultural centers, fostering innovation and global connectivity.
Historical Development Patterns
Primate cities, such as Bangkok or Paris, historically emerged as dominant urban centers due to centralized political power, colonial legacies, and economic activities concentrating population and resources. Metacities, like Tokyo or New York, developed through extensive urban sprawl and multi-nodal growth patterns fueled by globalization, technological advances, and diversified economic sectors. These differences in historical development highlight how primate cities reflect concentrated urban primacy while metacities embody complex regional integration and decentralized urbanization.
Economic and Social Impacts
Primate cities often dominate national economies by concentrating political power, financial institutions, and cultural resources, leading to significant regional disparities and urban-rural inequality. In contrast, metacities, characterized by multiple interconnected economic hubs, promote diversified industrial growth, reducing congestion and fostering balanced social development across metropolitan regions. The economic impact of primate cities includes high productivity but also challenges like housing shortages and infrastructure strain, whereas metacities support sustainable urban expansion and enhanced social cohesion through distributed governance and service provision.
Challenges Facing Primate Cities
Primate cities often face challenges such as overcrowding, traffic congestion, and inadequate infrastructure due to their disproportionate concentration of population and economic activities. These cities struggle with providing sufficient housing, healthcare, and sanitation services, leading to increased urban poverty and social inequality. In contrast, metacities, characterized by multiple interconnected urban centers, tend to distribute growth and resources more evenly, reducing the severity of these urban problems.
Urban Planning in Metacities
Metacities, characterized by populations exceeding 20 million, demand innovative urban planning strategies to manage complex infrastructure, environmental sustainability, and social equity challenges. Unlike primate cities, which dominate national urban hierarchies with centralized services and governance, metacities require decentralized, multi-nodal development to optimize resource distribution and reduce congestion. Effective urban planning in metacities integrates smart technologies, green spaces, and transit-oriented development to enhance livability and resilience amid rapid population growth.
Future Trends in Global Urbanization
Primate cities, characterized by their dominant population and economic activities, often face challenges of congestion and resource strain, prompting urban planners to explore the rise of metacities--vast interconnected urban regions exceeding 20 million inhabitants. Future trends in global urbanization suggest a shift towards metacity development as technological integration, sustainable infrastructure, and decentralized governance become essential to manage sprawling urban complexity. Innovations in smart city technology and transit-oriented development are expected to reshape these megaregions, balancing growth pressures and enhancing livability across diversified urban landscapes.
Primate city Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com