Rectangular drainage systems efficiently channel water away from surfaces to prevent flooding and erosion, improving soil stability and infrastructure longevity. Their shape allows for easy integration into urban and agricultural environments, optimizing water flow management. Explore the rest of the article to learn how rectangular drainage solutions can safeguard your property and enhance water management strategies.
Table of Comparison
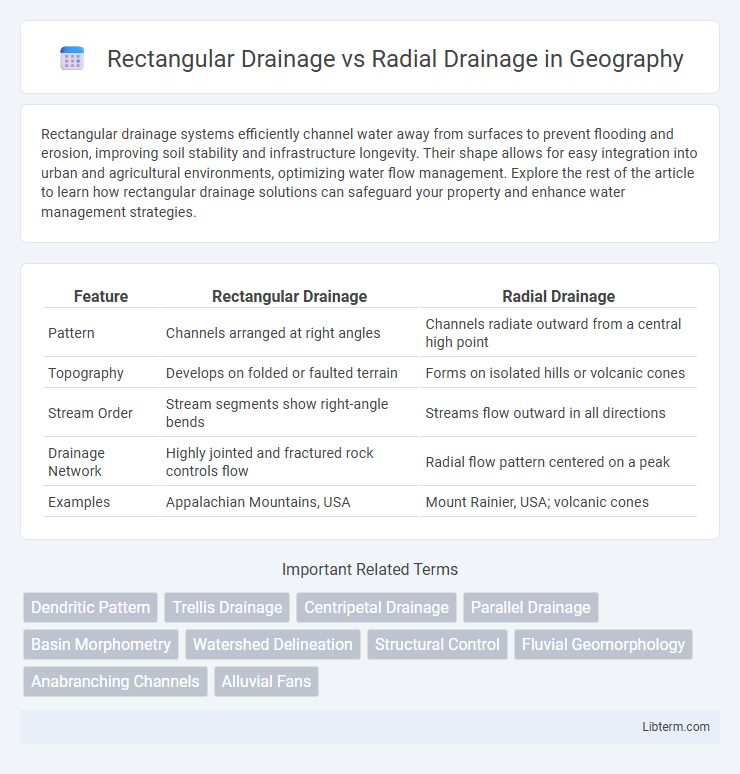
| Feature | Rectangular Drainage | Radial Drainage |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Channels arranged at right angles | Channels radiate outward from a central high point |
| Topography | Develops on folded or faulted terrain | Forms on isolated hills or volcanic cones |
| Stream Order | Stream segments show right-angle bends | Streams flow outward in all directions |
| Drainage Network | Highly jointed and fractured rock controls flow | Radial flow pattern centered on a peak |
| Examples | Appalachian Mountains, USA | Mount Rainier, USA; volcanic cones |
Introduction to Drainage Systems
Drainage systems are essential for managing surface water runoff, preventing soil erosion, and maintaining land stability. Rectangular drainage systems feature channels arranged in a grid-like pattern, enhancing water collection efficiency in urban areas with uniform slope and soil type. Radial drainage systems consist of channels radiating outward from a central high point, commonly found in volcanic or dome-shaped terrains where water flows outward in all directions.
Overview of Rectangular Drainage
Rectangular drainage systems feature channels arranged at right angles, creating a grid-like pattern that efficiently manages surface water flow in areas with uniform slope and soil type. These systems optimize water removal by directing runoff through a network of primary and secondary streams intersecting at approximately 90 degrees. Rectangular drainage is particularly effective in reducing soil erosion and enhancing land usability in agricultural and urban planning contexts.
Overview of Radial Drainage
Radial drainage systems feature streams radiating outward from a central high point, such as a volcano or dome, and are characterized by their circular drainage pattern that efficiently directs water away in multiple directions. This drainage type contrasts with rectangular drainage, which is dominated by right-angle junctions and follows faulted or jointed rock patterns. Radial drainage plays a crucial role in managing runoff in volcanic terrains and dome-shaped uplands by promoting effective water dispersion.
Key Differences Between Rectangular and Radial Drainage
Rectangular drainage features streams that intersect at right angles, creating a grid-like pattern often influenced by jointed or faulted rock structures, whereas radial drainage consists of streams radiating outward from a central high point like a volcano or dome. The rectangular pattern emphasizes structural control with dominant fractures directing water flow, while radial drainage highlights topographic highs causing water to flow outward in multiple directions. These distinct patterns reflect underlying geological formations and influence watershed management and soil erosion processes in their respective terrains.
Advantages of Rectangular Drainage
Rectangular drainage systems offer efficient water conveyance in urban areas with grid-patterned street layouts, minimizing flooding risks by channeling runoff directly into sewer networks. This design facilitates easier maintenance and predictable flow patterns, enhancing urban flood management. The systematic alignment with streets supports infrastructure integration, reducing construction and operational costs compared to more irregular radial drainage systems.
Advantages of Radial Drainage
Radial drainage systems offer superior efficiency in areas with dome-shaped or conical surfaces by facilitating rapid water runoff from a central high point to peripheral outlets. This drainage pattern minimizes soil erosion and reduces waterlogging risks due to its outward flow design, enhancing land stability. Radial drainage also supports improved groundwater recharge and better management of surface water compared to rectangular drainage layouts typically suited for flat terrains.
Applications and Suitability
Rectangular drainage systems are ideal for urban areas with grid-like street patterns, providing efficient water removal and preventing flooding in flat terrains. Radial drainage is suitable for circular or dome-shaped landscapes, such as volcanic regions and hillsides, efficiently channeling runoff from a central high point outward. Choosing between these systems depends on topography, urban design, and the need for effective water management in specific environments.
Installation Process Comparison
The installation process for rectangular drainage systems involves creating a grid pattern of perpendicular channels, requiring precise excavation and alignment to ensure effective water flow management. Radial drainage installation requires constructing channels that radiate outward from a central point, demanding careful planning to accommodate the topography and facilitate converging water flow. Rectangular drainage typically requires more extensive trenching, while radial drainage benefits from natural slopes but involves more complex grading for proper functioning.
Maintenance and Cost Analysis
Rectangular drainage systems require frequent maintenance to prevent sediment buildup in their straight channels, leading to higher operational costs over time compared to radial drainage layouts. Radial drainage systems, characterized by their spoke-like design directing water toward a central point, tend to offer reduced maintenance needs and improved efficiency in water flow management, resulting in lower long-term expenses. Initial installation costs for radial drainage are generally higher due to complex design and materials, but these costs are often offset by decreased maintenance requirements and enhanced durability.
Choosing the Right Drainage System
Choosing the right drainage system depends on the terrain and water flow patterns; rectangular drainage suits areas with uniform slopes and predictable water channels, providing efficient water removal through interconnected right-angled streams. Radial drainage is ideal for volcanic cones or domed landforms, where water flows outward from a central high point, effectively managing runoff in circular patterns. Assessing topography and hydrological behavior ensures optimal selection, minimizing erosion and maximizing drainage efficiency.
Rectangular Drainage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com