Playa offers sun-soaked beaches perfect for relaxation and water sports, catering to both adventure seekers and those longing for tranquility. Vibrant local culture and delicious cuisine enhance your experience, making every moment memorable. Discover how Playa can transform your next vacation by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
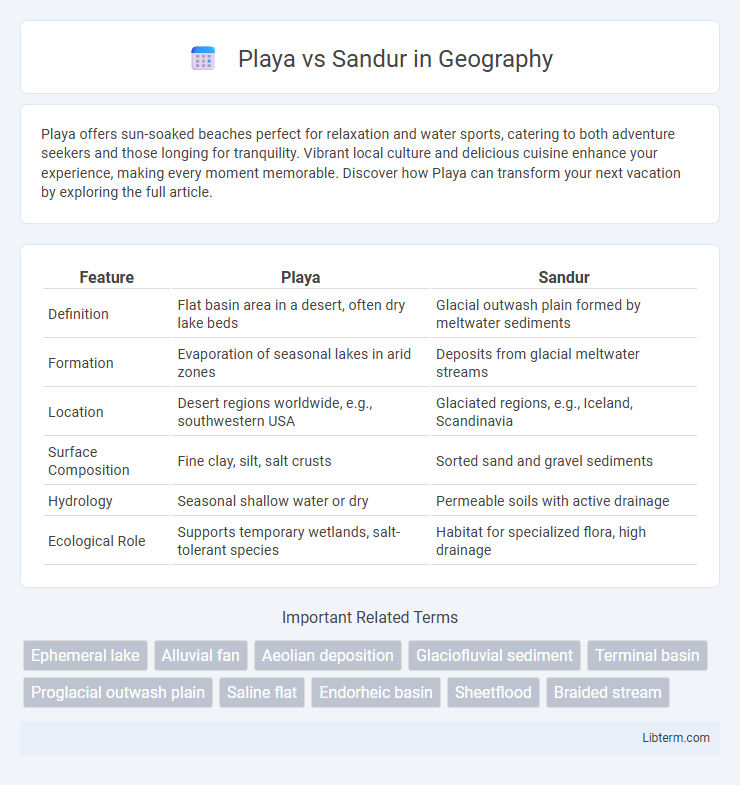
| Feature | Playa | Sandur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flat basin area in a desert, often dry lake beds | Glacial outwash plain formed by meltwater sediments |
| Formation | Evaporation of seasonal lakes in arid zones | Deposits from glacial meltwater streams |
| Location | Desert regions worldwide, e.g., southwestern USA | Glaciated regions, e.g., Iceland, Scandinavia |
| Surface Composition | Fine clay, silt, salt crusts | Sorted sand and gravel sediments |
| Hydrology | Seasonal shallow water or dry | Permeable soils with active drainage |
| Ecological Role | Supports temporary wetlands, salt-tolerant species | Habitat for specialized flora, high drainage |
Understanding Playa and Sandur: Key Definitions
A playa is a dry lake bed found in arid regions, characterized by flat, clay-rich surfaces that occasionally flood. A sandur is a glacial outwash plain formed by sediments deposited from meltwater streams, typically consisting of sand and gravel. Both landforms differ in origin and composition but play significant roles in sedimentary geology and landscape formation.
Geological Formation Processes: Playa vs Sandur
Playa formations develop in arid environments where intermittent lakes evaporate, leaving behind fine-grained sediments and evaporite minerals that accumulate in basin depressions. Sandurs form from glacial meltwater outwash, where braided river systems deposit well-sorted sands and gravels across outwash plains during deglaciation. The key geological difference lies in playas being closed hydrological basins dominated by evaporation, whereas sandurs are open depositional systems shaped by fluvial processes linked to glacial melting.
Environmental Conditions Influencing Playa and Sandur
Environmental conditions influencing playas include arid climates with intermittent water accumulation and high evaporation rates, leading to saline and alkaline soil characteristics. Sandurs form in glacial outwash plains where meltwater streams deposit sorted sediments, creating permeable, coarse-grained landscapes. Both landforms reflect distinct hydrological and sedimentary processes driven by regional climate and geological activity.
Physical Characteristics and Features
A playa is a flat-bottomed desert basin that occasionally fills with water, characterized by fine sediments like silt and clay, creating a hard, cracked surface when dry. Sandurs are broad, gently sloping outwash plains formed by glacial meltwater, composed primarily of sorted sand and gravel deposits. Unlike playas, sandurs exhibit well-developed drainage channels and consist of coarser sediment, reflecting their origin from glacial meltwater flows.
Global Distribution: Where Playas and Sandurs Occur
Playas predominantly occur in arid and semi-arid regions such as the southwestern United States, parts of Australia, and the Middle East, forming in desert basins where evaporation exceeds precipitation. Sandurs, also known as outwash plains, are typically found at the terminus of glaciers in polar and alpine regions, including Iceland, Alaska, and the Himalayas, where glacial meltwater deposits sediments. The global distribution of playas is closely tied to closed basin desert environments, while sandurs are linked to glaciated landscapes shaped by seasonal meltwater flows.
Sediment Composition and Texture
Playa sediments primarily consist of fine-grained clays and silts with occasional evaporite minerals, reflecting their deposition in arid, ephemeral lake beds. Sandur sediments are dominated by well-sorted sands and gravels derived from glacial meltwater streams, characterized by coarser textures and higher sorting due to consistent fluvial processes. The contrast in sediment composition and texture between playas and sandurs highlights their distinct depositional environments, with playas favoring fine, clay-rich deposits and sandurs accumulating coarser, sorted sediments.
Hydrological Dynamics: Water and Sediment Flow
Playa lakes exhibit episodic hydrological dynamics characterized by intermittent water accumulation and evaporation, leading to distinct sedimentation patterns dominated by fine clays and evaporites. In contrast, sandurs feature continuous water and sediment flow from glacial meltwater, depositing well-sorted sands and gravels in braided stream networks. The hydrological regime in playas results in closed basins with limited outflow, whereas sandurs represent active depositional environments with dynamic sediment transport and reworking.
Ecological Significance and Biodiversity
Playas are ephemeral, flat-bottomed basins in arid regions that collect water temporarily, supporting specialized flora and fauna adapted to saline or alkaline conditions. Sandurs, formed by glacial outwash, consist of extensive sand and gravel deposits that create unique habitats characterized by diverse plant communities and specialized animal species thriving in well-drained, nutrient-poor soils. Both ecosystems contribute significantly to regional biodiversity by providing niches for endemic and migratory species, playing crucial roles in water filtration, soil formation, and ecological succession.
Human Impact and Land Use Considerations
Human impact on playas often includes agriculture runoff and urban development, leading to changes in water quality and habitat disruption. Sandurs, formed from glacial outwash plains, face land use pressures such as mining and infrastructure expansion, which can destabilize sediment layers and alter hydrological patterns. Sustainable management requires balancing groundwater extraction and land development to preserve ecological functions of both playas and sandurs.
Comparing Playa and Sandur: Similarities and Differences
Playa and sandur are both sedimentary depositional landforms formed by glacial and fluvial processes, with playas typically found in arid basins where water evaporates leaving fine sediments, while sandurs are outwash plains composed primarily of sand and gravel deposited by meltwater streams from glaciers. Both landforms exhibit stratified sediment layers, but playas are usually flat, saline, and clay-rich, contrasting with the coarser, well-sorted sediments of sandurs that support braided river systems. Ecologically, playas often host unique salt-tolerant vegetation, whereas sandurs provide habitats for diverse riparian species due to their dynamic hydrology and coarse sediment textures.
Playa Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com