Crop rotation enhances soil fertility by alternating different crops, reducing nutrient depletion and minimizing pest buildup. This sustainable farming practice improves yield quality while promoting long-term soil health. Explore the rest of the article to understand how crop rotation can benefit your agricultural practices.
Table of Comparison
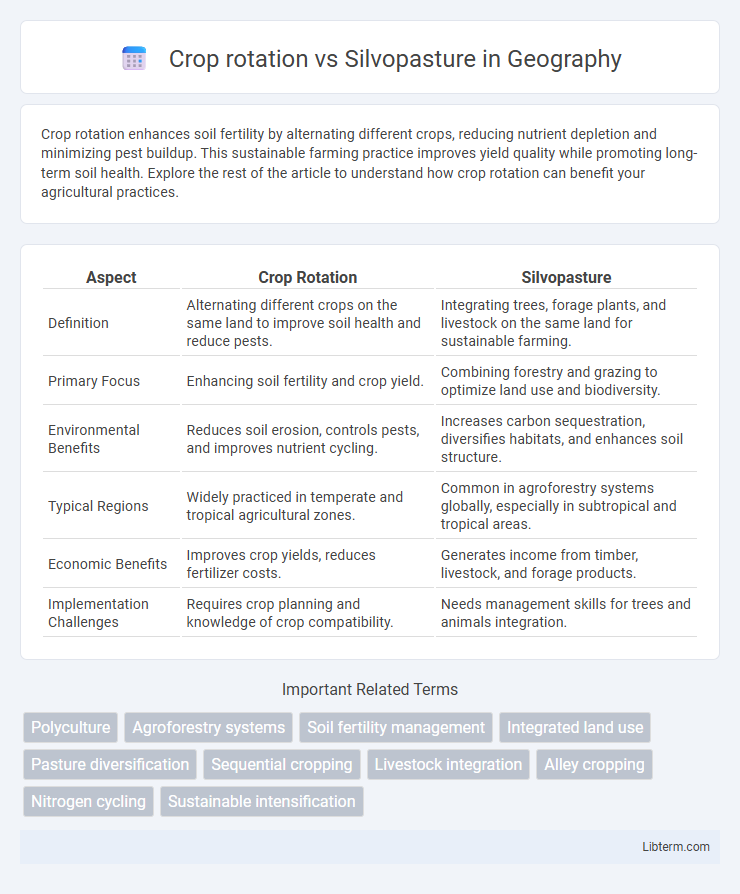
| Aspect | Crop Rotation | Silvopasture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alternating different crops on the same land to improve soil health and reduce pests. | Integrating trees, forage plants, and livestock on the same land for sustainable farming. |
| Primary Focus | Enhancing soil fertility and crop yield. | Combining forestry and grazing to optimize land use and biodiversity. |
| Environmental Benefits | Reduces soil erosion, controls pests, and improves nutrient cycling. | Increases carbon sequestration, diversifies habitats, and enhances soil structure. |
| Typical Regions | Widely practiced in temperate and tropical agricultural zones. | Common in agroforestry systems globally, especially in subtropical and tropical areas. |
| Economic Benefits | Improves crop yields, reduces fertilizer costs. | Generates income from timber, livestock, and forage products. |
| Implementation Challenges | Requires crop planning and knowledge of crop compatibility. | Needs management skills for trees and animals integration. |
Introduction to Crop Rotation and Silvopasture
Crop rotation is an agricultural practice that involves growing different types of crops sequentially on the same land to improve soil health, reduce pests, and enhance crop yields by diversifying nutrient demands. Silvopasture integrates trees, forage plants, and livestock simultaneously on the same land, promoting biodiversity, improving land use efficiency, and supporting sustainable livestock production. Both systems enhance ecosystem services but differ in their approach to land management and resource optimization.
Defining Crop Rotation: Principles and Practices
Crop rotation is an agricultural practice involving the sequential planting of different crops on the same land to enhance soil fertility, control pests, and reduce disease risk. Its core principles include diversifying crop types, adjusting planting sequences, and managing nutrient cycles to optimize soil health and productivity. Implementing systematic crop rotation supports sustainable agriculture by maintaining ecosystem balance and improving long-term yield stability.
Understanding Silvopasture: Key Components
Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock on the same land, enhancing biodiversity and improving soil health through natural nutrient cycling. Key components include selecting compatible tree species, managing rotational grazing to prevent overgrazing, and maintaining forage quality to support livestock nutrition. This agroforestry practice contrasts with crop rotation by combining perennial and animal agriculture, promoting sustainable land use and long-term productivity.
Environmental Benefits: Crop Rotation vs Silvopasture
Crop rotation enhances soil fertility by alternating crops, reducing pest and disease cycles, and minimizing chemical fertilizer use, which improves soil health and biodiversity. Silvopasture integrates trees with pastureland, sequestering carbon, reducing soil erosion, and promoting wildlife habitats, thereby enhancing ecosystem resilience. Both practices contribute significantly to sustainable agriculture by improving soil structure and increasing carbon storage, but silvopasture provides added benefits of tree canopy and habitat diversification.
Soil Health and Fertility Comparison
Crop rotation improves soil health by alternating nutrient-demanding crops with nitrogen-fixing plants, reducing pest buildup and enhancing soil organic matter. Silvopasture integrates trees with pasture, promoting deep root systems that increase soil carbon sequestration and microbial diversity, stabilizing soil structure and moisture retention. Compared to crop rotation, silvopasture offers longer-term fertility benefits through continuous organic inputs from tree litter and pasture biomass, resulting in sustained nutrient cycling and enhanced ecosystem resilience.
Impact on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Crop rotation enhances soil health and pest management by diversifying plant species over time, supporting microbial diversity and nutrient cycling crucial for sustainable agriculture. Silvopasture integrates trees, pasture, and livestock, creating complex habitats that increase species richness and provide ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, erosion control, and improved water regulation. While crop rotation primarily benefits below-ground biodiversity and soil functions, silvopasture offers a multifaceted approach, boosting above-ground biodiversity and long-term ecosystem resilience.
Economic Considerations and Farmer Profitability
Crop rotation enhances soil fertility and reduces pest management costs, boosting long-term agricultural yields and profitability through sustainable input use. Silvopasture integrates trees with pasture, providing diversified revenue streams from timber, forage, and livestock, often increasing land-use efficiency and farmer income stability. Economic evaluations show silvopasture can yield higher returns per acre, but requires greater initial investment and management complexity compared to conventional crop rotation.
Practical Challenges and Limitations
Crop rotation faces practical challenges including pest and disease management complexities, soil nutrient variability, and the need for precise timing to maximize yield benefits. Silvopasture requires significant initial investment, ongoing management of tree-crop-animal interactions, and potential competition for light and water resources that can limit productivity. Both systems demand specialized knowledge and labor intensity, posing barriers for widespread adoption among small-scale farmers.
Choosing the Right System: Factors to Consider
Selecting between crop rotation and silvopasture depends on land use goals, soil health, and climate adaptability. Crop rotation enhances soil fertility and controls pests by alternating plant species seasonally, ideal for annual crop production. Silvopasture integrates trees with pastureland, promoting biodiversity and providing multiple outputs like timber, forage, and livestock, suitable for long-term sustainability and diverse ecosystems.
Future Trends in Sustainable Agriculture
Future trends in sustainable agriculture emphasize integrating crop rotation and silvopasture to enhance soil health and biodiversity. Crop rotation advances nutrient cycling and pest management by alternating plant species, while silvopasture combines trees, forage, and livestock to increase carbon sequestration and resilience to climate change. Emerging technologies in remote sensing and data analytics optimize both practices for improved productivity and ecosystem services.
Crop rotation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com