Contour plowing follows the natural curves of the land to reduce soil erosion and enhance water absorption. This farming practice helps maintain soil fertility and prevents runoff that can damage crops and nearby ecosystems. Explore the rest of the article to discover how contour plowing can benefit your agricultural efforts.
Table of Comparison
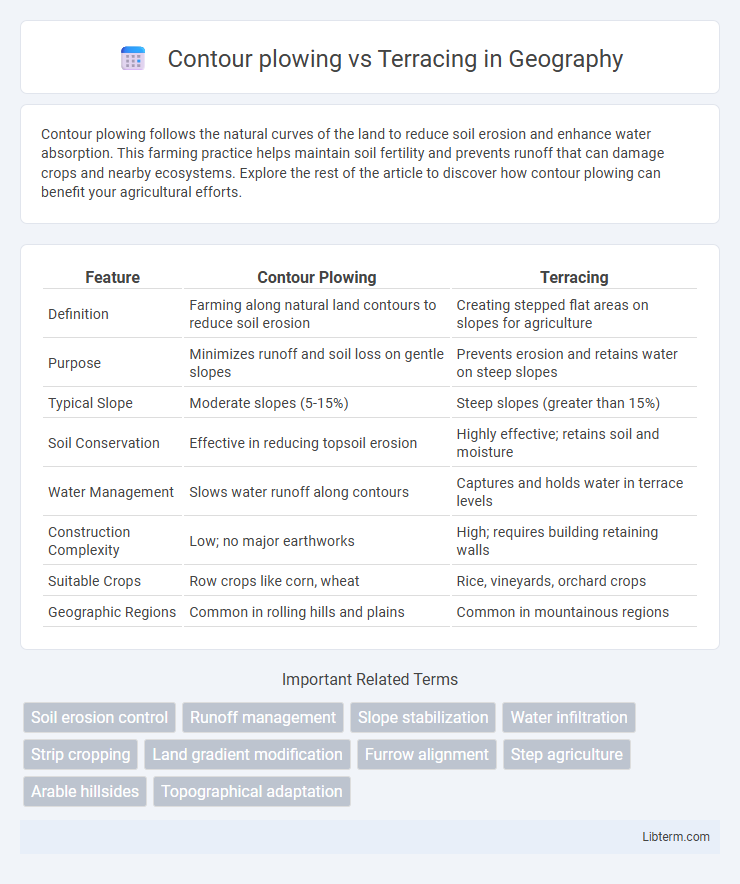
| Feature | Contour Plowing | Terracing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Farming along natural land contours to reduce soil erosion | Creating stepped flat areas on slopes for agriculture |
| Purpose | Minimizes runoff and soil loss on gentle slopes | Prevents erosion and retains water on steep slopes |
| Typical Slope | Moderate slopes (5-15%) | Steep slopes (greater than 15%) |
| Soil Conservation | Effective in reducing topsoil erosion | Highly effective; retains soil and moisture |
| Water Management | Slows water runoff along contours | Captures and holds water in terrace levels |
| Construction Complexity | Low; no major earthworks | High; requires building retaining walls |
| Suitable Crops | Row crops like corn, wheat | Rice, vineyards, orchard crops |
| Geographic Regions | Common in rolling hills and plains | Common in mountainous regions |
Introduction to Contour Plowing and Terracing
Contour plowing involves tilling soil along the natural contours of the land to reduce soil erosion and enhance water retention in sloped fields. Terracing creates stepped levels on steep terrain, transforming slopes into a series of flat platforms to control runoff and prevent soil degradation. Both techniques are essential soil conservation methods used in agriculture to maintain soil fertility and sustain crop production on hilly landscapes.
Understanding Contour Plowing
Contour plowing involves tilling the soil following the natural contours of the land, reducing soil erosion by creating natural barriers to water flow. This technique slows runoff and increases water infiltration, which enhances soil moisture retention and promotes healthier crop growth. Compared to terracing, contour plowing is less labor-intensive and suitable for gently sloping fields, preserving soil structure while preventing nutrient loss.
Exploring the Concept of Terracing
Terracing involves creating stepped levels on steep slopes to reduce soil erosion and manage water runoff effectively, making it ideal for hilly or mountainous terrain. Unlike contour plowing, which follows natural land contours to slow water flow, terracing transforms the landscape into flat areas, maximizing arable land use and improving crop production. This method supports sustainable agriculture by conserving soil nutrients and enhancing water retention in challenging environments.
Key Differences Between Contour Plowing and Terracing
Contour plowing involves tilling along the natural contours of the land to reduce soil erosion and water runoff, primarily on gentle slopes. Terracing transforms steep slopes into a series of flat platforms or steps, significantly minimizing erosion and improving water retention for agriculture. While contour plowing is suitable for moderate slopes, terracing is more effective on steep terrain, offering greater control over soil conservation and crop productivity.
Benefits of Contour Plowing for Soil Conservation
Contour plowing significantly reduces soil erosion by following the natural contours of the land, which slows water runoff and increases water infiltration. This method helps maintain soil fertility by preventing nutrient loss and preserving topsoil structure, thereby enhancing crop yields over time. Compared to terracing, contour plowing requires less labor and investment, making it an efficient and cost-effective soil conservation technique for gently sloping farmlands.
Advantages of Terracing in Erosion Control
Terracing significantly reduces soil erosion by creating flat platforms that slow water runoff and increase water infiltration, preventing the loss of fertile topsoil. This method is especially effective on steep slopes where contour plowing may not adequately prevent soil degradation. Terraces also enhance crop production by improving moisture retention and minimizing nutrient leaching.
Limitations and Challenges of Contour Plowing
Contour plowing reduces soil erosion by following the natural landscape contours but faces limitations such as reduced effectiveness on steep slopes and vulnerability to heavy rainfall causing water runoff. It requires precise equipment and skilled labor to maintain contour lines, and improper plowing can lead to soil degradation and crop damage. Compared to terracing, contour plowing provides less water retention and soil stabilization, making it less suitable for areas with intense erosion risk.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Terracing
Terracing, while effective for erosion control on steep slopes, presents significant drawbacks including high initial construction costs and labor intensity, making it less accessible for small-scale farmers. The maintenance requirements are substantial, as terraces can degrade rapidly without proper upkeep, leading to increased soil erosion and reduced agricultural productivity. Additionally, terracing may disrupt natural water flow and soil profiles, potentially causing waterlogging or reduced soil fertility over time.
Choosing the Right Technique: Factors to Consider
Choosing between contour plowing and terracing depends on factors such as slope gradient, soil type, and erosion risk. Contour plowing suits gentle slopes by reducing runoff and soil loss through plowing along elevation contours, while terracing is ideal for steep slopes, creating flat platforms that significantly prevent erosion and maximize water infiltration. Soil moisture retention, crop type, and available resources also influence the decision to ensure optimal land conservation and agricultural productivity.
Sustainable Farming: Integrating Contour Plowing and Terracing
Contour plowing and terracing are sustainable farming techniques designed to reduce soil erosion and enhance water retention on sloped land. Contour plowing involves tilling along the natural contours of the land, slowing runoff and preserving topsoil, while terracing creates stepped levels that physically prevent soil displacement and improve water infiltration. Combining these practices optimizes land use on hilly terrain, promotes soil fertility, and supports long-term agricultural productivity.
Contour plowing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com