Demography analyzes population structures to understand trends in birth rates, mortality, migration, and aging, which directly impact social and economic policies. Accurate demographic data guides governments and businesses in planning for future needs such as healthcare, education, and workforce development. Discover how key demographic factors shape your community and influence global challenges by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
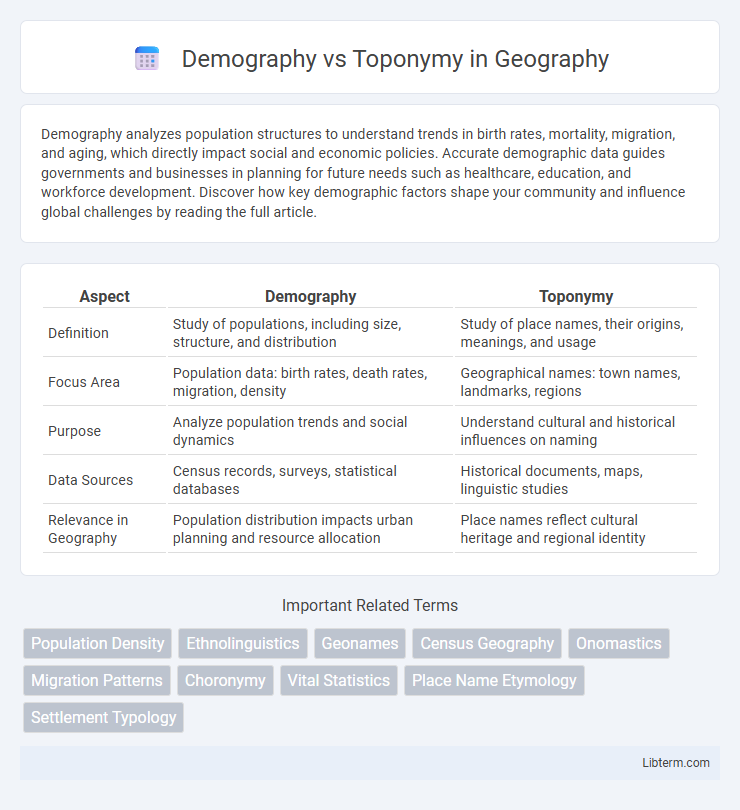
| Aspect | Demography | Toponymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of populations, including size, structure, and distribution | Study of place names, their origins, meanings, and usage |
| Focus Area | Population data: birth rates, death rates, migration, density | Geographical names: town names, landmarks, regions |
| Purpose | Analyze population trends and social dynamics | Understand cultural and historical influences on naming |
| Data Sources | Census records, surveys, statistical databases | Historical documents, maps, linguistic studies |
| Relevance in Geography | Population distribution impacts urban planning and resource allocation | Place names reflect cultural heritage and regional identity |
Introduction to Demography and Toponymy
Demography studies population size, structure, distribution, and changes over time through birth rates, death rates, migration, and aging patterns. Toponymy analyzes the origin, meaning, and use of place names, reflecting cultural, historical, and geographical influences on naming conventions. Both fields intersect by revealing how human populations shape and are shaped by their geographical environments.
Defining Demography: Study of Populations
Demography is the statistical study of human populations, focusing on size, structure, distribution, and changes over time due to births, deaths, migration, and aging. It analyzes population dynamics to inform public policy, urban planning, and social services. In contrast, toponymy studies place names, exploring their origins, meanings, and cultural significance without addressing population metrics.
Understanding Toponymy: Study of Place Names
Toponymy, the study of place names, explores the origins, meanings, and linguistic patterns of geographical names, providing insights into cultural, historical, and environmental contexts. Unlike demography, which analyzes population structures and dynamics, toponymy focuses on how human societies assign identities to locations through language and tradition. Understanding toponymy enhances geographical literacy and preserves heritage by tracing settlement histories and cultural influences embedded in place names.
Key Differences Between Demography and Toponymy
Demography studies population characteristics such as size, distribution, density, and growth patterns, focusing on human communities and their statistical analysis. Toponymy examines the origin, meaning, and usage of place names, exploring linguistic, historical, and cultural aspects tied to geographical locations. While demography analyzes human populations quantitatively, toponymy investigates the qualitative significance of geographical nomenclature.
Importance of Demography in Modern Research
Demography provides critical insights into population dynamics, such as birth rates, mortality, migration, and age distribution, which are essential for urban planning, public health, and economic development. Unlike toponymy, which studies place names and their origins to understand cultural and historical geography, demography offers quantifiable data that directly influence policy-making and resource allocation. Modern research relies heavily on demographic statistics to predict trends, address social challenges, and implement targeted interventions across diverse communities.
The Role of Toponymy in Cultural Identity
Toponymy plays a crucial role in cultural identity by preserving historical narratives and reflecting the linguistic heritage of a community. Place names serve as living records of ancestral stories, migration patterns, and socio-political influences, deeply anchoring people to their local environment. Unlike demography, which focuses on population statistics and social dynamics, toponymy emphasizes the symbolic and cultural meanings embedded in geographic names that shape collective memory and identity.
Intersections Between Demography and Toponymy
Demography and toponymy intersect primarily through the study of population distribution and place names, revealing how human settlement patterns influence and are influenced by geographic nomenclature. Analyzing toponyms provides insights into migration trends, cultural heritage, and demographic changes, while demographic data helps explain the historical context behind place names. This intersection aids urban planners, geographers, and historians in understanding spatial dynamics and cultural identity evolution over time.
Methods and Tools in Demographic Analysis
Demographic analysis relies heavily on quantitative methods such as census data collection, population surveys, and statistical modeling to measure variables like birth rates, mortality, migration patterns, and age distribution. Tools including Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and demographic software like SPSS or R enable spatial visualization and advanced data analysis to identify population trends and forecast demographic changes. These methods contrast with toponymy, which primarily employs linguistic analysis and historical research to study the origin and meaning of place names rather than population dynamics.
Techniques for Toponymic Research
Toponymic research employs techniques such as historical cartography analysis, linguistic morphology, and geographic information systems (GIS) to decode place name origins and distributions. Researchers often use archival documents and oral histories to trace the evolution and cultural significance embedded in toponyms. Spatial analysis through GIS allows for mapping toponymic patterns, revealing correlations with demographic shifts and migration trends.
Future Trends in Demography and Toponymy
Future trends in demography indicate significant shifts influenced by urbanization, aging populations, and migration patterns, with population data increasingly integrated into geographic information systems (GIS) for predictive analysis. Toponymy will evolve through digital mapping technologies and crowdsourced data, enhancing the accuracy and cultural relevance of place names while addressing issues of standardization and geopolitical changes. The intersection of demographic data and toponymic research will enable more dynamic spatial analyses, supporting urban planning, heritage preservation, and linguistic diversity efforts.
Demography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com