Dolomite is a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, commonly used in construction, agriculture, and manufacturing due to its durability and chemical properties. Its ability to neutralize acidity in soil and improve the strength of concrete makes it a valuable material for various industries. Discover how dolomite can enhance your projects and applications by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
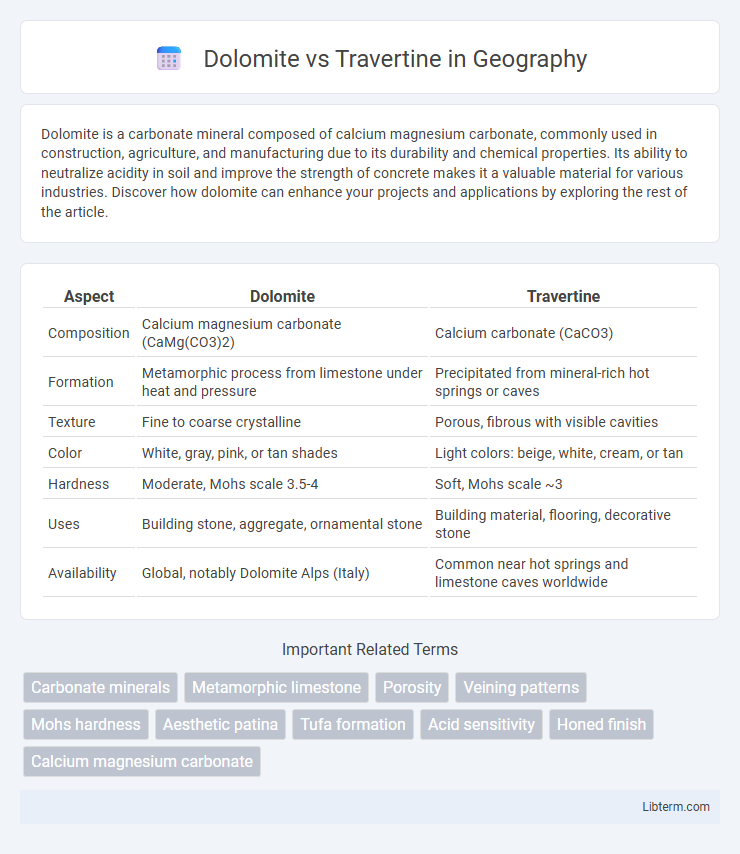
| Aspect | Dolomite | Travertine |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2) | Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) |
| Formation | Metamorphic process from limestone under heat and pressure | Precipitated from mineral-rich hot springs or caves |
| Texture | Fine to coarse crystalline | Porous, fibrous with visible cavities |
| Color | White, gray, pink, or tan shades | Light colors: beige, white, cream, or tan |
| Hardness | Moderate, Mohs scale 3.5-4 | Soft, Mohs scale ~3 |
| Uses | Building stone, aggregate, ornamental stone | Building material, flooring, decorative stone |
| Availability | Global, notably Dolomite Alps (Italy) | Common near hot springs and limestone caves worldwide |
Introduction to Dolomite and Travertine
Dolomite is a sedimentary carbonate rock composed primarily of the mineral dolomite, known for its durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for architectural and construction uses. Travertine, formed from mineral springs, is a type of limestone characterized by its porous texture and warm, natural earth tones, frequently used in flooring and decorative applications. Both stones are prized for their aesthetic appeal and versatility, but dolomite offers greater hardness while travertine provides a distinctive textured surface.
Geological Formation and Composition
Dolomite forms primarily through the chemical alteration of limestone by magnesium-rich fluids, resulting in a carbonate rock composed mainly of the mineral dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2). Travertine is a variety of limestone deposited by mineral springs, especially hot springs, characterized by its porous texture and mainly composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in the form of calcite or aragonite. Both stones differ in geological formation processes; dolomite undergoes diagenetic transformation, while travertine forms through rapid precipitation from carbonate-rich waters.
Physical Appearance and Color Variations
Dolomite features a granular texture with a crystalline structure that often appears white, gray, or light pink, exhibiting subtle veining and a smooth, matte finish. Travertine displays a porous surface with natural pitting and a range of warm earth tones such as beige, cream, tan, and honey, characterized by its distinctive banded patterns and natural holes. The color variations in dolomite tend to be more muted and uniform, while travertine offers richer hues and a textured, rustic look due to its porous composition.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Dolomite exhibits higher durability and hardness compared to travertine, making it more resistant to scratches and wear in high-traffic areas. With a Mohs hardness rating of around 3.5 to 4, dolomite surpasses travertine's rating of 3, indicating better performance under heavy use and abrasive conditions. Travertine's softer composition makes it prone to chipping and erosion, whereas dolomite provides greater longevity and structural integrity for flooring and countertops.
Common Applications in Architecture and Design
Dolomite is commonly used in flooring, wall cladding, and decorative facades due to its durability and fine grain, offering a sleek, modern aesthetic often preferred in commercial and residential projects. Travertine's porous texture and warm tones make it a popular choice for outdoor patios, pool surrounds, and bathroom surfaces, providing a natural, rustic appeal that enhances Mediterranean and classical architectural styles. Both materials serve functional and decorative purposes, but dolomite's hardness suits high-traffic areas while travertine excels in environments where aesthetic aging and natural weathering are desired.
Maintenance Requirements and Care
Dolomite exhibits high durability and low porosity, requiring minimal maintenance with occasional sealing to prevent staining and preserve its polished surface. Travertine, characterized by its porous structure, demands more frequent sealing and gentle cleaning with pH-neutral products to avoid etching and discoloration. Both natural stones benefit from prompt spill cleanup and avoid harsh chemicals to extend lifespan and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Cost and Affordability
Dolomite generally offers a higher cost compared to travertine due to its denser composition and durability, making it a long-term investment for flooring or countertops. Travertine tends to be more affordable and widely available, appealing to budget-conscious homeowners seeking natural stone with a classic appearance. When evaluating cost and affordability, travertine provides a cost-effective option without compromising on aesthetic appeal, whereas dolomite commands a premium price for enhanced strength and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dolomite and travertine differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability; dolomite, a carbonate mineral, typically requires more intensive mining processes that can disrupt ecosystems and increase carbon emissions. Travertine forms through natural springs and can be harvested with less environmental disturbance, making it a more sustainable choice in many cases. Sustainable sourcing practices and recycling of both materials are crucial to minimizing ecological footprints and promoting long-term resource conservation.
Pros and Cons: Dolomite vs Travertine
Dolomite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to travertine, making it ideal for high-traffic outdoor applications, while travertine provides unique, porous textures that enhance aesthetic appeal but may require more maintenance. Travertine's natural water absorption makes it prone to staining and erosion, limiting its use in wet environments, whereas dolomite's dense composition offers better stain resistance and longevity. Dolomite typically requires less sealing and upkeep, whereas travertine's distinctive veined patterns and warm tones are preferred for decorative interior designs despite potential vulnerability.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Dolomite offers superior hardness and durability compared to travertine, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and exterior applications. Travertine's natural porous texture and warm tones provide a classic aesthetic suitable for indoor flooring and decorative accents. Selecting the right stone depends on project requirements such as wear resistance, maintenance needs, and desired visual appeal.
Dolomite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com