Paleogeography explores the historical distribution of land and seas, revealing how Earth's continents, mountains, and oceans have shifted over millions of years. Understanding these ancient landscapes helps decode climate patterns, evolutionary paths, and tectonic activities that shaped our planet. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover how paleogeographic studies can deepen your knowledge of Earth's dynamic history.
Table of Comparison
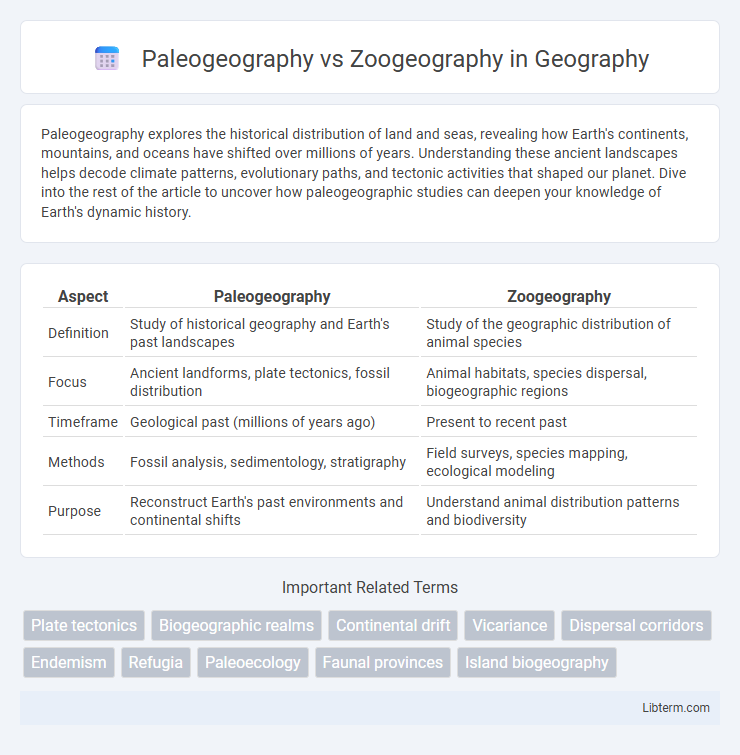
| Aspect | Paleogeography | Zoogeography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of historical geography and Earth's past landscapes | Study of the geographic distribution of animal species |
| Focus | Ancient landforms, plate tectonics, fossil distribution | Animal habitats, species dispersal, biogeographic regions |
| Timeframe | Geological past (millions of years ago) | Present to recent past |
| Methods | Fossil analysis, sedimentology, stratigraphy | Field surveys, species mapping, ecological modeling |
| Purpose | Reconstruct Earth's past environments and continental shifts | Understand animal distribution patterns and biodiversity |
Introduction to Paleogeography and Zoogeography
Paleogeography studies the historical distribution of Earth's landmasses, climates, and environments, reconstructing past geographical settings from fossil records and sediment analysis. Zoogeography examines the spatial distribution of animal species and populations, analyzing patterns influenced by ecological factors and evolutionary history. Both fields integrate geological and biological data to understand how earth's physical changes shape biodiversity over time.
Defining Paleogeography: Concepts and Importance
Paleogeography studies the historical distribution of Earth's landforms and environments through geological time, reconstructing ancient continents, oceans, and climates. It provides critical context for understanding past biological evolution, climatic changes, and plate tectonics. This field supports zoogeography by explaining how shifts in paleoenvironments influenced the spatial patterns and dispersal of animal species.
Exploring Zoogeography: Scope and Significance
Zoogeography examines the geographic distribution of animal species and populations, linking biological diversity with environmental factors and evolutionary history. This field maps patterns of animal habitats, migration routes, and species interactions to understand biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics across terrestrial and aquatic environments. By integrating climate data, geological changes, and species adaptions, zoogeography reveals critical insights into conservation strategies and the impacts of habitat fragmentation and climate change on wildlife.
Historical Development of Both Disciplines
Paleogeography emerged in the 19th century with scientists like Alfred Wegener proposing continental drift, emphasizing Earth's historical landmass and ocean distribution changes. Zoogeography developed concurrently, tracing the geographical distribution of animal species through time, with key contributions from Alfred Russel Wallace defining biogeographical realms. Both disciplines advanced through fossil evidence and geological data, establishing frameworks to understand past environments and the evolution of fauna across shifting continents.
Key Methods Used in Paleogeography
Paleogeography employs key methods such as sedimentology, fossil analysis, and plate tectonics to reconstruct ancient landforms and environmental conditions. Techniques like stratigraphic correlation and paleomagnetic studies provide insights into the historical positioning of continents and ocean basins. These methods collectively enable scientists to understand Earth's past geographic configurations and their influence on biodiversity patterns.
Analytical Techniques in Zoogeography
Zoogeography employs Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and spatial analysis to map and analyze species distribution patterns and habitat connectivity. Techniques such as species distribution modeling and phylogeographic analysis help interpret evolutionary processes and biogeographic barriers influencing fauna dispersal. These analytical tools enable precise assessment of biodiversity hotspots and guide conservation strategies based on ecological and geographical data.
Comparative Analysis: Paleogeography vs Zoogeography
Paleogeography studies the ancient geographical distribution of landmasses and environmental changes over geological time, whereas zoogeography focuses on the spatial distribution of animal species and ecosystems in both past and present contexts. Comparative analysis reveals that paleogeography provides the foundational context for zoogeographic patterns by explaining how continental drift, sea-level changes, and climate shifts influence species dispersal and habitat formation. Understanding the interplay between paleogeographic tectonics and zoogeographic biodiversity helps elucidate evolutionary processes and biogeographic boundaries across different geological epochs.
Interconnections Between Earth’s History and Animal Distribution
Paleogeography studies the historical changes in the Earth's physical landscapes, such as continental drift and ancient climates, which have directly influenced zoogeography by shaping animal distribution patterns over geological time. Fossil evidence and tectonic movements reveal how habitat shifts and landmass separations created barriers or corridors, driving species migration and evolutionary divergence. Understanding these interconnections allows scientists to trace biodiversity patterns and predict future changes in species distribution in response to ongoing geological processes.
Major Case Studies Illustrating Both Fields
Major case studies in paleogeography include the reconstruction of the supercontinent Pangaea, illustrating continental drift and plate tectonics over millions of years. In zoogeography, the distribution of marsupials across Australia and South America highlights evolutionary history shaped by geographic isolation. Both fields use fossil evidence and modern species distribution to understand Earth's historical and biological changes.
Future Perspectives in Paleogeography and Zoogeography
Future perspectives in paleogeography emphasize the integration of high-resolution geospatial data and advanced climate modeling to reconstruct past Earth environments with unprecedented accuracy. Innovations in spatial analysis and machine learning are expected to enhance zoogeography by refining species distribution models and predicting biodiversity shifts under climate change scenarios. Synergizing paleogeographic reconstructions with zoogeographic patterns will provide critical insights into evolutionary processes and guide conservation planning in response to ongoing environmental transformations.
Paleogeography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com