The Sassanian Empire, reigning from 224 to 651 AD, was pivotal in shaping Persian culture and influencing neighboring civilizations through its advanced art, architecture, and governance. Known for its military prowess and Zoroastrian state religion, the empire established a legacy that impacted Islamic culture and beyond. Discover how the Sassanian era continues to affect your understanding of ancient history by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
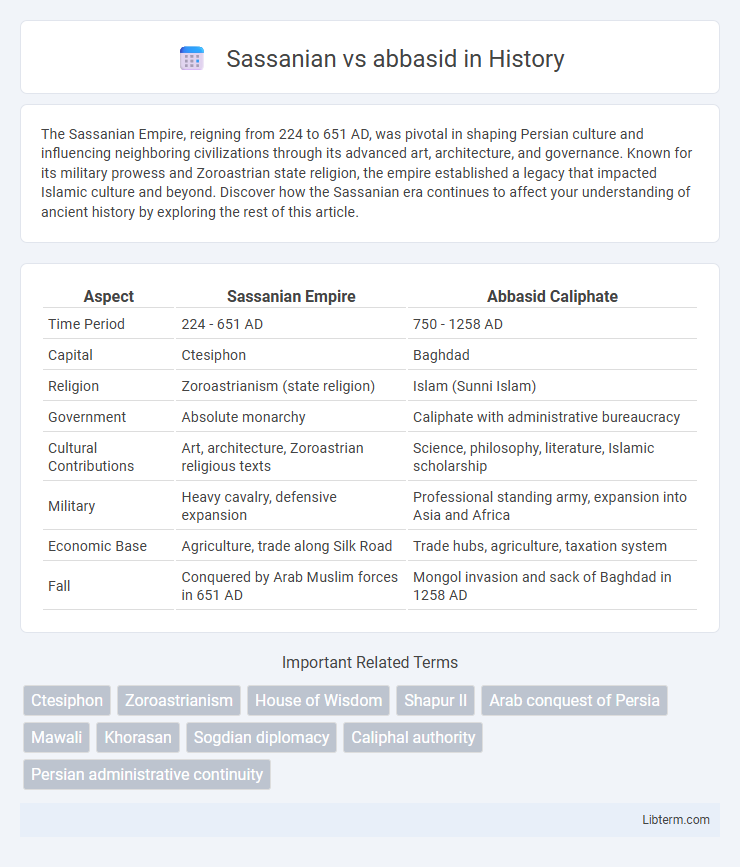
| Aspect | Sassanian Empire | Abbasid Caliphate |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 224 - 651 AD | 750 - 1258 AD |
| Capital | Ctesiphon | Baghdad |
| Religion | Zoroastrianism (state religion) | Islam (Sunni Islam) |
| Government | Absolute monarchy | Caliphate with administrative bureaucracy |
| Cultural Contributions | Art, architecture, Zoroastrian religious texts | Science, philosophy, literature, Islamic scholarship |
| Military | Heavy cavalry, defensive expansion | Professional standing army, expansion into Asia and Africa |
| Economic Base | Agriculture, trade along Silk Road | Trade hubs, agriculture, taxation system |
| Fall | Conquered by Arab Muslim forces in 651 AD | Mongol invasion and sack of Baghdad in 1258 AD |
Origins and Rise: Sassanian Empire vs Abbasid Caliphate
The Sassanian Empire originated in 224 CE under Ardashir I, who overthrew the Parthian dynasty to restore Persian dominance and establish a centralized, Zoroastrian state. The Abbasid Caliphate rose in 750 CE, born from the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate, rooted in the Abbasid family's claim of descent from Prophet Muhammad's uncle, which helped them gain widespread support. Both empires emerged through strategic military conquests and ideological legitimacy, with the Sassanian focus on reviving Persian heritage and the Abbasids emphasizing Islamic leadership and cultural integration.
Political Structures and Governance
The Sassanian Empire featured a centralized monarchy with a rigid hierarchical system led by the Shahanshah, supported by a network of satraps and a powerful priestly class influencing governance. The Abbasid Caliphate employed a caliphate system combining religious and political authority under the Caliph, who utilized a bureaucracy largely staffed by Persian and Arab officials to administer provinces. Both empires emphasized territorial control but differed in integrating religious legitimacy, with the Sassanians rooted in Zoroastrian divine kingship and the Abbasids emphasizing Islamic law and caliphal leadership.
Religious Systems: Zoroastrianism and Islam
The Sassanian Empire embraced Zoroastrianism as its state religion, emphasizing dualistic cosmology, fire worship, and the authority of the Magi priesthood, which shaped social and political structures. In contrast, the Abbasid Caliphate established Islam as the foundation of governance, law, and daily life, promoting the Quran and Sharia as central religious texts and integrating diverse Muslim communities under caliphal authority. The transition from Zoroastrianism to Islam marked significant transformations in religious practices, cultural identity, and administrative frameworks across the Middle East.
Military Organization and Strategies
The Sassanian military organization relied heavily on heavy cavalry called cataphracts, supported by infantry and archers, with a structured chain of command emphasizing centralized control under the shahanshah. In contrast, the Abbasid military incorporated a more diverse set of forces, including Turkish slave soldiers (Mamluks) and Arab tribal levies, with a flexible command structure adapting to evolving frontier threats. Sassanian strategies focused on fortified cities and defensive warfare against Roman and nomadic incursions, while the Abbasids employed rapid cavalry raids and mobile warfare to expand and maintain their vast empire.
Economic Foundations and Trade Networks
The Sassanian Empire established an extensive economic foundation rooted in agriculture, craftsmanship, and a sophisticated taxation system, facilitating vibrant trade networks across the Silk Road connecting Persia to the Roman Empire and India. The Abbasid Caliphate inherited and expanded these trade routes, enhancing commercial activity through innovations like the establishment of Baghdad as a major economic hub and the introduction of new financial instruments including bills of exchange. Both empires leveraged their strategic geographical locations to stimulate transcontinental trade, promoting the exchange of luxury goods, spices, textiles, and precious metals that underpinned their economic prosperity.
Cultural Achievements and Contributions
The Sassanian Empire excelled in architecture, metalwork, and the codification of Zoroastrian religious texts, laying the foundation for Persian art and culture. The Abbasid Caliphate advanced science, mathematics, and literature, with achievements including the House of Wisdom in Baghdad and significant contributions to algebra, astronomy, and philosophy. Both empires played pivotal roles in shaping Middle Eastern culture, with the Sassanians influencing administrative and artistic traditions and the Abbasids fostering intellectual and cultural flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age.
Art, Architecture, and Urban Development
Sassanian art is characterized by intricate rock reliefs, stucco decorations, and silverwork that emphasize royal power and Zoroastrian themes, contrasting with the Abbasid period's emphasis on calligraphy, geometric patterns, and arabesques in artistic expression. Architectural innovations during the Sassanian era include grand palaces like the Taq-e Kasra with its massive vaulted iwan, whereas the Abbasids introduced monumental structures such as the Great Mosque of Samarra and developed the hypostyle mosque layout. Urban development under the Sassanian Empire featured fortified cities with planned layouts, while Abbasid rulers advanced city-building by founding new capitals like Baghdad, designed with concentric circular walls to enhance defense and administration.
Social Hierarchy and Daily Life
The Sassanian Empire featured a rigid social hierarchy dominated by the king, nobility, priests, and warriors, with peasants and artisans forming the lower classes, emphasizing Zoroastrian religious influence in daily life. The Abbasid Caliphate introduced a more diversified society, including Arabs, Persians, Turks, and other ethnic groups, where social mobility was more fluid due to Islamic principles and urbanization fostering trade and intellectual activities. Daily life under the Abbasids included vibrant cultural and scientific advancements in cities like Baghdad, contrasting with the Sassanian emphasis on agricultural and military duty.
Decline and Fall: Causes and Consequences
The Sassanian Empire's decline was primarily due to prolonged warfare with the Byzantine Empire, internal political instability, and the devastating impact of the Arab Muslim conquests that culminated in the Battle of al-Qadisiyyah in 636 CE. In contrast, the Abbasid Caliphate faced decline from internal fragmentation, including the rise of regional powers and the loss of centralized control, compounded by the Mongol invasion that led to the sack of Baghdad in 1258 CE. The fall of both empires resulted in significant cultural and political transformations, with the Sassanian collapse marking the rise of Islamic governance in Persia and the Abbasid decline paving the way for regional dynasties and the eventual shift to Ottoman dominance.
Sassanian and Abbasid Legacy in World History
The Sassanian Empire established enduring contributions in art, architecture, and state administration that influenced Islamic governance and culture during the Abbasid Caliphate. The Abbasid legacy, marked by scientific advancements, literary achievements, and the promotion of Islamic scholarship, built upon the Sassanian foundation by preserving and expanding knowledge across Eurasia. Both empires played pivotal roles in shaping world history by fostering cultural exchanges and institutional innovations that impacted subsequent civilizations.
Sassanian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com