Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultures, fostering mutual respect and understanding within societies. Embracing cultural diversity enhances social cohesion, creativity, and economic growth by valuing different perspectives. Discover how multiculturalism can enrich your community and personal experiences in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
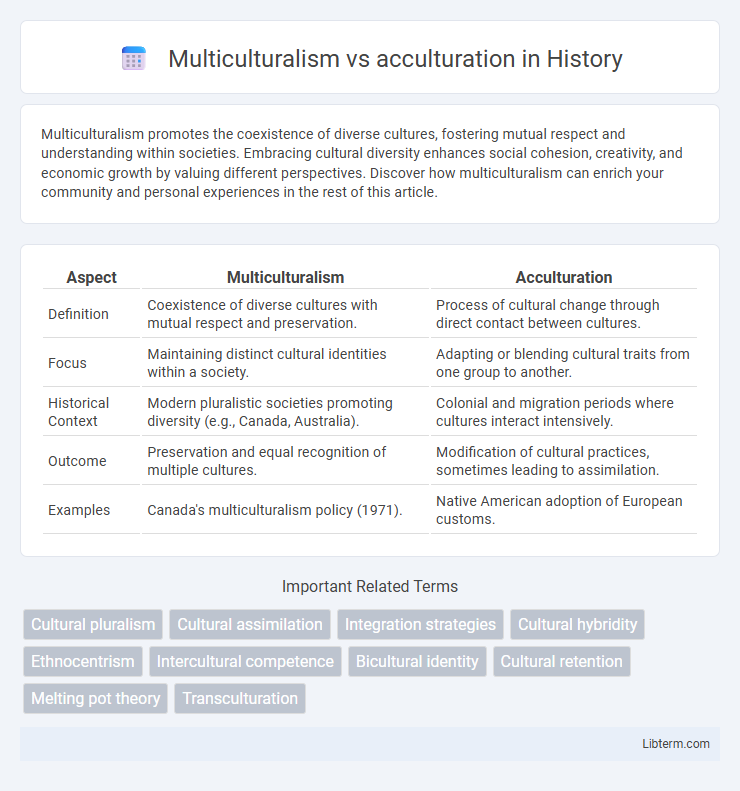
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Acculturation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures with mutual respect and preservation. | Process of cultural change through direct contact between cultures. |
| Focus | Maintaining distinct cultural identities within a society. | Adapting or blending cultural traits from one group to another. |
| Historical Context | Modern pluralistic societies promoting diversity (e.g., Canada, Australia). | Colonial and migration periods where cultures interact intensively. |
| Outcome | Preservation and equal recognition of multiple cultures. | Modification of cultural practices, sometimes leading to assimilation. |
| Examples | Canada's multiculturalism policy (1971). | Native American adoption of European customs. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: A Brief Overview
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, encouraging respect and equal recognition for different ethnic groups. It emphasizes cultural preservation and mutual understanding rather than cultural assimilation. This differs from acculturation, which involves adapting or adopting aspects of another culture, often leading to changes in cultural identity.
Defining Acculturation: Key Concepts
Acculturation refers to the process through which individuals or groups adopt cultural traits or social patterns of another group, often occurring during sustained contact between different cultures. Key concepts in acculturation include assimilation, integration, separation, and marginalization, each describing different ways individuals balance their original culture with the dominant culture. Unlike multiculturalism, which promotes the coexistence of diverse cultures while maintaining distinct identities, acculturation emphasizes the dynamic adaptation process involving cultural exchange and change.
Historical Roots of Multiculturalism and Acculturation
Multiculturalism historically emerged as a political ideology in the 20th century, rooted in post-colonial societies seeking to recognize and preserve diverse cultural identities within nation-states. Acculturation, by contrast, has ancient origins linked to the contact and exchange between different cultural groups, resulting in the adaptation of cultural traits over time. Key studies in anthropology and sociology highlight acculturation as a dynamic process affecting immigrant and indigenous populations, while multiculturalism emphasizes institutional policies that promote cultural pluralism.
Core Differences: Multiculturalism vs Acculturation
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence and equal respect of diverse cultural identities within a single society, encouraging preservation of original cultural practices. Acculturation involves the process where individuals or groups adopt elements of another culture, often leading to cultural blending or changes in identity. Core differences lie in multiculturalism emphasizing cultural diversity maintenance, while acculturation focuses on cultural adaptation and integration.
Benefits of Embracing Multiculturalism
Embracing multiculturalism fosters social cohesion by promoting respect and understanding among diverse cultural groups, enhancing community resilience and innovation. It supports mental well-being and a sense of belonging for individuals from varied backgrounds, leading to decreased discrimination and increased social equity. Multicultural environments also drive economic growth by attracting global talent and enabling creative problem-solving through diverse perspectives.
Challenges and Critiques of Acculturation
Acculturation often faces challenges such as identity loss, psychological stress, and cultural conflicts, as individuals struggle to balance heritage with dominant cultural norms. Critics argue that acculturation can lead to assimilation pressures, marginalizing minority cultures and eroding cultural diversity. Unlike multiculturalism, which promotes coexistence and equal cultural recognition, acculturation may prioritize adaptation over cultural preservation.
Social Integration: Finding a Balance
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, encouraging respect and preservation of individual cultural heritage while fostering social cohesion. Acculturation involves adapting and blending cultural traits, which can facilitate smoother social integration but may also risk loss of distinct cultural identities. Balancing multiculturalism and acculturation is essential for achieving social integration that supports both cultural diversity and shared social unity, enhancing community resilience and mutual understanding.
Impact on Identity and Community Cohesion
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities, enhancing community cohesion by valuing multiple perspectives and fostering mutual respect. Acculturation often involves adapting to a dominant culture, which can lead to identity shifts or hybrid identities but may risk cultural assimilation and weaken original community bonds. The impact on identity varies, with multiculturalism supporting cultural preservation and acculturation influencing integration dynamics within communities.
Policy Approaches: Supporting Diversity
Policy approaches to multiculturalism emphasize the promotion and protection of cultural diversity through legal frameworks and inclusive education systems that recognize and support various ethnic identities. In contrast, acculturation-focused policies often prioritize integration strategies that encourage adaptation to the dominant culture while facilitating selective retention of cultural traits. Effective diversity support policies balance respecting cultural heritage with fostering social cohesion, promoting equal opportunities and intercultural dialogue.
Future Perspectives: Multiculturalism and Acculturation in a Globalized World
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities, fostering social inclusion and mutual respect amid global interconnectivity. Acculturation involves the adaptation processes that individuals or groups experience when encountering new cultural environments, highlighting dynamic identity transformations. Future perspectives emphasize integrating multicultural policies with adaptive acculturation strategies to enhance cross-cultural understanding and cooperation in increasingly interconnected societies.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com