Patronage plays a crucial role in nurturing emerging artists, fostering creativity, and preserving cultural heritage through financial support and networking opportunities. This relationship often benefits both patrons, who influence artistic trends, and creators, who gain resources to realize their vision. Discover how understanding patronage can enhance your appreciation of the arts and its impact on society by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
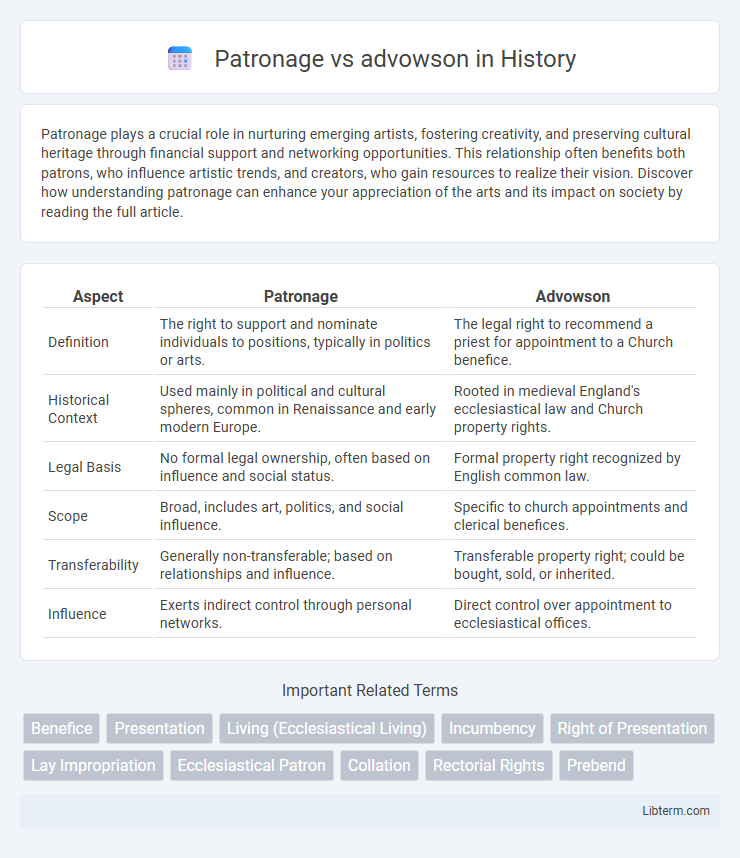
| Aspect | Patronage | Advowson |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The right to support and nominate individuals to positions, typically in politics or arts. | The legal right to recommend a priest for appointment to a Church benefice. |
| Historical Context | Used mainly in political and cultural spheres, common in Renaissance and early modern Europe. | Rooted in medieval England's ecclesiastical law and Church property rights. |
| Legal Basis | No formal legal ownership, often based on influence and social status. | Formal property right recognized by English common law. |
| Scope | Broad, includes art, politics, and social influence. | Specific to church appointments and clerical benefices. |
| Transferability | Generally non-transferable; based on relationships and influence. | Transferable property right; could be bought, sold, or inherited. |
| Influence | Exerts indirect control through personal networks. | Direct control over appointment to ecclesiastical offices. |
Understanding Patronage: Definition and Origins
Patronage refers to the practice where influential individuals or institutions provide support, appointments, or privileges to others, often in a religious or political context. Its origins trace back to Roman times, where patrons offered protection and benefits to clients in exchange for loyalty and service, evolving into medieval systems of ecclesiastical influence. Unlike advowson, which specifically concerns the right to appoint clergy to a church living, patronage encompasses a broader spectrum of social and political favor.
Advowson Explained: Historical Context
Advowson, a medieval legal right in England, allowed a patron to present a nominee for a parish church benefice, reflecting the intertwined nature of religious and feudal authority. Historically rooted in the Norman Conquest, advowson was a property right that could be inherited, sold, or transferred, highlighting its economic and social significance within the ecclesiastical system. Unlike general patronage, advowson specifically pertained to church appointments, embodying the legal framework that regulated the selection of clergy in the English ecclesiastical hierarchy.
Key Differences Between Patronage and Advowson
Patronage refers to the right to recommend a clergyman for a church office, while advowson specifically denotes the legal right to present a nominee to a parish benefice. Key differences include that patronage is a broader concept involving influence or support in appointments, whereas advowson is a formal property right recognized in English ecclesiastical law. Advowson entails ownership and transferability, often treated as a hereditary or saleable right, unlike the more informal or honorary nature of general patronage.
The Evolution of Patronage in Ecclesiastical Appointments
Patronage and advowson represent key historical mechanisms in ecclesiastical appointments, with patronage broadly referring to the right to recommend clergy and advowson specifically denoting the legal right to present a nominee to a church benefice. The evolution of patronage in ecclesiastical appointments reflects shifting power dynamics between the church, monarchy, and local landowners, particularly from the medieval period through the Reformation, where secular and religious authorities contested control over advowsons. Modern reforms have curtailed traditional advowson rights, emphasizing institutional appointments and reducing lay influence in clerical nominations to enhance ecclesiastical autonomy and meritocracy.
Legal Framework Surrounding Advowson Rights
Advowson rights, rooted in English common law, regulate the legal entitlement to recommend a clergyman for a parish church, distinct from broader patronage powers that may encompass various ecclesiastical appointments. The legal framework governing advowson involves statutes such as the Patronage (Benefices) Measure 1986, which outlines procedures for the presentation and collation of clergy, ensuring adherence to canonical and civil requirements. Judicial precedents clarify disputes over advowson ownership and succession, emphasizing the secular courts' role in resolving claims linked to historic property rights tied to ecclesiastical benefices.
Patronage and Advowson in Medieval England
Patronage in Medieval England referred to the right of a patron, often a noble or religious institution, to appoint clergy to church benefices, thereby influencing local ecclesiastical authority and community leadership. Advowson, a legal right closely linked to patronage, specifically denoted the entitlement to present a nominee to a vacant parish benefice, allowing patrons to control church appointments and revenue. This system underscored the intertwining of secular and religious power, with advowsons frequently bought, sold, or inherited, reflecting the socioeconomic dynamics of medieval society.
The Transfer and Sale of Advowson
The transfer and sale of advowson historically involved the legal right to present a nominee to a church benefice, often treated as a property right distinct from patronage, which referred more generally to influence over appointments. Advowsons could be conveyed by grant, sale, or inheritance, but such transactions required formal procedures to ensure the bishop or ecclesiastical authority's approval. Despite restrictions, the sale of advowsons persisted as a means to control clerical appointments, impacting ecclesiastical law and the church's autonomy in medieval and early modern England.
Modern Implications of Patronage vs Advowson
Modern implications of patronage and advowson highlight the evolution of ecclesiastical influence and property rights within church law. While advowson traditionally refers to the legal right to present a clergy member to a benefice, patronage now encompasses broader aspects such as lay participation and community influence in church appointments. The shift from strict advowson rights to contemporary patronage practices reflects changing legal frameworks and democratization in church governance.
Case Studies: Notable Patronage and Advowson Disputes
Notable patronage and advowson disputes often arose over the right to appoint clergy to parish churches, with landmark cases such as the 17th-century conflict between the Earl of Derby and local boroughs over advowson rights highlighting the intricate interplay of local power and ecclesiastical authority. The dispute over the advowson of St. Peter's Church in Northampton exemplifies tensions between noble families and ecclesiastical institutions, resulting in prolonged legal battles that shaped church patronage law. Such case studies underscore the significance of advowson as a medieval legal concept tied to property rights, contrasting with broader patronage systems involving political or social influence in clerical appointments.
The Future of Church Appointments: Patronage or Advowson?
The future of church appointments hinges on the evolution of patronage and advowson systems, where patronage involves a broader range of individuals or bodies holding the right to nominate clergy, while advowson remains a historical legal right tied to property ownership, enabling patrons to present candidates to ecclesiastical benefices. Modern reforms tend to favor transparency and community involvement in appointments, reducing the exclusive control traditionally held by private patrons under advowson. Increasingly, diocesan boards and church authorities are integrating both systems to balance historical rights with contemporary governance, ensuring appointments reflect both legal traditions and congregational needs.
Patronage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com