Memoirs offer a unique window into personal experiences and historical moments, capturing emotions and lessons that resonate across time. Crafting your own memoir can preserve memories and inspire future generations with authentic storytelling. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips for writing compelling memoirs that truly connect with readers.
Table of Comparison
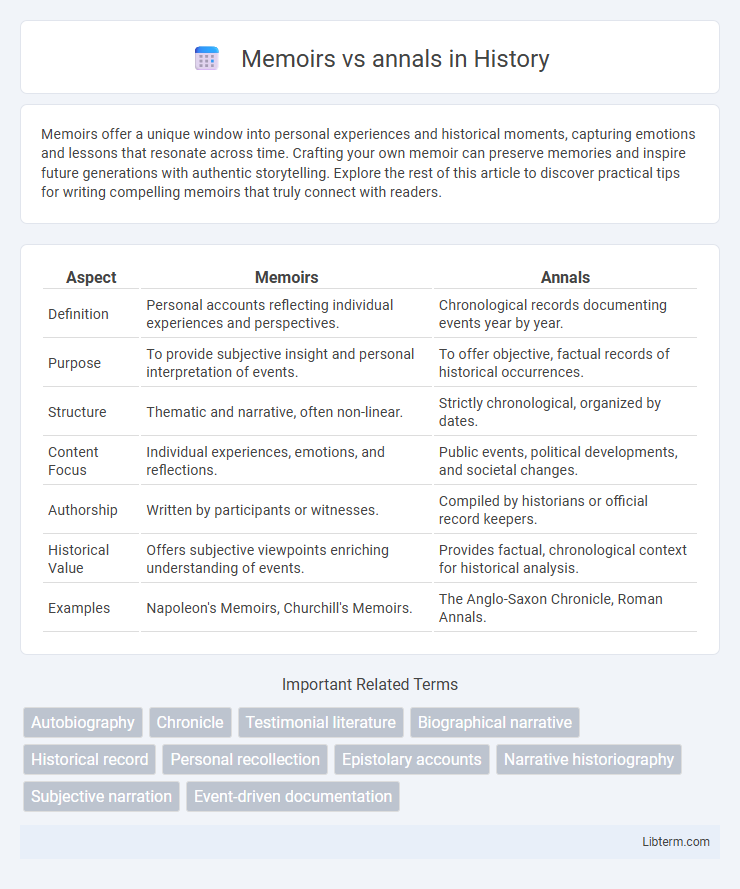
| Aspect | Memoirs | Annals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal accounts reflecting individual experiences and perspectives. | Chronological records documenting events year by year. |
| Purpose | To provide subjective insight and personal interpretation of events. | To offer objective, factual records of historical occurrences. |
| Structure | Thematic and narrative, often non-linear. | Strictly chronological, organized by dates. |
| Content Focus | Individual experiences, emotions, and reflections. | Public events, political developments, and societal changes. |
| Authorship | Written by participants or witnesses. | Compiled by historians or official record keepers. |
| Historical Value | Offers subjective viewpoints enriching understanding of events. | Provides factual, chronological context for historical analysis. |
| Examples | Napoleon's Memoirs, Churchill's Memoirs. | The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, Roman Annals. |
Defining Memoirs and Annals
Memoirs are personal narratives that provide detailed, subjective accounts of an individual's experiences, often emphasizing emotions and personal insights. Annals are chronological records of events, focusing on objective, factual documentation organized by date without personal interpretation. Both serve historical purposes, but memoirs highlight personal perspective while annals prioritize systematic, date-based reporting.
Historical Background of Memoirs and Annals
Memoirs originated as personal recollections written by individuals reflecting on their own experiences, offering subjective perspectives on historical events, whereas annals developed as chronological records maintained by institutions or chroniclers to document events year by year. The historical background of memoirs is rooted in classical antiquity, with figures like Julius Caesar providing firsthand accounts, while annals have their origins in early medieval monastic traditions serving as official repositories of communal history. Memoirs emphasize narrative and personal insight, contrasting with the systematic, factual approach characteristic of annals, making both essential complementary sources in historical research.
Purpose and Function: Memoirs vs Annals
Memoirs serve to provide a personal and subjective account of events, emphasizing individual experiences, emotions, and interpretations. Annals aim to record events chronologically with factual accuracy, focusing on objective documentation and historical order. The purpose of memoirs is to offer insight into personal perspectives, whereas annals function as systematic records for reference and historical analysis.
Narrative Style and Structure Differences
Memoirs employ a personal, subjective narrative style, emphasizing individual experiences and emotional reflections organized thematically or chronologically with a fluid, intimate structure. Annals utilize an objective, factual approach, presenting events in strict chronological order with concise, date-specific entries that prioritize accuracy and completeness. The narrative style of memoirs fosters emotional engagement, contrasting with annals' structured documentation aimed at historical record-keeping.
Subjectivity vs Objectivity in Memoirs and Annals
Memoirs emphasize subjectivity by presenting personal experiences and emotions, offering subjective interpretations of events shaped by the author's perspective. Annals maintain objectivity through chronological documentation of historical facts, aiming to provide an impartial and accurate record without personal bias. The contrast in subjectivity and objectivity distinguishes memoirs as reflective narratives and annals as factual chronicles.
Types of Content in Memoirs and Annals
Memoirs often contain personal reflections, detailed anecdotes, and subjective interpretations of events, providing intimate insights into the author's experiences and emotions. Annals primarily present chronological records of historical events, focusing on factual accuracy, dates, and significant occurrences without personal commentary. The content in memoirs is narrative and interpretive, while annals emphasize objective documentation and year-by-year reporting.
Use of Personal Perspective and Voice
Memoirs emphasize a personal perspective and intimate voice, offering subjective reflections and emotional insights from the author's viewpoint. Annals present an objective, chronological record of events without personal bias, focusing on factual accuracy and historical context. The memoir's narrative style allows for deeper connection and interpretation, whereas annals prioritize documentation over personal narrative.
Chronological Organization and Thematic Focus
Memoirs prioritize a thematic focus, often exploring personal experiences and introspections, whereas annals emphasize strict chronological organization by recording events year by year. Memoirs provide subjective narratives that reveal the author's perspective on specific themes or periods, contrasting with annals' objective, date-centric approach that highlights historical accuracy and sequence. This distinction makes memoirs valuable for understanding individual insights, while annals serve as comprehensive chronological records.
Notable Examples of Memoirs and Annals
Notable examples of memoirs include "The Diary of Anne Frank," which provides a personal perspective on World War II, and "Long Walk to Freedom" by Nelson Mandela, detailing his life and struggle against apartheid. Famous annals such as the "Anglo-Saxon Chronicle" offer a yearly record of events in medieval England, while the "Annals of Tacitus" chronicle the history of the Roman Empire under Tiberius and Claudius. These works serve distinct purposes: memoirs provide intimate, subjective accounts, whereas annals present chronological, objective historical records.
Impact and Relevance in Historical Writing
Memoirs provide personal perspectives that offer intimate insights and emotional depth, enriching historical narratives with subjective experiences. Annals present chronological, factual accounts that establish a systematic framework for understanding historical events and their broader impact. Combining memoirs with annals enhances historical writing by balancing subjective reflection with objective documentation, increasing overall relevance and depth.
Memoirs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com