Monarchists advocate for a government system led by a king, queen, or emperor, emphasizing tradition, stability, and national identity. They believe in the symbolic and sometimes political role of monarchy as a unifying force that preserves cultural heritage and continuity. Discover how monarchist principles impact modern governance and why this ideology still resonates with many around the world.
Table of Comparison
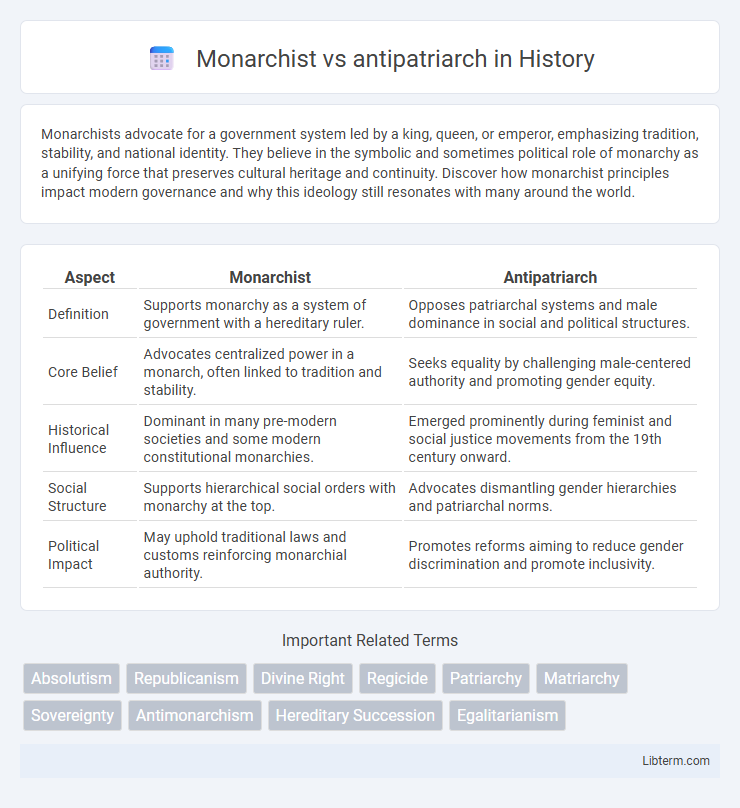
| Aspect | Monarchist | Antipatriarch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supports monarchy as a system of government with a hereditary ruler. | Opposes patriarchal systems and male dominance in social and political structures. |
| Core Belief | Advocates centralized power in a monarch, often linked to tradition and stability. | Seeks equality by challenging male-centered authority and promoting gender equity. |
| Historical Influence | Dominant in many pre-modern societies and some modern constitutional monarchies. | Emerged prominently during feminist and social justice movements from the 19th century onward. |
| Social Structure | Supports hierarchical social orders with monarchy at the top. | Advocates dismantling gender hierarchies and patriarchal norms. |
| Political Impact | May uphold traditional laws and customs reinforcing monarchial authority. | Promotes reforms aiming to reduce gender discrimination and promote inclusivity. |
Understanding Monarchism: Core Principles
Monarchism centers on the principle of a hereditary sovereign as the legitimate head of state, emphasizing continuity, stability, and tradition within governance. It advocates for a hierarchical political structure where authority is vested in a monarch, often justified by historical legitimacy or divine right. In contrast, antipatriarch perspectives challenge centralized hereditary authority, promoting egalitarianism and rejecting systemic power imbalances inherent in monarchial rule.
Defining Antipatriarchy: Key Concepts
Antipatriarchy challenges the traditional power structures upheld by monarchist systems, emphasizing gender equality and dismantling male dominance entrenched in political and social hierarchies. Key concepts include the critique of hereditary rule as a form of patriarchal authority that perpetuates inequality and the advocacy for inclusive governance models promoting equal representation. Antipatriarchal theory highlights the intersection of patriarchy with other oppressive systems, calling for a comprehensive restructure of power beyond monarchist legitimacy.
Historical Roots of Monarchist Ideologies
Monarchist ideologies trace their historical roots to medieval Europe, where centralized royal authority was believed to ensure social order and divine right legitimized the monarch's power. These ideologies emphasize tradition, hierarchy, and continuity, rooted in dynastic rule and feudal systems that reinforced the monarch's sovereignty over land and subjects. In contrast, antipatriarchal movements challenge the gendered power structures embedded in monarchist history, advocating for dismantling hereditary privilege and advocating for egalitarian governance models.
The Evolution of Patriarchy in Monarchical Systems
Monarchical systems historically institutionalized patriarchy by centralizing power within male sovereigns, perpetuating gender hierarchies through dynastic inheritance and legal frameworks favoring men. The evolution of patriarchy in such systems reveals tensions between monarchist ideals preserving male dominance and antipatriarchal movements challenging these power structures to promote gender equality. Contemporary critiques highlight how monarchical traditions intertwine with patriarchal values, necessitating reforms to dismantle systemic gender biases embedded in royal governance.
Monarchist Justifications for Hierarchical Rule
Monarchists justify hierarchical rule by emphasizing the stability and continuity provided by a single, hereditary sovereign, who embodies the unity and tradition of the nation. They argue that monarchy ensures effective governance by centralizing authority, preventing factionalism and power struggles common in fragmented democratic systems. Historical examples such as the British and Japanese monarchies highlight how monarchs serve as apolitical symbols of national identity and continuity.
Antipatriarchal Critiques of Monarchies
Antipatriarchal critiques of monarchies highlight how hereditary rule often reinforces patriarchal power structures, limiting gender equality and perpetuating male dominance in political leadership. Scholars argue that monarchies institutionalize gender hierarchies by privileging male succession and marginalizing women's political agency. These critiques emphasize the inseparability of monarchical governance and patriarchal oppression, calling for systems that promote egalitarian representation instead.
Gender Roles in Monarchist Societies
Monarchist societies often enforce traditional gender roles, where men typically hold positions of power such as kings or princes, and women are expected to fulfill supportive, domestic, or ceremonial roles like queens or consorts. Antipatriarch movements challenge these roles by advocating for gender equality and dismantling hierarchical systems that reinforce male dominance in monarchy structures. The clash between monarchist gender norms and contemporary gender rights activism highlights ongoing debates about power, identity, and social organization in historical and modern contexts.
Intersection of Tradition and Reform: Monarchists vs. Antipatriarchs
Monarchists advocate for preserving hierarchical structures rooted in historical traditions, emphasizing the continuity of established authority and cultural heritage. Antipatriarchs challenge these systems by promoting egalitarian principles and reforming institutional norms that perpetuate gender and power imbalances. The intersection of tradition and reform reveals a complex dialogue where monarchists seek stability through lineage-based governance, while antipatriarchs demand progressive transformation to dismantle patriarchal frameworks within society.
Contemporary Debates on Monarchy and Patriarchy
Contemporary debates on monarchy and patriarchy critically examine the intersection of political authority and gender hierarchies, highlighting monarchist support for traditional, often male-dominated governance structures versus antipatriarchal critiques advocating egalitarian social orders. Monarchist discourse frequently emphasizes historical continuity, national identity, and stability linked to hereditary rule, whereas antipatriarchal perspectives challenge the embedded privileges and gender-based exclusion perpetuated by monarchical institutions. These debates engage with feminist theory, democratic values, and calls for inclusive governance that dismantles patriarchal norms inherent in monarchical systems.
Future Perspectives: Reconciling Heritage with Equality
Monarchists advocate preserving historical traditions and hierarchical structures that symbolize national identity and continuity. Antipatriarch critics emphasize dismantling entrenched gender and power inequalities perpetuated by monarchical systems to achieve social justice and equality. Future perspectives focus on integrating respect for cultural heritage with progressive reforms promoting inclusivity, gender equality, and democratic representation within modern governance frameworks.
Monarchist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com