A fief was a central element of feudal society, consisting of land granted by a lord to a vassal in exchange for military service and loyalty. This system structured medieval political and economic life, influencing land ownership, governance, and social hierarchy. Explore the rest of the article to understand how fiefs shaped medieval Europe and affected your historical perspective.
Table of Comparison
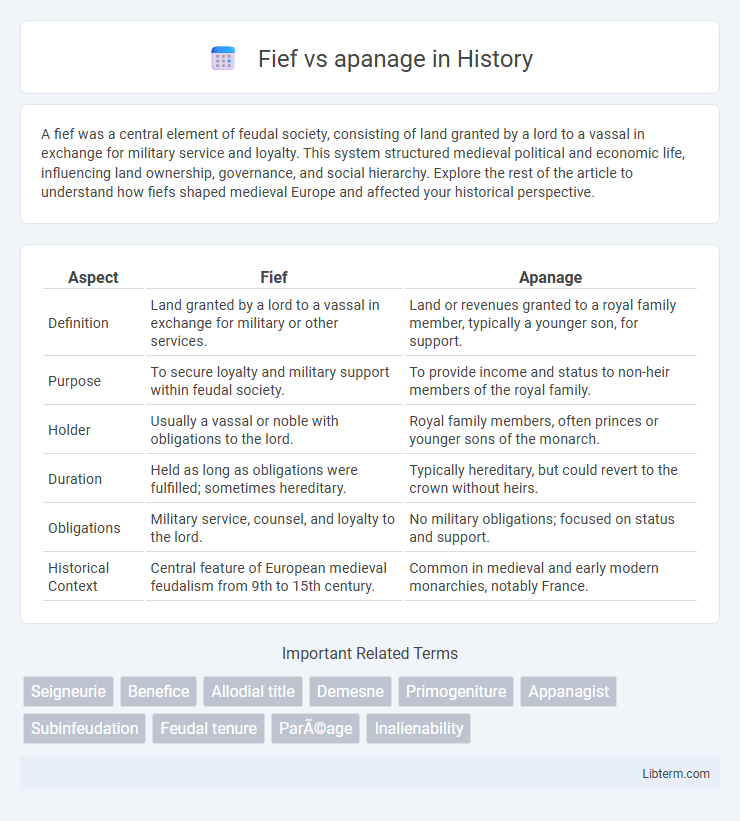
| Aspect | Fief | Apanage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Land granted by a lord to a vassal in exchange for military or other services. | Land or revenues granted to a royal family member, typically a younger son, for support. |
| Purpose | To secure loyalty and military support within feudal society. | To provide income and status to non-heir members of the royal family. |
| Holder | Usually a vassal or noble with obligations to the lord. | Royal family members, often princes or younger sons of the monarch. |
| Duration | Held as long as obligations were fulfilled; sometimes hereditary. | Typically hereditary, but could revert to the crown without heirs. |
| Obligations | Military service, counsel, and loyalty to the lord. | No military obligations; focused on status and support. |
| Historical Context | Central feature of European medieval feudalism from 9th to 15th century. | Common in medieval and early modern monarchies, notably France. |
Understanding Fief and Apanage: Definitions
A fief is a land grant given by a lord to a vassal in medieval feudal society, establishing a relationship of mutual obligation, including military service and loyalty. An apanage refers to a provision of land or revenue granted by a monarch to a younger child or relative, ensuring their financial support without dividing the core inheritance. Both terms involve land allocation, but a fief emphasizes feudal duties, while an apanage centers on familial economic maintenance.
Historical Origins of Fief and Apanage
Fiefs originated in the European medieval feudal system as land grants given by lords to vassals in exchange for military service and loyalty, symbolizing a contractual relationship central to feudal governance. Apanages, by contrast, developed primarily in French and other monarchical contexts as hereditary land grants or incomes bestowed by sovereigns upon younger royal family members to support their status without fragmenting the kingdom's core territories. The historical origins of fiefs relate closely to decentralizing feudal authority, while apanages served to maintain dynastic stability and prevent internal conflicts within ruling families.
The Role of Fief in Feudal Society
Fiefs were central to feudal society, serving as land grants from lords to vassals in exchange for military service and loyalty, thus structuring the political and economic hierarchy. Unlike apanages, which were typically smaller land parcels given to royal family members to support their status without distributing broader power, fiefs created a complex network of obligations and governance. This system enabled decentralized control, where vassals administered territories, collected taxes, and maintained order under the authority of their liege lord.
Apanage: Purpose and Function
Apanage serves as a territorial grant given primarily to younger royal family members to provide them with income and status without threatening the central authority of the monarchy. Unlike fiefs, which are typically granted in exchange for military or service obligations under the feudal system, apanages are bestowed to ensure the support and loyalty of royal relatives while maintaining political stability. The primary function of apanage is to sustain the nobility's wealth and influence within a controlled framework that prevents fragmentation of the realm.
Legal Distinctions Between Fief and Apanage
A fief is a conditional grant of land or revenue given by a lord to a vassal in exchange for military or other services, inherently tied to feudal obligations and subject to revocation upon failure to fulfill duties. An apanage is a hereditary grant, typically of land or revenue, given by a sovereign to a younger royal family member to support their status without the expectation of service or forfeiture, emphasizing dynastic maintenance rather than feudal service. The legal distinction lies in the fief's service-based conditional tenure versus the apanage's unconditional hereditary right aimed at sustaining royal lineage.
Inheritance and Succession Rules
Fiefs typically followed feudal inheritance laws favoring primogeniture, where the eldest son inherited the entire estate, while apanages were granted to younger royal children to maintain their status without dividing the main territory. Succession in fiefs could be contested if no direct heirs existed, often reverting to the lord or monarch, whereas apanages were revocable grants that did not create hereditary noble titles but ensured maintenance within the royal family. Both systems aimed to preserve land integrity and political stability but differed in legal flexibility and the scope of hereditary rights.
Social and Political Implications
Fief and apanage systems significantly shaped medieval social hierarchies and political power distribution by allocating land and resources to nobles and royal family members, respectively. Fiefs reinforced feudal loyalty through vassalage bonds, enabling decentralized governance, while apanages often fostered internal dynastic stability but sometimes triggered fragmentation and rivalries within ruling houses. These land grants institutionalized aristocratic privileges, influencing governance structures and succession politics in European medieval societies.
Regional Variations in Practice
Fiefs and apanages varied significantly across regions, reflecting local feudal customs and governance structures. In France, apanages were granted primarily to royal family members to provide autonomous income without fragmenting the kingdom, while fiefs were widely distributed among the nobility under complex vassalage systems. In contrast, the English feudal system emphasized strict hierarchical vassal-lord relationships, where fiefs often came with military obligations, and apanages were less prominent, highlighting regional variations in political and economic control.
Evolution Over Time: From Medieval to Modern
Fiefs and apanages both originated as land grants in medieval Europe, where fiefs were primarily granted by lords to vassals in exchange for military service, while apanages were royal land allocations given to younger sons to support their status without dividing the kingdom. Over time, fiefs evolved into hereditary estates that laid the groundwork for modern feudal property rights, whereas apanages became more regulated to prevent the fragmentation of royal authority. By the modern period, fiefs gradually transitioned into private property under centralized state systems, while apanages largely diminished as monarchies centralized power and reformed land inheritance practices.
Comparative Analysis: Fief vs Apanage
Fiefs and apanages both served as land grants in feudal societies, but fiefs were typically bestowed by a lord to a vassal in exchange for military service, emphasizing a reciprocal feudal relationship. Apanages were often granted by monarchs to their younger sons or relatives to sustain their status without dividing the kingdom, focusing more on dynastic maintenance than military obligations. The economic and political implications differ, with fiefs reinforcing feudal loyalty and apanages addressing succession and governance within royal families.
Fief Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com