Discover how optimizing your website's SEO can drive more traffic and improve your search engine rankings. Implementing strategic keywords, quality content, and mobile-friendly design are essential for attracting and retaining visitors. Explore the rest of the article to learn actionable SEO tips that will elevate your online presence.
Table of Comparison
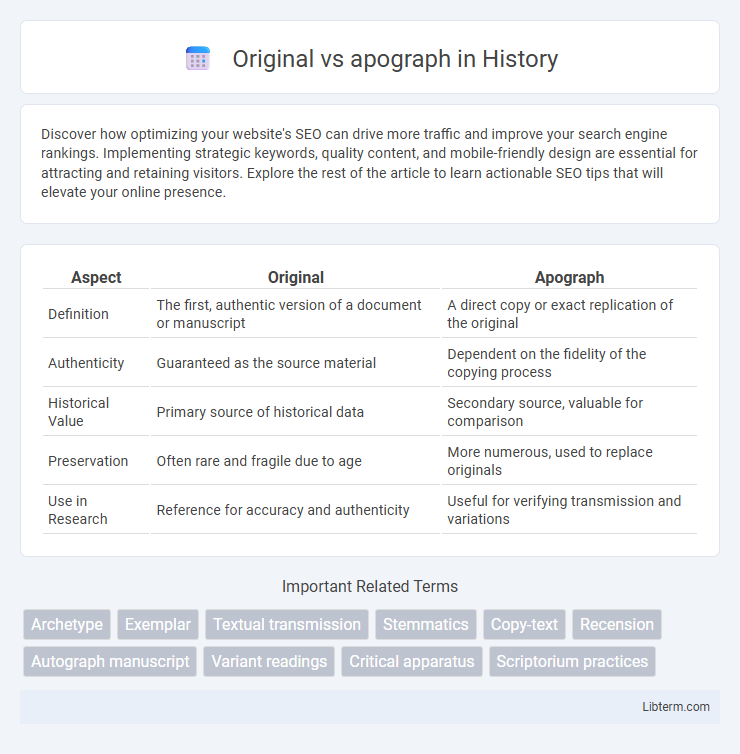
| Aspect | Original | Apograph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The first, authentic version of a document or manuscript | A direct copy or exact replication of the original |
| Authenticity | Guaranteed as the source material | Dependent on the fidelity of the copying process |
| Historical Value | Primary source of historical data | Secondary source, valuable for comparison |
| Preservation | Often rare and fragile due to age | More numerous, used to replace originals |
| Use in Research | Reference for accuracy and authenticity | Useful for verifying transmission and variations |
Understanding the Concepts: Original vs Apograph
Understanding the concepts of original and apograph revolves around distinguishing the primary source from its copies. An original denotes the authentic, first-created document or artifact, serving as the authoritative reference in legal, historical, or literary contexts. Conversely, an apograph is a faithful reproduction or transcription, often used to preserve the content when access to the original is limited or the original is at risk of damage.
Historical Context of Originals and Apographs
Original manuscripts, often penned by the author or closely linked to their time, provide direct insights into historical contexts, including language, culture, and intent, reflecting the period of creation. Apographs, as precise copies of these originals, serve as critical vessels for preserving texts through centuries, especially when originals are lost or damaged, allowing scholars to trace textual transmission and variations. Understanding the historical context of originals versus apographs is key to unraveling the evolution of texts and the authenticity of historical documents.
Defining "Original" in Textual Transmission
The term "original" in textual transmission refers to the earliest or first version of a manuscript or document created by the author, serving as the authoritative source for all subsequent copies or editions. An original embodies the intended content, structure, and meaning as conceived by the creator, whereas an apograph is any exact copy or duplicate derived from the original. Understanding the distinction between originals and apographs is crucial for scholars in establishing textual authenticity, tracing transmission history, and resolving variations across manuscript traditions.
What is an Apograph?
An apograph is an exact copy or transcript of an original document, often used in legal and historical contexts to preserve the content when the original is lost or damaged. Unlike an original, which is the first or primary version created, an apograph replicates all details accurately but holds secondary evidentiary value. Apographs are crucial in archival preservation and documentary authenticity verification.
Importance of Originals in Document Preservation
Original documents hold paramount importance in document preservation due to their authenticity, providing the most accurate and reliable evidence for historical, legal, and academic purposes. Unlike apographs, which are copies and may contain transcription errors or alterations, originals maintain the integrity of the author's intent and context. Preserving originals ensures the protection of cultural heritage and supports the verification processes essential to archival research and legal validation.
Role of Apographs in Historical Scholarship
Apographs play a crucial role in historical scholarship by serving as accurate copies of original manuscripts when the originals are lost or inaccessible. These faithful reproductions enable researchers to study and verify historical texts, preserving the transmission of knowledge across generations. The reliability of apographs is essential for textual criticism, helping scholars reconstruct authentic versions of documents with minimal alterations.
Differences in Authenticity: Original vs Apograph
The original document holds primary authenticity as it is the first-hand source created by the author or authority, containing the initial and unaltered content. An apograph, being a copy or reproduction, lacks the original's legal and historical authority, often subject to transcription errors or deliberate alterations. Authenticity differences between an original and an apograph significantly impact their credibility, with originals preferred in legal, academic, and archival contexts.
Common Misconceptions about Apographs
Apographs are handwritten or printed copies of original manuscripts, often mistaken for original documents due to their identical textual content. A common misconception is that apographs hold the same historical or legal value as originals, when in fact their authenticity and provenance differ significantly. Understanding the distinction is crucial for accurate historical analysis and legal validation.
Modern Applications: Originals and Apographs in Digital Era
Originals in the digital era represent authentic, primary sources such as raw data files, while apographs are exact digital copies or replicas used for analysis, distribution, and backup. Modern applications rely heavily on apographs for collaborative work, cloud storage, and version control systems, ensuring data integrity and accessibility without compromising the original file. Technologies like blockchain and digital watermarking enhance trust in original digital documents by providing immutable proof of authenticity and provenance.
Evaluating Source Reliability: Which Should You Trust?
Evaluating source reliability hinges on distinguishing between an original document and its apograph, which is a handwritten or typed copy of the original manuscript. Originals hold the highest credibility due to their direct connection to the source, while apographs may contain transcription errors or unauthorized alterations impacting their reliability. Scholars and historians prioritize originals for accurate information but may rely on verified apographs when originals are lost or inaccessible, emphasizing the importance of provenance and authentication in trustworthiness assessments.
Original Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com