The emirate is a political territory ruled by an emir, often characterized by a unique blend of traditional governance and modern development. Rich in cultural heritage and economic significance, emirates play a vital role in regional stability and global markets. Discover how your understanding of emirates can deepen by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
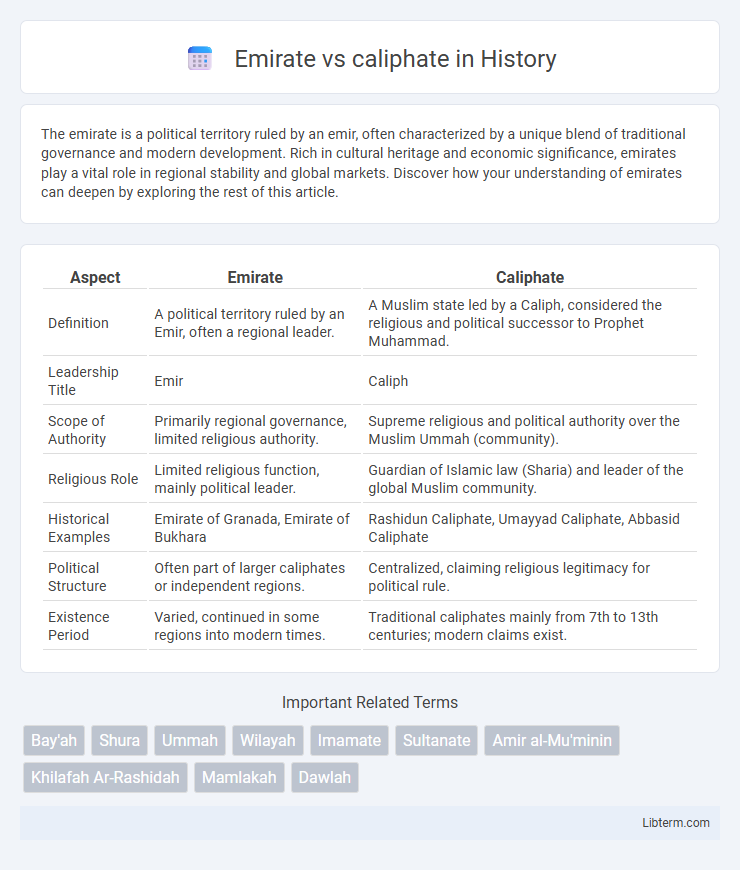
| Aspect | Emirate | Caliphate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A political territory ruled by an Emir, often a regional leader. | A Muslim state led by a Caliph, considered the religious and political successor to Prophet Muhammad. |
| Leadership Title | Emir | Caliph |
| Scope of Authority | Primarily regional governance, limited religious authority. | Supreme religious and political authority over the Muslim Ummah (community). |
| Religious Role | Limited religious function, mainly political leader. | Guardian of Islamic law (Sharia) and leader of the global Muslim community. |
| Historical Examples | Emirate of Granada, Emirate of Bukhara | Rashidun Caliphate, Umayyad Caliphate, Abbasid Caliphate |
| Political Structure | Often part of larger caliphates or independent regions. | Centralized, claiming religious legitimacy for political rule. |
| Existence Period | Varied, continued in some regions into modern times. | Traditional caliphates mainly from 7th to 13th centuries; modern claims exist. |
Definition of Emirate and Caliphate
An emirate is a political territory or state ruled by an emir, a title used by Muslim rulers who govern regions with autonomy or under larger sovereign structures. A caliphate is an Islamic state led by a caliph, considered the political and religious successor to the Prophet Muhammad, combining both governance and spiritual leadership over the Muslim community. While emirates often denote localized governance, caliphates embody a broader, centralized authority uniting diverse Muslim populations under a single religious and political leader.
Historical Origins of Emirates and Caliphates
Emirates and caliphates originated from distinct historical and political contexts in Islamic history, with emirates often emerging as smaller, regional principalities led by an emir, a title derived from the Arabic word for "commander" or "prince." Caliphates trace their roots to the early Islamic community following the death of Prophet Muhammad, representing a centralized religious and political leadership under a caliph, considered the successor to the Prophet. The Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates played crucial roles in shaping the political and religious landscape of the Islamic world, while emirates often served as localized governance systems within or alongside these larger caliphate structures.
Governance Structures: Emir vs Caliph
An emir governs an emirate, typically exercising regional authority with military and administrative powers, often subordinate to a higher sovereign or state framework. A caliph, as the leader of a caliphate, holds supreme religious and political authority over the Muslim community, embodying both spiritual leadership as the successor to Prophet Muhammad and temporal governance of the Islamic state. The caliphate's governance structure integrates religious legitimacy and centralized control, while emirates feature localized rule with varying degrees of autonomy under broader Islamic or national sovereignty.
Religious Authority in Emirate and Caliphate
The caliphate embodies supreme religious authority as the caliph is considered the political and spiritual leader of the entire Muslim community, responsible for upholding Islamic law and guiding religious unity. In contrast, an emirate is primarily a political or administrative region governed by an emir, whose religious authority is limited and often subordinate to broader religious institutions or the caliphate when it exists. The caliphate's role integrates both governance and religious leadership, while emirates typically focus more on territorial control and may defer to religious scholars for spiritual matters.
Territorial Scope and Expansion
An emirate typically governs a defined territory under the authority of an emir, with expansion often limited to regional influence and consolidation rather than large-scale conquest. In contrast, a caliphate encompasses a broader Islamic empire, aiming for extensive territorial expansion across diverse regions to unify the Muslim world under a single caliph's religious and political leadership. Historical caliphates like the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties expanded across vast areas spanning the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe and Asia, illustrating their far-reaching ambitions.
Succession and Leadership Selection
In an emirate, succession is often hereditary, with leadership passing through a ruling family or dynasty, ensuring continuity within a specific lineage. Caliphates typically emphasize selection by consensus or appointment among religious and political elites, adhering to Islamic principles that prioritize community legitimacy and piety over bloodline. Leadership in a caliphate carries both spiritual and temporal authority, while an emirate primarily centers on political and military governance.
Examples of Emirates in History
Emirates are political territories governed by emirs, with historic examples including the Emirate of Granada in Spain, which was the last Muslim state on the Iberian Peninsula, and the Emirate of Bukhara, a Central Asian state prominent in the 18th and 19th centuries. Unlike caliphates, which claim religious and political leadership over the entire Muslim community, emirates typically have localized governance without asserting universal Islamic authority. The Emirate of Dubai stands as a modern example, evolving from a small sheikhdom into a significant global city within the United Arab Emirates.
Prominent Caliphates Through Time
Prominent caliphates such as the Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and Ottoman Caliphates played pivotal roles in Islamic history, governing vast territories and influencing religion, culture, and politics across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Asia and Europe. Each caliphate represented a centralized Islamic state led by a caliph who was considered both a political and religious successor to the Prophet Muhammad. In contrast, emirates are typically smaller, often regional territories ruled by an emir with limited religious authority, focusing primarily on political or military leadership.
Political Influence and Legacy
Emirates function as regional political entities ruled by emirs, often with limited sovereignty under a larger state or caliphate, influencing governance primarily through localized authority and administrative control. Caliphates historically held supreme political and religious leadership over the entire Muslim community, shaping Islamic law, culture, and international relations across vast territories. The legacy of emirates is reflected in modern state systems with decentralized governance, while caliphates have left enduring impacts on Islamic political theory and unity across diverse Muslim populations.
Modern Relevance of Emirates and Caliphates
Modern emirates function as stable, often wealthy political entities characterized by hereditary leadership and integration within federal systems, exemplified by the United Arab Emirates. Caliphates historically represented a unified religious and political authority in Islam, but their modern relevance is largely symbolic, with attempts to establish new caliphates facing widespread geopolitical resistance and lack of international recognition. Contemporary emirates play significant roles in global economics and diplomacy, while caliphates remain more associated with ideological movements than established governance.
Emirate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com