Vicus was a type of small settlement in ancient Roman times, often serving as a local village or neighborhood within larger municipal areas. These communities played a crucial role in daily life, acting as hubs for trade, social interaction, and local administration. Discover how understanding the significance of vicus can enrich Your knowledge of Roman history and culture in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
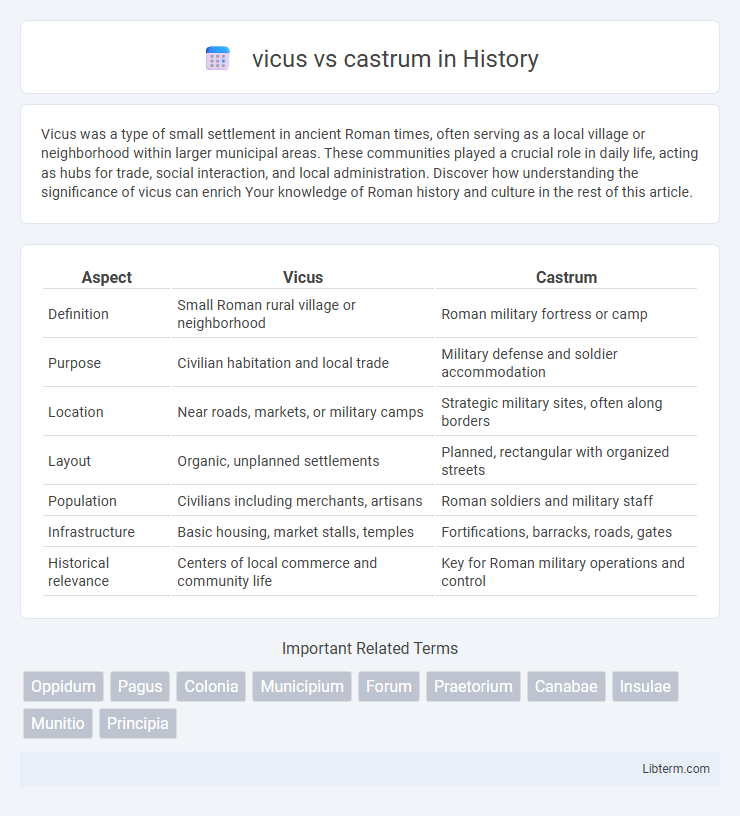
| Aspect | Vicus | Castrum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small Roman rural village or neighborhood | Roman military fortress or camp |
| Purpose | Civilian habitation and local trade | Military defense and soldier accommodation |
| Location | Near roads, markets, or military camps | Strategic military sites, often along borders |
| Layout | Organic, unplanned settlements | Planned, rectangular with organized streets |
| Population | Civilians including merchants, artisans | Roman soldiers and military staff |
| Infrastructure | Basic housing, market stalls, temples | Fortifications, barracks, roads, gates |
| Historical relevance | Centers of local commerce and community life | Key for Roman military operations and control |
Introduction to Vicus and Castrum
A vicus was a small, often unplanned settlement in Roman territories, primarily serving as a local commercial or residential area outside military control. A castrum, by contrast, was a fortified military camp designed with precise engineering to house Roman legions and secure strategic locations. Both played crucial roles in the Empire's expansion, with vicus supporting civilian life and castrum enforcing military dominance.
Historical Origins of Vicus and Castrum
The historical origins of vicus trace back to Roman times, where vicus referred to small rural settlements or neighborhoods often found outside larger urban centers, functioning as hubs for local trade and daily life. Castrum, originating as a Roman military term, denoted fortified camps designed for strategic defense and soldier accommodation during campaigns, with origins linking to Roman military expansion and road networks. These distinct origins highlight the vicus as civilian-centered, organically evolved settlements, while the castrum represents planned military infrastructure integral to Rome's territorial control.
Defining Vicus: Structure and Purpose
Vicus refers to a small, often semi-permanent settlement or neighborhood within or adjacent to larger Roman towns, characterized by organic street layouts and mixed residential and commercial functions. Unlike the castrum, which is a fortified military camp designed with a strict grid plan for defense and troop accommodation, the vicus developed more spontaneously to support civilian life and local trade. The vicus's primary purpose was to serve as a hub for artisans, merchants, and families, facilitating everyday economic and social activities outside the military sphere.
Defining Castrum: Structure and Purpose
A castrum refers to a Roman military fortification designed with a standardized rectangular layout featuring defensive walls, gates, and internal streets, serving as a base for troop deployments and command. Its primary purpose was to provide protection, organization, and strategic control within conquered territories. The structured design ensured efficient defense, housing of soldiers, and logistical support essential for maintaining imperial authority.
Key Differences Between Vicus and Castrum
Vicus refers to a civilian settlement or village often located near Roman military forts, while castrum denotes a fortified Roman military camp or fortress designed for defense and strategic control. The primary difference lies in the function: vicus served as a residential and commercial hub supporting daily life, whereas castrum was a tactical base for military operations. Architecturally, castra are characterized by standardized layouts with walls and gates, contrasting with the more organic, less formal arrangement of vicus settlements.
Social and Economic Roles in Roman Society
Vicus functioned as civilian settlements that supported daily social interaction and local trade, fostering community life outside military domains. Castrum served as fortified military camps housing soldiers and administrators, acting as hubs for logistical control and economic regulation in occupied territories. Together, vicus and castrum facilitated economic exchange and social organization, integrating military presence with civilian life in Roman society.
Architectural Features: Vicus vs Castrum
A vicus typically features irregular, organic street patterns and smaller, simpler buildings reflecting civilian settlements, while a castrum is characterized by a rigid, rectangular grid plan with fortified walls, gates, and military barracks designed for defense and organization. Castra contain structured elements such as principia (headquarters), praetorium (commander's house), and granaries, showcasing a systematic approach to military architecture. In contrast, a vicus lacks formal fortifications and displays a more heterogeneous architectural style driven by commerce and daily civilian life.
Military Significance of Castra
Castra served as fortified military bases designed for the Roman army, strategically placed to control territories and facilitate rapid troop deployment. Unlike vicus, which developed as civilian settlements around these forts, castra featured defensive structures like walls, ditches, and towers, ensuring protection against enemy attacks. The military significance of castra lay in their role as command centers and supply hubs, reinforcing Rome's dominance across conquered regions.
Evolution of Vicus and Castrum Over Time
The vicus originated as a civilian settlement adjacent to a Roman castrum, gradually evolving from temporary market towns into more established communities with distinct social and economic functions. The castrum, initially a fortified military camp designed for strategic control, often expanded into permanent urban centers as Roman control solidified and military needs diminished. Over time, many vici integrated civilian life and infrastructure, reflecting a transition from military outposts to complex civic settlements that contributed to regional Romanization.
Legacy and Influence on Modern Settlements
Vici and castra represent foundational Roman settlement models, with castra serving as military forts that evolved into administrative and urban centers influencing the grid layouts and organization of many modern European towns. Vici, originally civilian settlements near military posts, contributed to the decentralized growth patterns seen in rural and suburban areas today. The legacy of Roman urban planning, derived from both vici and castra, persists in contemporary infrastructure, road networks, and municipal zoning concepts across regions once under Roman control.
vicus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com